One Transistor FM Radio With Improved Audio Gain
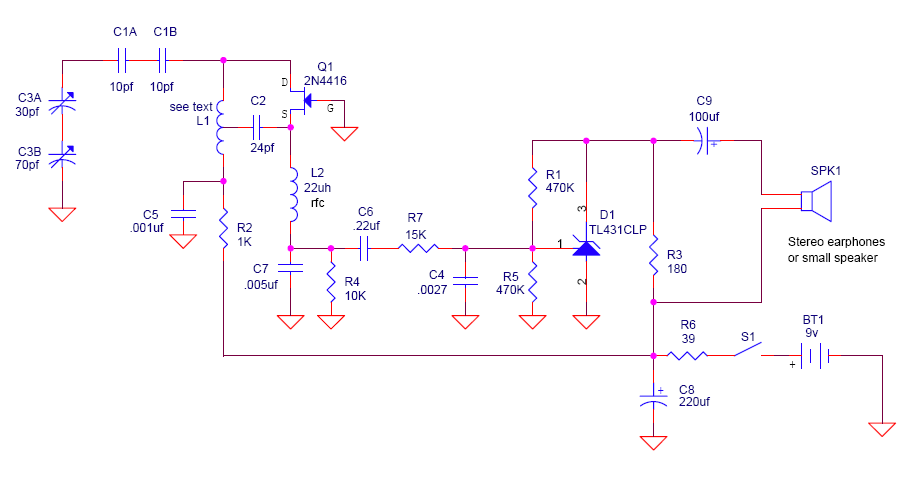
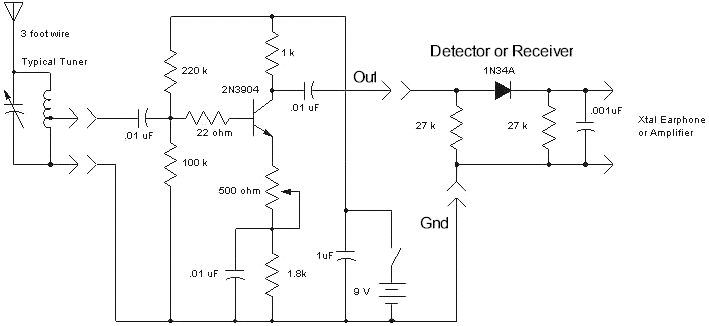
The following circuit presents a schematic diagram for a one-transistor FM radio with enhanced audio gain. Features include a super-regenerative design.
The one-transistor FM radio circuit utilizes a super-regenerative architecture, which is known for its simplicity and efficiency in receiving FM signals. The core component of the circuit is a single transistor, which serves both as the radio frequency (RF) amplifier and the detector. This design significantly reduces the number of components required, making it compact and cost-effective.
In this schematic, the transistor is configured to operate in the super-regenerative mode, which allows for improved sensitivity and audio gain compared to traditional radio designs. The circuit typically includes an LC tank circuit, consisting of an inductor and a capacitor, which is tuned to the desired FM frequency. This tank circuit is crucial as it selects the frequency of the incoming signal while simultaneously providing feedback to the transistor to enhance its gain.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for biasing the transistor, capacitors for coupling and bypassing, and possibly a variable capacitor to allow for fine-tuning of the frequency. An audio output stage is also included, which may consist of additional transistors or operational amplifiers to further amplify the audio signal before it is sent to a speaker or headphones.
The design benefits from a minimalistic approach, making it suitable for educational purposes, hobbyist projects, or low-cost radio applications. The improved audio gain achieved through the super-regenerative design enhances the listening experience by providing clearer and more robust sound output.The following circuit shows a Schematic diagram for the One Transistor FM Radio with Improved Audio Gain. Features: super-regenerative design, .. 🔗 External reference
The one-transistor FM radio circuit utilizes a super-regenerative architecture, which is known for its simplicity and efficiency in receiving FM signals. The core component of the circuit is a single transistor, which serves both as the radio frequency (RF) amplifier and the detector. This design significantly reduces the number of components required, making it compact and cost-effective.
In this schematic, the transistor is configured to operate in the super-regenerative mode, which allows for improved sensitivity and audio gain compared to traditional radio designs. The circuit typically includes an LC tank circuit, consisting of an inductor and a capacitor, which is tuned to the desired FM frequency. This tank circuit is crucial as it selects the frequency of the incoming signal while simultaneously providing feedback to the transistor to enhance its gain.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for biasing the transistor, capacitors for coupling and bypassing, and possibly a variable capacitor to allow for fine-tuning of the frequency. An audio output stage is also included, which may consist of additional transistors or operational amplifiers to further amplify the audio signal before it is sent to a speaker or headphones.
The design benefits from a minimalistic approach, making it suitable for educational purposes, hobbyist projects, or low-cost radio applications. The improved audio gain achieved through the super-regenerative design enhances the listening experience by providing clearer and more robust sound output.The following circuit shows a Schematic diagram for the One Transistor FM Radio with Improved Audio Gain. Features: super-regenerative design, .. 🔗 External reference