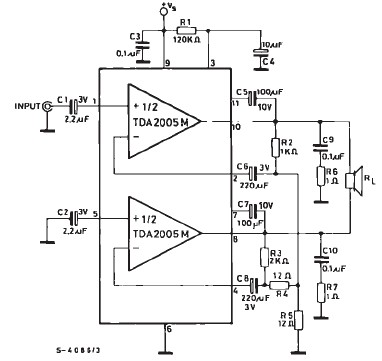
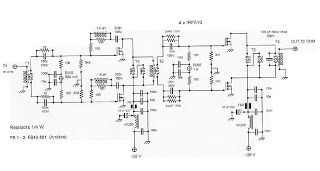
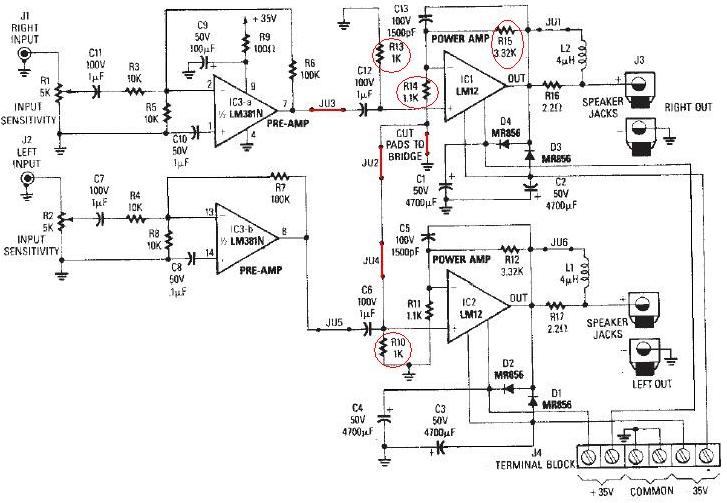
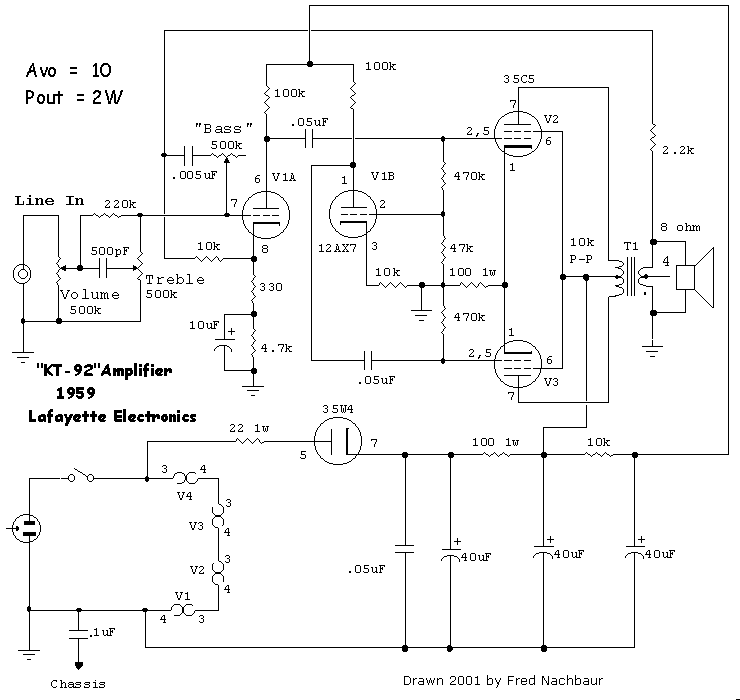
Horizontal Deflection Amplifier for Oscilloscope
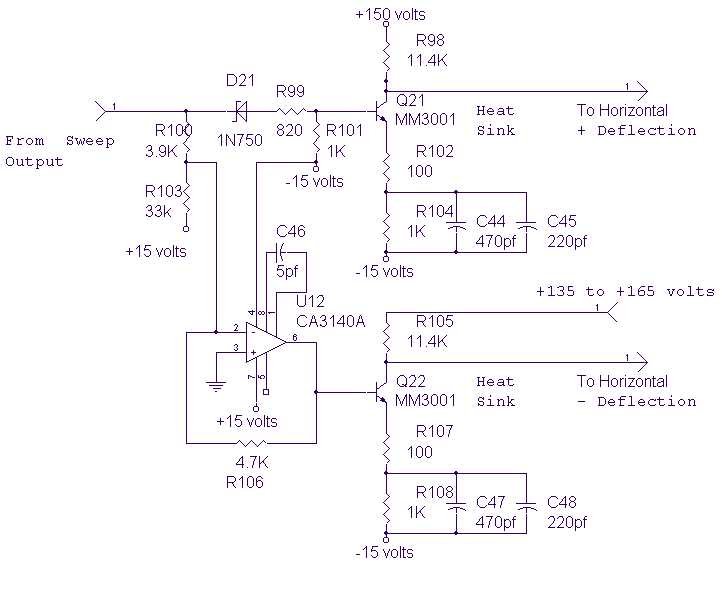
The circuit below provides the horizontal drive voltage. The supply voltage on one end, +135 to +165, is made variable for the horizontal position control.
The described circuit is designed to generate a horizontal drive voltage, which is essential in applications such as display technology, including CRTs (Cathode Ray Tubes) and certain types of LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays). The supply voltage range of +135 to +165 volts indicates that the circuit operates at high voltage levels, which are typical for horizontal deflection systems in display devices.
The circuit likely incorporates a variable resistor or a potentiometer that allows for the adjustment of the voltage supplied for horizontal positioning. This feature enables fine-tuning of the horizontal position of the display, ensuring that the image is correctly centered and aligned.
Key components of such a circuit may include a high-voltage power supply, a voltage regulator or feedback control loop to maintain stability, and possibly a transformer to step up or isolate the voltage levels as required. The output stage may utilize transistors or other switching devices that can handle high voltages and currents, ensuring reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Furthermore, protection mechanisms such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF or voltage spikes, which could potentially damage sensitive components. Additionally, filtering capacitors are essential to smooth out any fluctuations in the voltage supply, contributing to the overall stability of the horizontal drive voltage.
In summary, this circuit plays a critical role in controlling the horizontal positioning in display technologies, with a focus on providing a variable high-voltage output that can be adjusted for precise alignment of images on the screen.The circuit below provides the horizontal drive voltage. The supply voltage on one end, +135 to +165, is made variable for the horizontal position control. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to generate a horizontal drive voltage, which is essential in applications such as display technology, including CRTs (Cathode Ray Tubes) and certain types of LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays). The supply voltage range of +135 to +165 volts indicates that the circuit operates at high voltage levels, which are typical for horizontal deflection systems in display devices.
The circuit likely incorporates a variable resistor or a potentiometer that allows for the adjustment of the voltage supplied for horizontal positioning. This feature enables fine-tuning of the horizontal position of the display, ensuring that the image is correctly centered and aligned.
Key components of such a circuit may include a high-voltage power supply, a voltage regulator or feedback control loop to maintain stability, and possibly a transformer to step up or isolate the voltage levels as required. The output stage may utilize transistors or other switching devices that can handle high voltages and currents, ensuring reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Furthermore, protection mechanisms such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF or voltage spikes, which could potentially damage sensitive components. Additionally, filtering capacitors are essential to smooth out any fluctuations in the voltage supply, contributing to the overall stability of the horizontal drive voltage.
In summary, this circuit plays a critical role in controlling the horizontal positioning in display technologies, with a focus on providing a variable high-voltage output that can be adjusted for precise alignment of images on the screen.The circuit below provides the horizontal drive voltage. The supply voltage on one end, +135 to +165, is made variable for the horizontal position control. 🔗 External reference