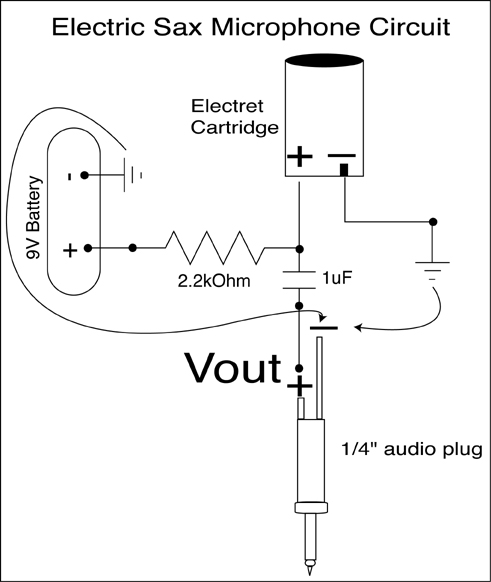
Mic pre amp
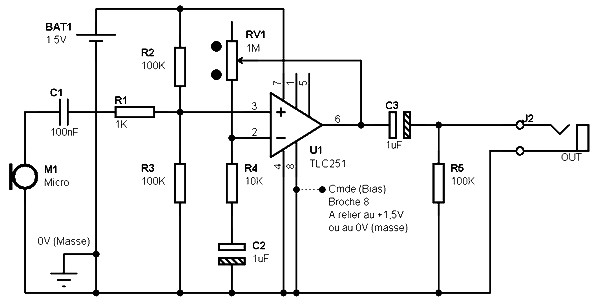
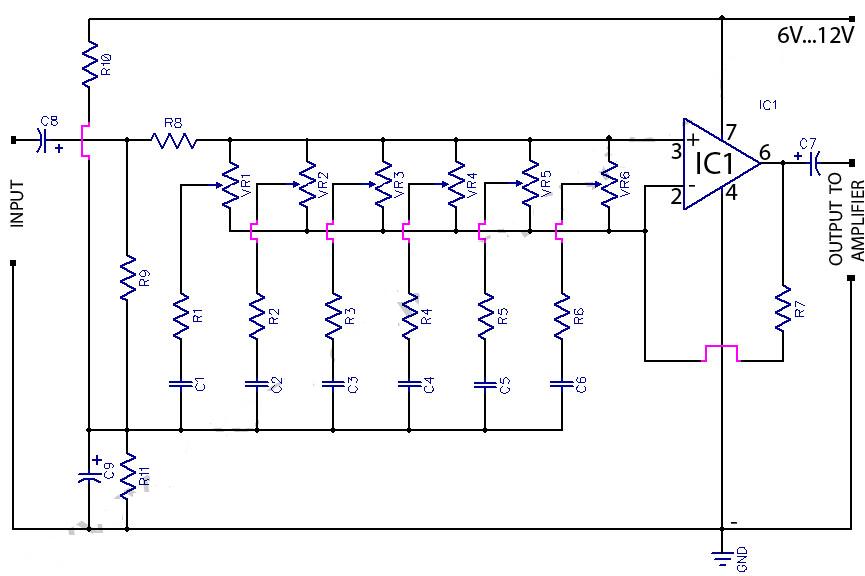
The schematic for a microphone preamplifier utilizes the TLC251, a programmable low-power operational amplifier. A control input, referred to as BIAS (pin 8), determines the operational mode of the amplifier. When this pin is connected to the positive potential of the power supply, the circuit's power consumption is minimized to 10 microamps.
The microphone preamplifier circuit based on the TLC251 is designed to amplify low-level audio signals from microphones while maintaining low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The TLC251 is notable for its low quiescent current, which is particularly beneficial in portable applications.
The BIAS pin plays a crucial role in configuring the operational mode of the amplifier. By applying a positive voltage to this pin, the circuit enters a low-power state, which is essential for extending battery life in mobile applications. In this state, the operational amplifier operates efficiently, ensuring that audio signals are amplified without significant power drain.
The schematic typically includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors that set the gain of the amplifier and filter out unwanted noise. Input capacitors may be used to block DC offsets from the microphone signal, while feedback resistors determine the gain of the amplifier. The output stage may also include coupling capacitors to ensure that the amplified signal is appropriately interfaced with subsequent stages in the audio processing chain.
Overall, the design of the microphone preamplifier using the TLC251 is optimized for low power consumption while providing high-quality audio amplification, making it a reliable choice for various audio applications.Mic pre amp schematic based TLC251. TLC251 is a Programmable Low-Power Operational Amplifiers. This is indeed a control input, called BIAS (pin 8), which determines the mode of operation. When the pin is worn on the positive potential of power supply, the consumption of the circuit is reduced to a minimum, which is 10 uA (ten micro-amps). 🔗 External reference
The microphone preamplifier circuit based on the TLC251 is designed to amplify low-level audio signals from microphones while maintaining low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The TLC251 is notable for its low quiescent current, which is particularly beneficial in portable applications.
The BIAS pin plays a crucial role in configuring the operational mode of the amplifier. By applying a positive voltage to this pin, the circuit enters a low-power state, which is essential for extending battery life in mobile applications. In this state, the operational amplifier operates efficiently, ensuring that audio signals are amplified without significant power drain.
The schematic typically includes additional components such as resistors and capacitors that set the gain of the amplifier and filter out unwanted noise. Input capacitors may be used to block DC offsets from the microphone signal, while feedback resistors determine the gain of the amplifier. The output stage may also include coupling capacitors to ensure that the amplified signal is appropriately interfaced with subsequent stages in the audio processing chain.
Overall, the design of the microphone preamplifier using the TLC251 is optimized for low power consumption while providing high-quality audio amplification, making it a reliable choice for various audio applications.Mic pre amp schematic based TLC251. TLC251 is a Programmable Low-Power Operational Amplifiers. This is indeed a control input, called BIAS (pin 8), which determines the mode of operation. When the pin is worn on the positive potential of power supply, the consumption of the circuit is reduced to a minimum, which is 10 uA (ten micro-amps). 🔗 External reference