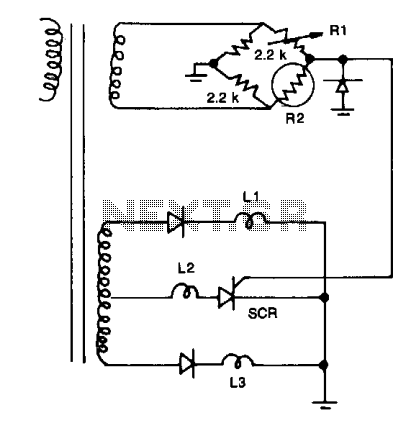
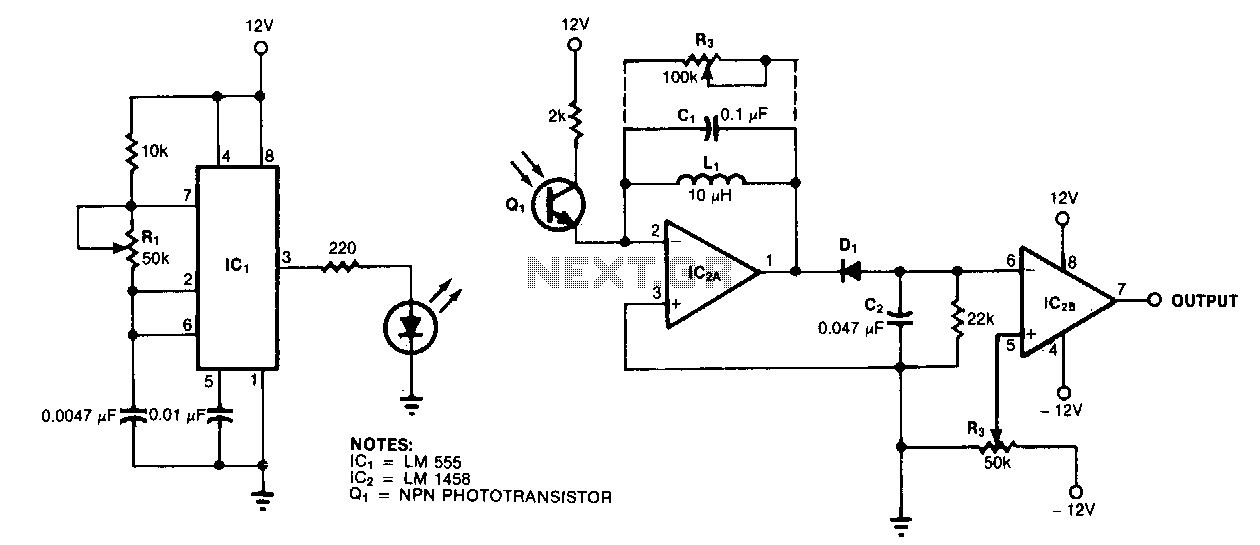
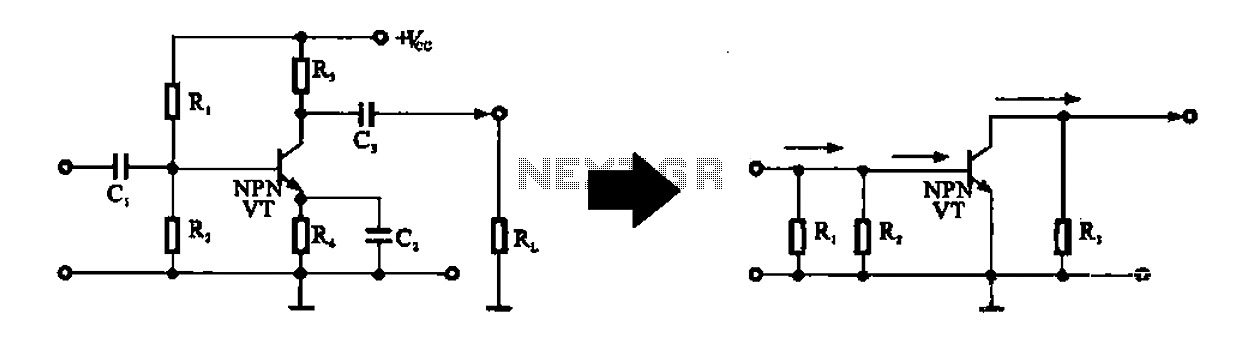
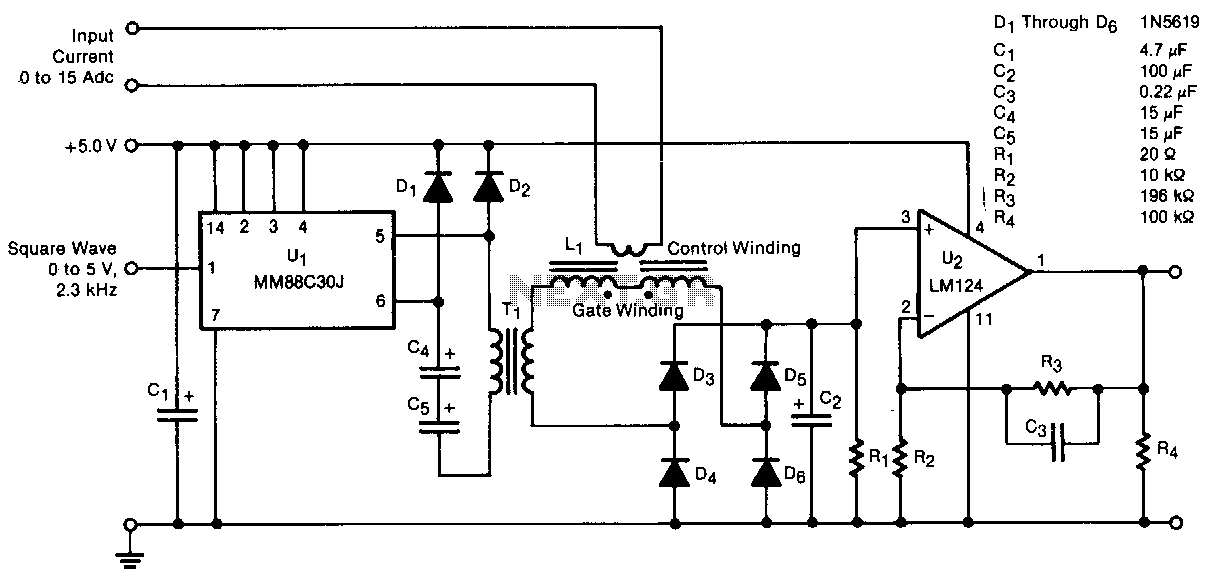
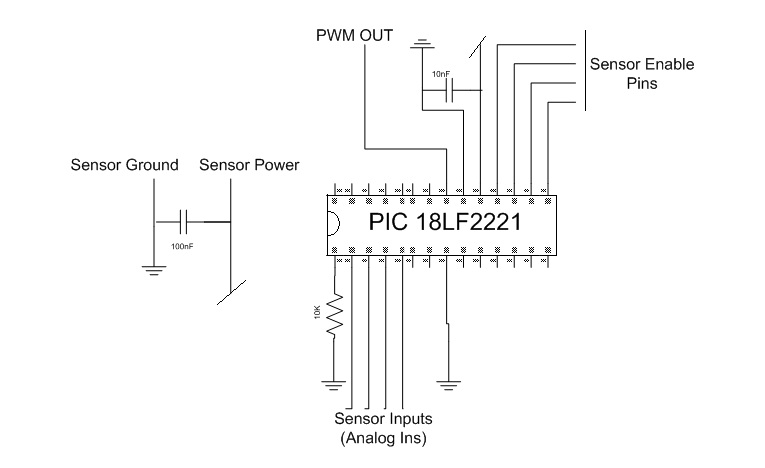
High-Gain Current Sensor
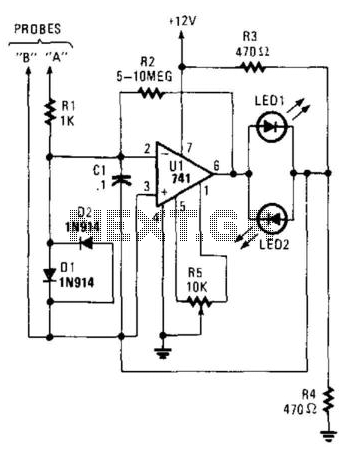
A high-gain amplifier utilizing a UA741 is employed to sense the relative voltage drop across a conductor, thereby measuring the current flowing through it. The sensitivity can be enhanced by increasing i2 to 10. LED1 and LED2 serve as indicators for polarity. This circuit is applicable for detecting current in a printed circuit board (PCB) trace and for identifying shorts and opens.
The circuit operates by leveraging the UA741 operational amplifier, which is configured in a non-inverting or inverting mode to amplify the small voltage drop across the conductor. The voltage drop is proportional to the current flowing through the conductor according to Ohm's law, allowing for accurate current measurement. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by modifying the feedback resistor values, thereby allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the application.
LED1 and LED2 are connected to the output of the amplifier in a manner that indicates the polarity of the current. When the current flows in one direction, one LED will illuminate, while the other will remain off, providing a clear visual indication of the current's direction. This feature is particularly useful in troubleshooting applications where understanding the flow of current is crucial.
The circuit can be effectively used on a PCB to monitor traces for current flow, which is essential in ensuring that the circuit operates within its designed parameters. Additionally, it can help in locating shorts (unintended connections between traces) and opens (disconnections in the circuit), which can lead to circuit failure. By employing this high-gain amplifier configuration, the circuit achieves a high level of sensitivity, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics. A high-gain amplifier using a UA741 is used to sense relative voltage drop in a conductor, and therefore current i n the conductor. i2 can be increased to 10 for increased sensitivity. LED1 and LED2 provide polarity indication. This circuit can be used to detect current flowing in a PC board trace, and also for locating shorts and opens.
The circuit operates by leveraging the UA741 operational amplifier, which is configured in a non-inverting or inverting mode to amplify the small voltage drop across the conductor. The voltage drop is proportional to the current flowing through the conductor according to Ohm's law, allowing for accurate current measurement. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted by modifying the feedback resistor values, thereby allowing for customization based on the specific requirements of the application.
LED1 and LED2 are connected to the output of the amplifier in a manner that indicates the polarity of the current. When the current flows in one direction, one LED will illuminate, while the other will remain off, providing a clear visual indication of the current's direction. This feature is particularly useful in troubleshooting applications where understanding the flow of current is crucial.
The circuit can be effectively used on a PCB to monitor traces for current flow, which is essential in ensuring that the circuit operates within its designed parameters. Additionally, it can help in locating shorts (unintended connections between traces) and opens (disconnections in the circuit), which can lead to circuit failure. By employing this high-gain amplifier configuration, the circuit achieves a high level of sensitivity, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians in the field of electronics. A high-gain amplifier using a UA741 is used to sense relative voltage drop in a conductor, and therefore current i n the conductor. i2 can be increased to 10 for increased sensitivity. LED1 and LED2 provide polarity indication. This circuit can be used to detect current flowing in a PC board trace, and also for locating shorts and opens.