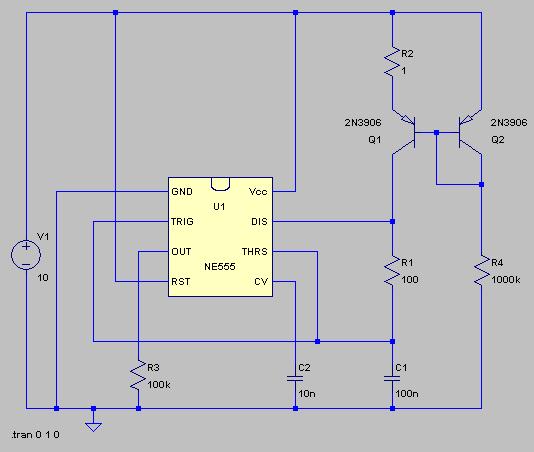
Metronome with CA741
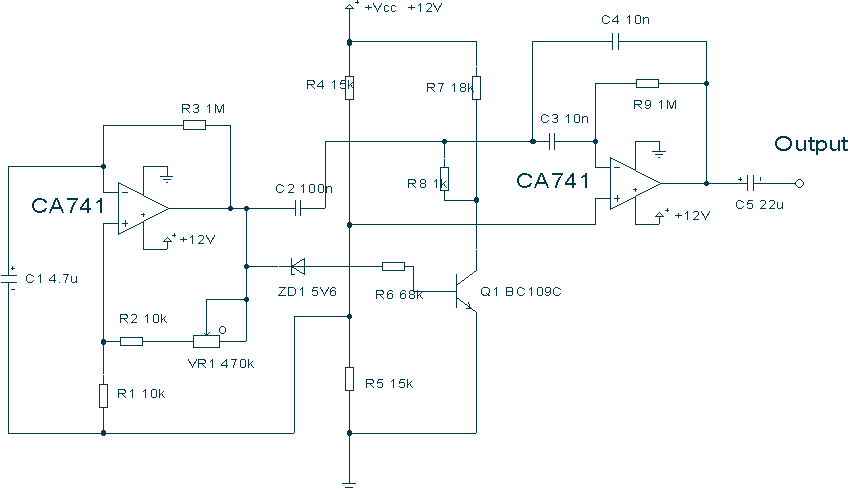
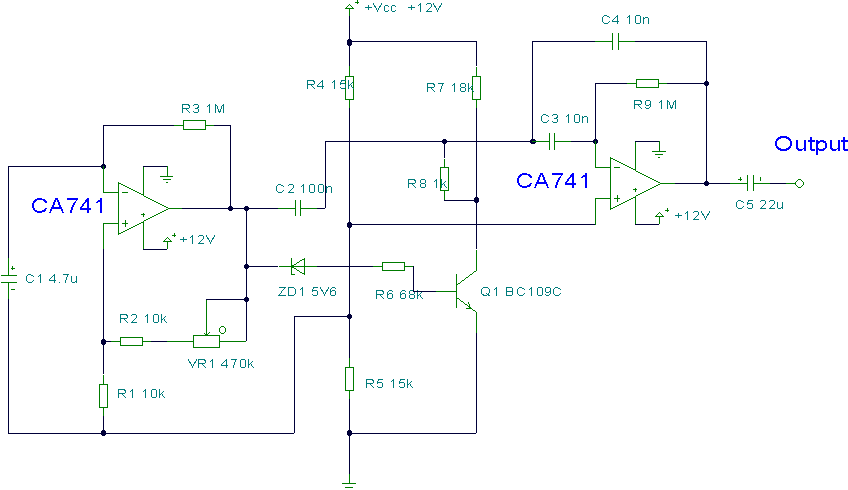
This circuit uses a couple of Op-amps to produce an interesting sound effect. The left hand CA741 is wired as a standard astable and produces the timing pulses, controlled by C1, R2 and VR1. The output is fed via C2 to the second op-amp and is also direct coupled via the zener ZD1 to Q1. The right hand CA741 is configured as an integrator, its purpose being to distort the output pulse from the first op-amp. More: This produces a ringing effect on the output pulse and gives the circuit a characteristic "tick" sound. The output pulse at the first op-amp will cause the zener and Q1 to conduct on every positive transition. The 1k resistor R8 then acts as a
This circuit utilizes two CA741 operational amplifiers to generate a distinctive sound effect characterized by a "tick" sound. The first op-amp is configured in an astable multivibrator configuration, producing continuous timing pulses. The frequency of these pulses is determined by the timing components, which include capacitor C1, resistor R2, and variable resistor VR1. The astable configuration allows for the generation of square wave signals, where the duty cycle can be adjusted using VR1.
The output from the first op-amp is coupled to the second op-amp through capacitor C2. This coupling allows for AC signal transmission while blocking any DC components. Additionally, the output is directly coupled to transistor Q1 via the zener diode ZD1. The role of the zener diode is to provide a reference voltage, ensuring that Q1 operates correctly in response to the output pulses from the first op-amp.
The second op-amp is configured as an integrator, which processes the square wave output from the first op-amp. This configuration effectively distorts the square wave into a triangular waveform, contributing to the overall sound effect. The integration process introduces a ringing effect, which enhances the characteristic "tick" sound produced by the circuit.
The output pulse generated by the first op-amp triggers the conduction of the zener diode and transistor Q1 upon each positive transition. The resistor R8, valued at 1k ohms, serves to limit the current flowing through Q1, ensuring safe operation and preventing potential damage to the transistor. This current limiting is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the circuit while achieving the desired sound effect.
Overall, this circuit design is a creative application of operational amplifiers and passive components to produce a unique auditory effect, suitable for various electronic sound applications.This circuit uses a couple of Op-amps to produce an interesting sound effect. The left hand CA741 is wired as a standard astable and produces the timing pulses, controlled by C1, R2 and VR1. The output is fed via C2 to the second op-amp and is also direct coupled via the zener ZD1 to Q1. The right hand CA741 is configured as an integrator, its purpose being to distort the output pulse from the first op-amp.
This produces a ringing effect on the output pulse and gives the circuit a characteristic "tick" sound. The output pulse at the first op-amp will cause the zener and Q1 to conduct on every positive transition.
The 1k resistor R8 then acts as a 🔗 External reference
This circuit utilizes two CA741 operational amplifiers to generate a distinctive sound effect characterized by a "tick" sound. The first op-amp is configured in an astable multivibrator configuration, producing continuous timing pulses. The frequency of these pulses is determined by the timing components, which include capacitor C1, resistor R2, and variable resistor VR1. The astable configuration allows for the generation of square wave signals, where the duty cycle can be adjusted using VR1.
The output from the first op-amp is coupled to the second op-amp through capacitor C2. This coupling allows for AC signal transmission while blocking any DC components. Additionally, the output is directly coupled to transistor Q1 via the zener diode ZD1. The role of the zener diode is to provide a reference voltage, ensuring that Q1 operates correctly in response to the output pulses from the first op-amp.
The second op-amp is configured as an integrator, which processes the square wave output from the first op-amp. This configuration effectively distorts the square wave into a triangular waveform, contributing to the overall sound effect. The integration process introduces a ringing effect, which enhances the characteristic "tick" sound produced by the circuit.
The output pulse generated by the first op-amp triggers the conduction of the zener diode and transistor Q1 upon each positive transition. The resistor R8, valued at 1k ohms, serves to limit the current flowing through Q1, ensuring safe operation and preventing potential damage to the transistor. This current limiting is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the circuit while achieving the desired sound effect.
Overall, this circuit design is a creative application of operational amplifiers and passive components to produce a unique auditory effect, suitable for various electronic sound applications.This circuit uses a couple of Op-amps to produce an interesting sound effect. The left hand CA741 is wired as a standard astable and produces the timing pulses, controlled by C1, R2 and VR1. The output is fed via C2 to the second op-amp and is also direct coupled via the zener ZD1 to Q1. The right hand CA741 is configured as an integrator, its purpose being to distort the output pulse from the first op-amp.
This produces a ringing effect on the output pulse and gives the circuit a characteristic "tick" sound. The output pulse at the first op-amp will cause the zener and Q1 to conduct on every positive transition.
The 1k resistor R8 then acts as a 🔗 External reference