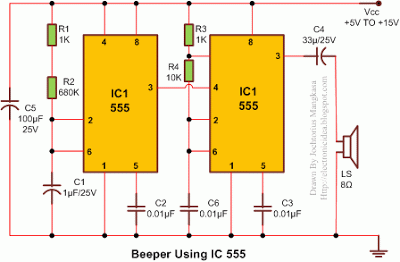
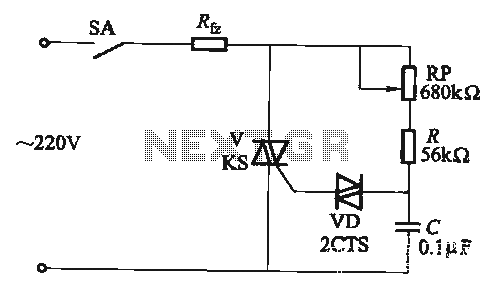
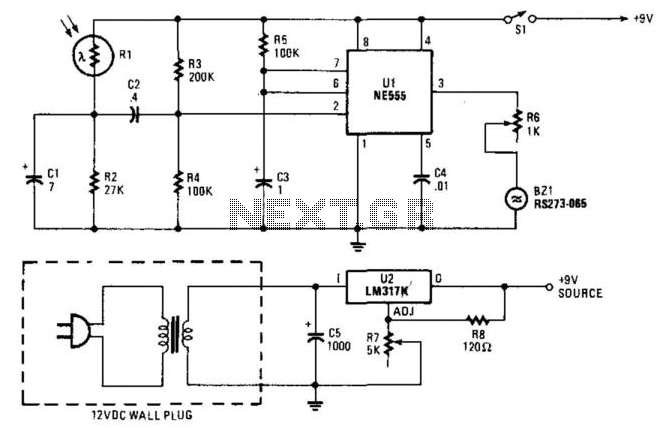
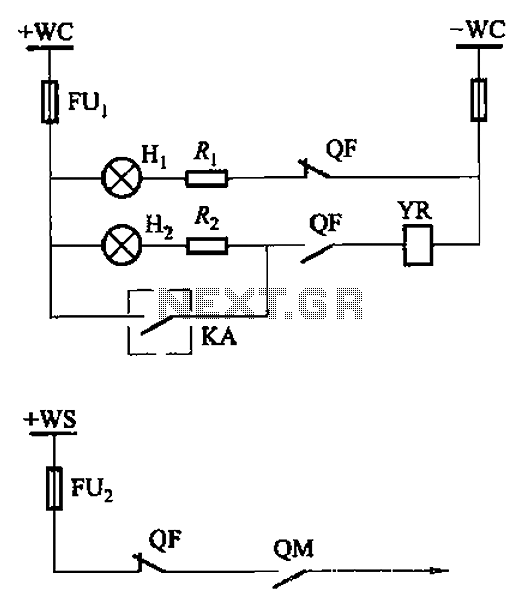
Under-Over-Voltage Beep for Manual Stabiliser
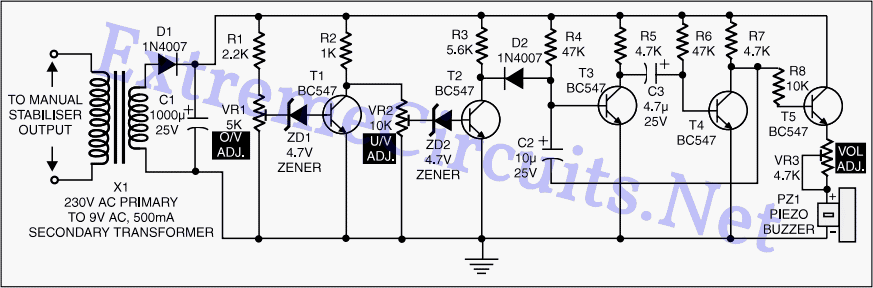
Manual stabilizers remain popular due to their straightforward construction, affordability, and high reliability, as they do not incorporate any relays.
Manual stabilizers are widely utilized in various electronic applications, primarily due to their effective voltage regulation capabilities. These devices function by adjusting the output voltage to maintain a consistent level despite fluctuations in the input voltage. The simplicity of their design often includes a transformer, rectifier, and filter circuit, which work together to stabilize the output.
The absence of relays in manual stabilizers contributes significantly to their reliability and longevity. Without mechanical components, the risk of failure from wear and tear is minimized, making them suitable for environments where durability is essential.
In terms of construction, a typical manual stabilizer may consist of a step-down transformer that reduces the high voltage AC input to a lower level. The output from the transformer is then rectified using diodes, converting AC to DC. Following this, a filter capacitor smooths out the rectified voltage, providing a steady DC output.
Additionally, manual stabilizers often feature adjustable output settings, allowing users to select the desired voltage level. This adjustability is achieved through a potentiometer or variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the output voltage to meet specific requirements.
Overall, the combination of simple circuitry, cost-effectiveness, and robust performance makes manual stabilizers a preferred choice for many applications, including powering sensitive electronic devices and ensuring stable operation in varying electrical conditions.Manual stabilisers are still popular because of their simple construction, low cost, and high reliability due to the absence of any relays while covering.. 🔗 External reference
Manual stabilizers are widely utilized in various electronic applications, primarily due to their effective voltage regulation capabilities. These devices function by adjusting the output voltage to maintain a consistent level despite fluctuations in the input voltage. The simplicity of their design often includes a transformer, rectifier, and filter circuit, which work together to stabilize the output.
The absence of relays in manual stabilizers contributes significantly to their reliability and longevity. Without mechanical components, the risk of failure from wear and tear is minimized, making them suitable for environments where durability is essential.
In terms of construction, a typical manual stabilizer may consist of a step-down transformer that reduces the high voltage AC input to a lower level. The output from the transformer is then rectified using diodes, converting AC to DC. Following this, a filter capacitor smooths out the rectified voltage, providing a steady DC output.
Additionally, manual stabilizers often feature adjustable output settings, allowing users to select the desired voltage level. This adjustability is achieved through a potentiometer or variable resistor, enabling fine-tuning of the output voltage to meet specific requirements.
Overall, the combination of simple circuitry, cost-effectiveness, and robust performance makes manual stabilizers a preferred choice for many applications, including powering sensitive electronic devices and ensuring stable operation in varying electrical conditions.Manual stabilisers are still popular because of their simple construction, low cost, and high reliability due to the absence of any relays while covering.. 🔗 External reference