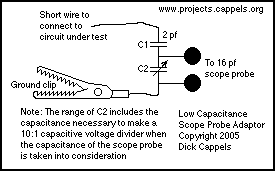
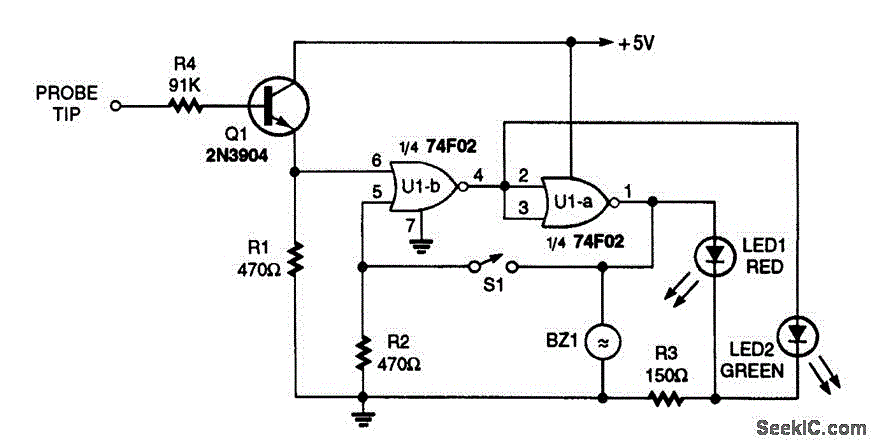
Rf probe for vtvm
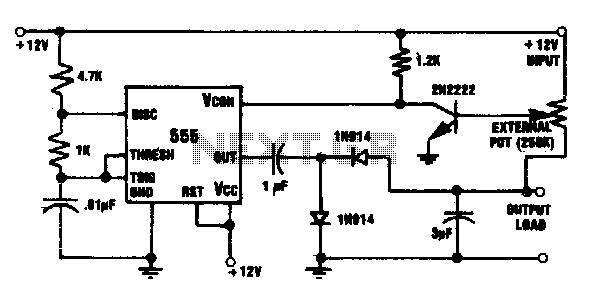
This circuit integrates a 555 timer with a 2N2222 transistor and an external potentiometer. The potentiometer adjusts the output voltage to the desired level. The 2N2222 transistor regulates the output voltage by varying the control voltage of the 555 timer IC, which alters the pulse repetition rate. A 1 kΩ resistor serves as a collector load, and the base of the transistor is driven by the external potentiometer. When the output voltage becomes less negative, the control voltage approaches ground, leading to an increase in the repetition rate of the 555 timer. Consequently, the 3 µF capacitor charges more frequently. The output voltage of the circuit ranges from 0 to 10 V, adjustable via the external potentiometer. The output regulation is maintained within five percent for current levels between 0 to 10 mA and less than five percent for 0 to 0 mA.
The circuit operates based on the principles of pulse width modulation (PWM) and voltage regulation. The 555 timer is configured in astable mode, which allows it to generate a square wave output. The frequency of this output is determined by the timing components, including the external potentiometer and the capacitor. The 2N2222 transistor acts as a switch that controls the flow of current through the load based on the varying control voltage from the 555 timer.
In this configuration, the external potentiometer serves as a variable resistor that adjusts the base current of the 2N2222 transistor. As the resistance of the potentiometer changes, it modifies the voltage at the base of the transistor, which in turn alters the collector current flowing through the load. This change in collector current affects the output voltage, providing a means to achieve the desired voltage level.
The use of a 1 kΩ resistor in the collector circuit ensures that the transistor operates within its safe limits while allowing sufficient current to flow to the load. The 3 µF capacitor plays a critical role in smoothing out the output voltage, filtering the rapid changes caused by the PWM signal generated by the 555 timer. This capacitor charges and discharges in response to the switching of the transistor, effectively stabilizing the output voltage.
The output voltage range of 0 to 10 V is suitable for various applications, and the regulation specifications ensure that the circuit can maintain a stable output even when the load current varies. The design is efficient and can be used in applications requiring precise voltage control, such as in power supplies for sensors or actuators. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve effective voltage regulation with minimal complexity.This circuit combines a 555 timer with a 2N2222 transistor and an external potentiometer. The pot adjusts the output voltage to the desired value. To regulate the output voltage, the 2N2222 varies the control voltage of the 555 IC, increasing or decreasing the pulse repetition rate. A 1 K resistor is used as a collector load. The transistor base is driven from the external pot. If the output voltage becomes less negative, the control voltage moves closer to ground, causing the repetition rate of the 555 to increase, which, in turn, causes the 3 µf capacitor to charge more frequently
Output voltage for the circuit is 0 to 10 V, adjusted by the external pot. Output regulation is less than five percent for 0 to 10 mA and less than 5 percent for 0 to 0 mA.
The circuit operates based on the principles of pulse width modulation (PWM) and voltage regulation. The 555 timer is configured in astable mode, which allows it to generate a square wave output. The frequency of this output is determined by the timing components, including the external potentiometer and the capacitor. The 2N2222 transistor acts as a switch that controls the flow of current through the load based on the varying control voltage from the 555 timer.
In this configuration, the external potentiometer serves as a variable resistor that adjusts the base current of the 2N2222 transistor. As the resistance of the potentiometer changes, it modifies the voltage at the base of the transistor, which in turn alters the collector current flowing through the load. This change in collector current affects the output voltage, providing a means to achieve the desired voltage level.
The use of a 1 kΩ resistor in the collector circuit ensures that the transistor operates within its safe limits while allowing sufficient current to flow to the load. The 3 µF capacitor plays a critical role in smoothing out the output voltage, filtering the rapid changes caused by the PWM signal generated by the 555 timer. This capacitor charges and discharges in response to the switching of the transistor, effectively stabilizing the output voltage.
The output voltage range of 0 to 10 V is suitable for various applications, and the regulation specifications ensure that the circuit can maintain a stable output even when the load current varies. The design is efficient and can be used in applications requiring precise voltage control, such as in power supplies for sensors or actuators. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve effective voltage regulation with minimal complexity.This circuit combines a 555 timer with a 2N2222 transistor and an external potentiometer. The pot adjusts the output voltage to the desired value. To regulate the output voltage, the 2N2222 varies the control voltage of the 555 IC, increasing or decreasing the pulse repetition rate. A 1 K resistor is used as a collector load. The transistor base is driven from the external pot. If the output voltage becomes less negative, the control voltage moves closer to ground, causing the repetition rate of the 555 to increase, which, in turn, causes the 3 µf capacitor to charge more frequently
Output voltage for the circuit is 0 to 10 V, adjusted by the external pot. Output regulation is less than five percent for 0 to 10 mA and less than 5 percent for 0 to 0 mA.