Low-Drift Dc Voltmeter Circuit
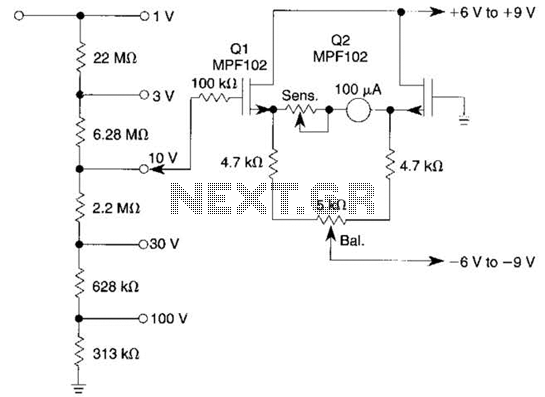
This voltmeter utilizes a pair of JFETs in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. Q1 and Q2 should be matched within 10% for IDSS. This configuration minimizes meter drift and maintains bridge balance over temperature.
The described voltmeter is an advanced measurement instrument that employs a balanced-bridge configuration using Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) as the core sensing elements. The use of two matched JFETs, Q1 and Q2, is critical for achieving high accuracy in voltage measurement. The matching criterion of 10% for the drain-source saturation current (IDSS) ensures that both transistors operate under similar conditions, thereby improving the linearity and stability of the output signal.
The balanced-bridge design is particularly advantageous because it effectively cancels out common-mode noise and reduces the impact of temperature variations on the measurement accuracy. By maintaining a precise balance between the two branches of the bridge, the circuit can provide a stable output voltage that is directly proportional to the input voltage being measured. This stability is essential for applications where precision is paramount, such as in laboratory settings or high-precision instrumentation.
In terms of circuit implementation, the source-follower configuration allows for high input impedance, which is beneficial when measuring voltages from high-impedance sources without loading them down. The output of the source followers can be connected to additional signal processing stages or directly to a digital voltmeter for display.
Overall, this voltmeter design represents a sophisticated approach to voltage measurement, leveraging the characteristics of JFETs and a balanced-bridge topology to achieve reliable and accurate results across varying environmental conditions. This voltmeter uses a pair of JFETs in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. Q1 and Q2 should be matched within 10% for IDSS. This minimizes meter drift and maintains bridge balance over temperature.
The described voltmeter is an advanced measurement instrument that employs a balanced-bridge configuration using Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFETs) as the core sensing elements. The use of two matched JFETs, Q1 and Q2, is critical for achieving high accuracy in voltage measurement. The matching criterion of 10% for the drain-source saturation current (IDSS) ensures that both transistors operate under similar conditions, thereby improving the linearity and stability of the output signal.
The balanced-bridge design is particularly advantageous because it effectively cancels out common-mode noise and reduces the impact of temperature variations on the measurement accuracy. By maintaining a precise balance between the two branches of the bridge, the circuit can provide a stable output voltage that is directly proportional to the input voltage being measured. This stability is essential for applications where precision is paramount, such as in laboratory settings or high-precision instrumentation.
In terms of circuit implementation, the source-follower configuration allows for high input impedance, which is beneficial when measuring voltages from high-impedance sources without loading them down. The output of the source followers can be connected to additional signal processing stages or directly to a digital voltmeter for display.
Overall, this voltmeter design represents a sophisticated approach to voltage measurement, leveraging the characteristics of JFETs and a balanced-bridge topology to achieve reliable and accurate results across varying environmental conditions. This voltmeter uses a pair of JFETs in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. Q1 and Q2 should be matched within 10% for IDSS. This minimizes meter drift and maintains bridge balance over temperature.