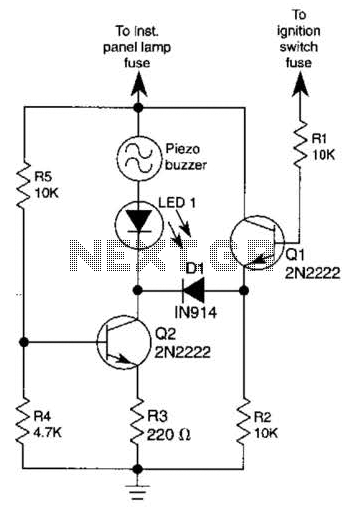
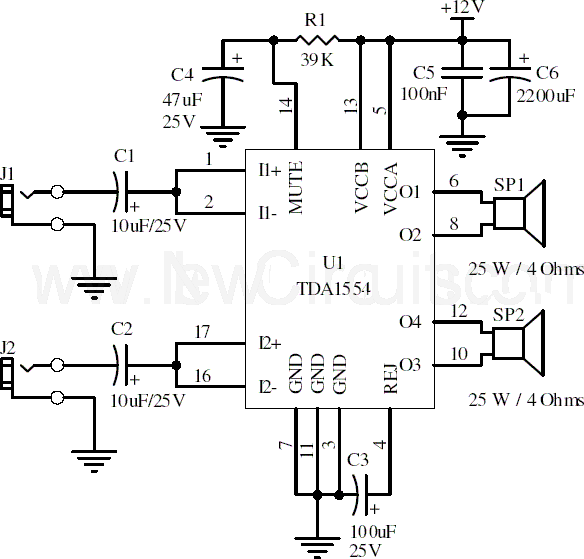
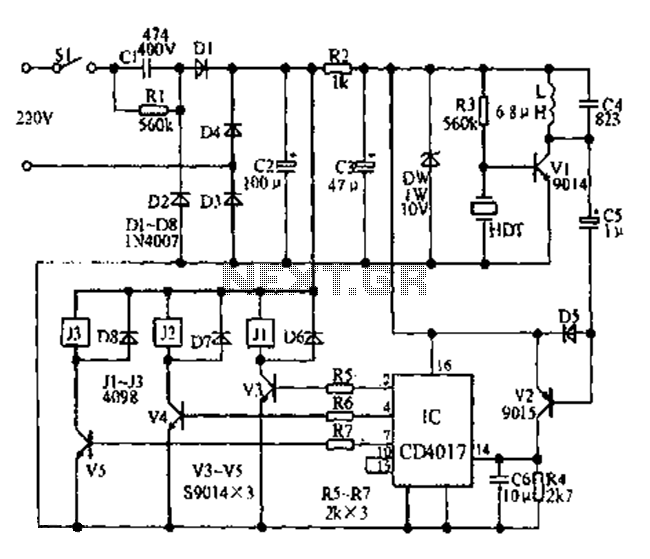
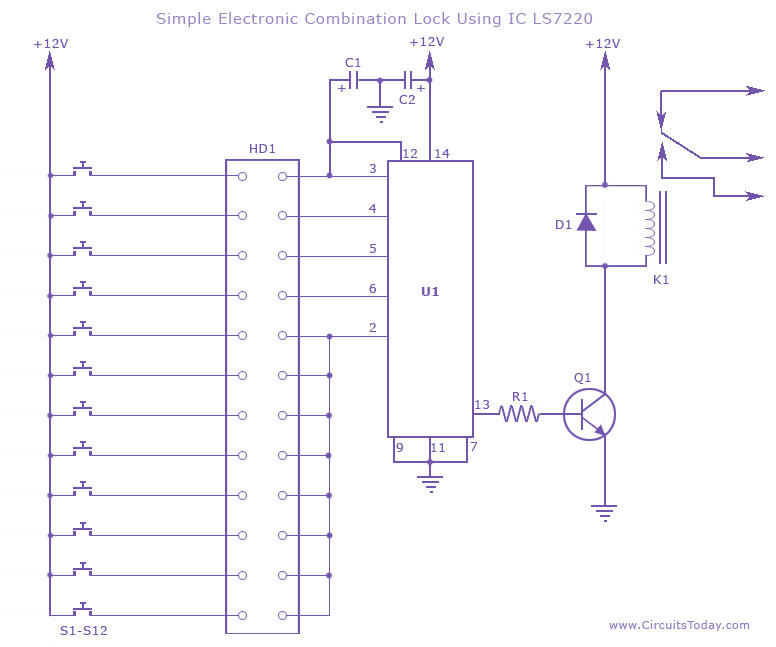
UHF amplifier circuit
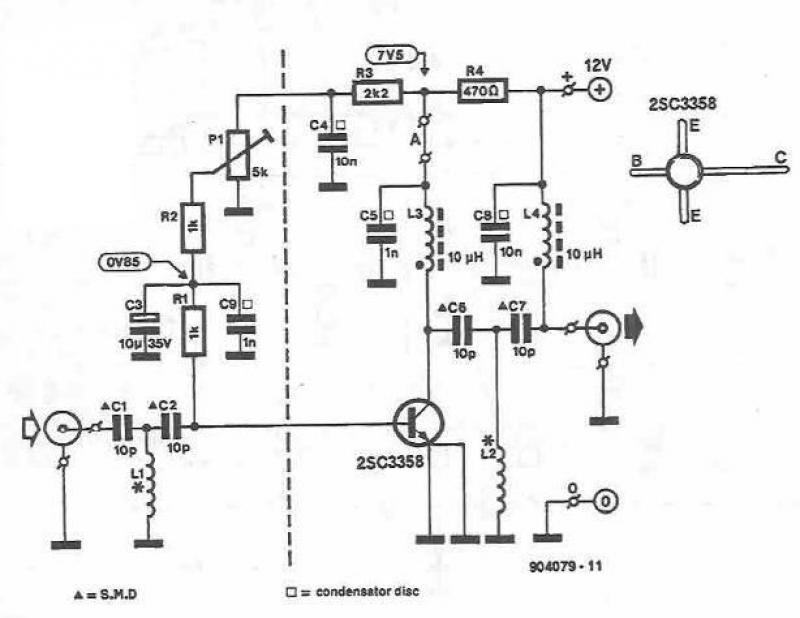
This UHF amplifier circuit project is beneficial for enhancing weak TV signals. The amplifier provides a gain of 10-15 dB within a frequency range of 400 to 850 MHz. To ensure optimal performance and reliability, the PCB tracks should be coated with tin. Certain disc capacitors (C4, C5, C8, and C9) are to be directly adhered to the board, while all other terminals should be kept as short as possible, utilizing SMD components. The power supply can be derived from a simple 12 V source with a 78L12 voltage regulator. The TV will connect to the amplifier through a small coupling capacitor (10-47 pF). For calibration, the cursor of potentiometer P1 should be positioned in the middle of its range and then adjusted for the best image quality, typically resulting in a collector current of the transistor between 5-15 mA.
The UHF amplifier circuit is designed to improve the reception of television signals, particularly in areas where the signal strength is insufficient for clear viewing. The circuit operates efficiently within the UHF band, specifically from 400 to 850 MHz, making it suitable for a wide variety of television broadcasts. The gain of 10-15 dB indicates that the amplifier can significantly enhance weak signals, making it easier for the television to process and display the incoming data.
The printed circuit board (PCB) design is critical for the performance of the amplifier. The recommendation to cover the PCB tracks with tin serves to improve solderability and reduce oxidation, which can degrade circuit performance over time. The use of surface-mount device (SMD) components allows for a compact design and minimizes the length of signal paths, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies.
The power supply circuit is straightforward, utilizing a 78L12 voltage regulator to provide a stable 12 V output. This regulator is efficient for low-current applications and helps ensure that the amplifier operates within its specified voltage range, thereby maximizing reliability. The coupling capacitor, which connects the TV to the amplifier, is crucial for blocking any DC voltage while allowing the AC signal to pass through. The specified values of 10-47 pF for this capacitor are appropriate for maintaining the frequency response of the circuit.
Calibration of the amplifier is an important step to ensure optimal performance. The adjustment of the potentiometer P1 allows for fine-tuning of the gain to match the specific signal conditions. By starting with the cursor in the middle of its range, the user can make adjustments based on the received signal quality, aiming for a collector current of 5-15 mA, which indicates that the transistor is operating effectively within its linear region. This careful calibration process is essential for achieving the best possible image quality on the television.This UHF amplifier circuit electronic project can be useful in situations where the TV signal is weak. The UHF amplifier circuit has a gain of 10-15 dB in a frequency range between 400 and 850 MHz. To obtain optimum performance and good reliability, the PCB tracks should be covered with tin. At each disc capacitors C4, C5, C8 and C9, by one of the girls is glued directly on board. All other terminals are to be cut as short as possible and will use SMD components. Power is from a simple source of 12 V built 78L12 stabilizer would be appropriate. TV will be connected to the amplifier through a small coupling capacitor (10-47pF). To calibrate the assembly bring P1 cursor in the middle of his race and then adjust it to obtain the best image quality (in practice, and you get the collector current of transistor of 5-15 mA). 🔗 External reference
The UHF amplifier circuit is designed to improve the reception of television signals, particularly in areas where the signal strength is insufficient for clear viewing. The circuit operates efficiently within the UHF band, specifically from 400 to 850 MHz, making it suitable for a wide variety of television broadcasts. The gain of 10-15 dB indicates that the amplifier can significantly enhance weak signals, making it easier for the television to process and display the incoming data.
The printed circuit board (PCB) design is critical for the performance of the amplifier. The recommendation to cover the PCB tracks with tin serves to improve solderability and reduce oxidation, which can degrade circuit performance over time. The use of surface-mount device (SMD) components allows for a compact design and minimizes the length of signal paths, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies.
The power supply circuit is straightforward, utilizing a 78L12 voltage regulator to provide a stable 12 V output. This regulator is efficient for low-current applications and helps ensure that the amplifier operates within its specified voltage range, thereby maximizing reliability. The coupling capacitor, which connects the TV to the amplifier, is crucial for blocking any DC voltage while allowing the AC signal to pass through. The specified values of 10-47 pF for this capacitor are appropriate for maintaining the frequency response of the circuit.
Calibration of the amplifier is an important step to ensure optimal performance. The adjustment of the potentiometer P1 allows for fine-tuning of the gain to match the specific signal conditions. By starting with the cursor in the middle of its range, the user can make adjustments based on the received signal quality, aiming for a collector current of 5-15 mA, which indicates that the transistor is operating effectively within its linear region. This careful calibration process is essential for achieving the best possible image quality on the television.This UHF amplifier circuit electronic project can be useful in situations where the TV signal is weak. The UHF amplifier circuit has a gain of 10-15 dB in a frequency range between 400 and 850 MHz. To obtain optimum performance and good reliability, the PCB tracks should be covered with tin. At each disc capacitors C4, C5, C8 and C9, by one of the girls is glued directly on board. All other terminals are to be cut as short as possible and will use SMD components. Power is from a simple source of 12 V built 78L12 stabilizer would be appropriate. TV will be connected to the amplifier through a small coupling capacitor (10-47pF). To calibrate the assembly bring P1 cursor in the middle of his race and then adjust it to obtain the best image quality (in practice, and you get the collector current of transistor of 5-15 mA). 🔗 External reference