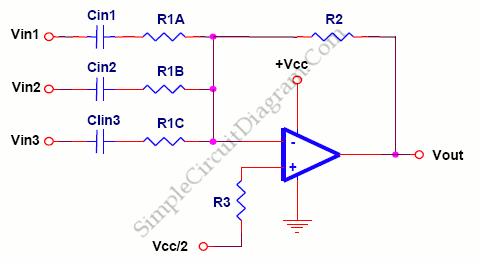
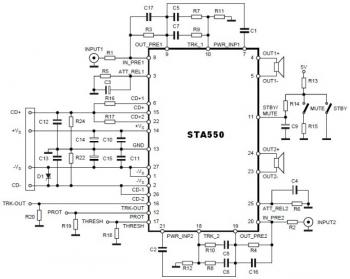
Low Noise Power Supply for Audio Circuits

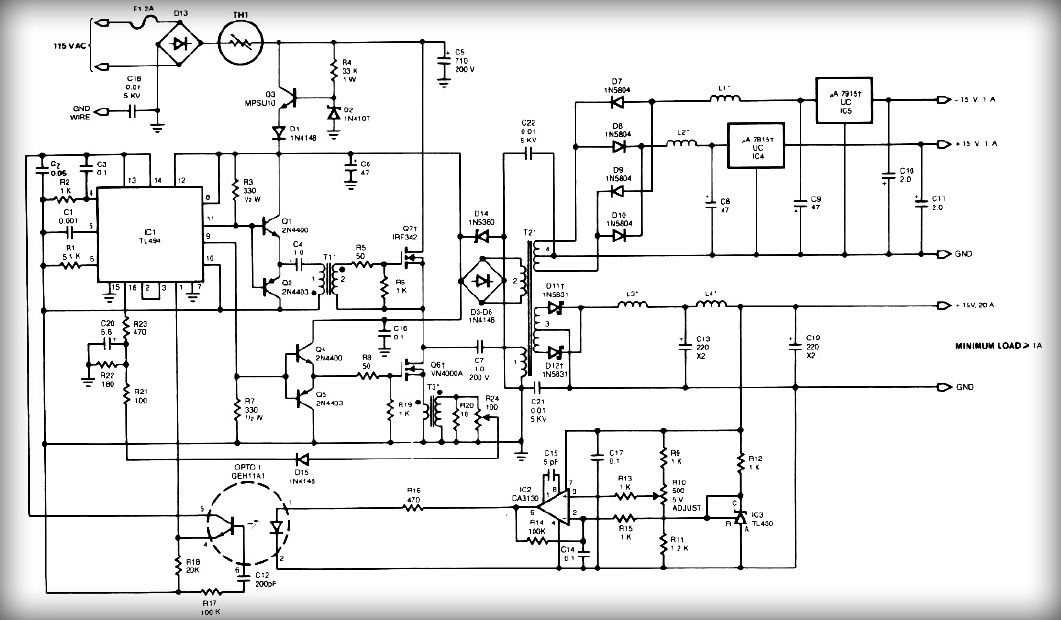
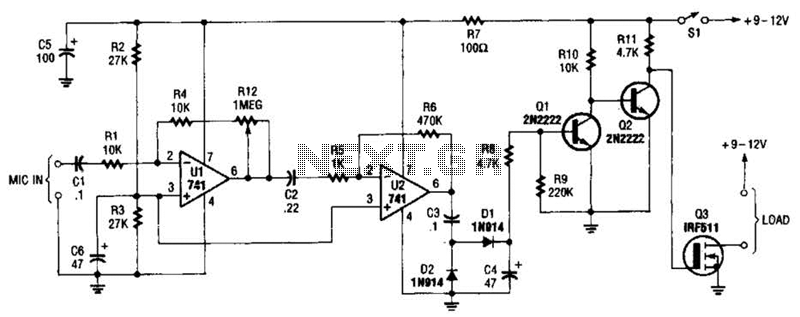
This low noise audio power supply circuit can reduce noise and ripple voltage by 40 dB over the 100 Hz to 20 kHz audio range. In portable applications such as...
This low noise audio power supply circuit is designed to significantly minimize electrical noise and ripple voltage, achieving a reduction of 40 dB in the frequency range of 100 Hz to 20 kHz. This performance is critical for audio applications where clarity and fidelity are paramount, particularly in portable devices that may be susceptible to interference from various sources.
The circuit typically employs a combination of linear voltage regulation and filtering techniques to achieve its low noise specifications. A well-designed low-dropout (LDO) regulator can be used to maintain a stable output voltage while rejecting high-frequency noise. To further enhance performance, capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) are recommended for decoupling and smoothing the output. These capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the load to minimize inductive effects and provide optimal transient response.
Additionally, the incorporation of ferrite beads or inductors in series with the power supply lines can help suppress high-frequency noise generated by digital circuits or RF interference. The layout of the circuit board is also crucial; a star ground configuration is advisable to prevent ground loops and ensure that the sensitive audio signals are not compromised.
For portable applications, considerations such as power efficiency and thermal management are essential. The use of switching regulators, when designed properly, can offer a good balance between efficiency and noise performance, although they require careful filtering to mitigate switching noise.
Overall, this low noise audio power supply circuit is an essential component for high-fidelity audio systems, ensuring that audio signals remain clean and free from unwanted interference, thereby enhancing the overall listening experience.This low noise audio power supply circuit can reduces noise and ripple voltage by 40dB over the 100Hz to 20kHz audio range. In portable application such as.. 🔗 External reference
This low noise audio power supply circuit is designed to significantly minimize electrical noise and ripple voltage, achieving a reduction of 40 dB in the frequency range of 100 Hz to 20 kHz. This performance is critical for audio applications where clarity and fidelity are paramount, particularly in portable devices that may be susceptible to interference from various sources.
The circuit typically employs a combination of linear voltage regulation and filtering techniques to achieve its low noise specifications. A well-designed low-dropout (LDO) regulator can be used to maintain a stable output voltage while rejecting high-frequency noise. To further enhance performance, capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) are recommended for decoupling and smoothing the output. These capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the load to minimize inductive effects and provide optimal transient response.
Additionally, the incorporation of ferrite beads or inductors in series with the power supply lines can help suppress high-frequency noise generated by digital circuits or RF interference. The layout of the circuit board is also crucial; a star ground configuration is advisable to prevent ground loops and ensure that the sensitive audio signals are not compromised.
For portable applications, considerations such as power efficiency and thermal management are essential. The use of switching regulators, when designed properly, can offer a good balance between efficiency and noise performance, although they require careful filtering to mitigate switching noise.
Overall, this low noise audio power supply circuit is an essential component for high-fidelity audio systems, ensuring that audio signals remain clean and free from unwanted interference, thereby enhancing the overall listening experience.This low noise audio power supply circuit can reduces noise and ripple voltage by 40dB over the 100Hz to 20kHz audio range. In portable application such as.. 🔗 External reference