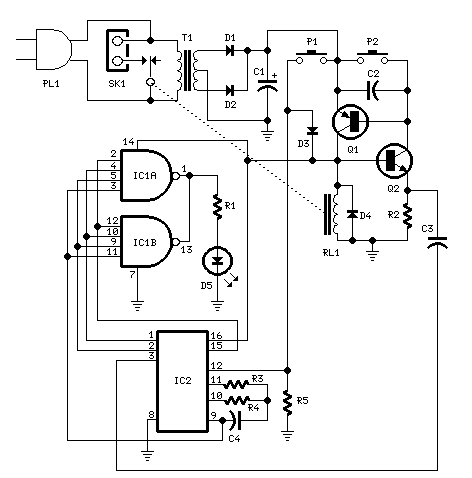
10 minute time delay by fet 2n3819
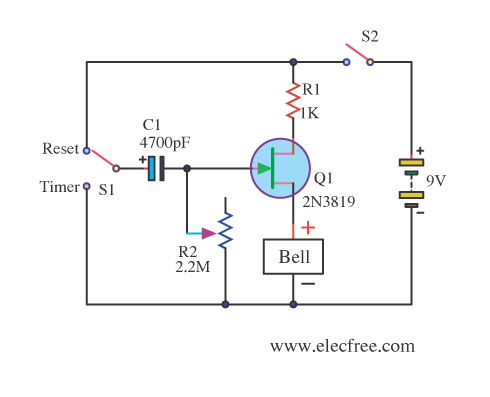
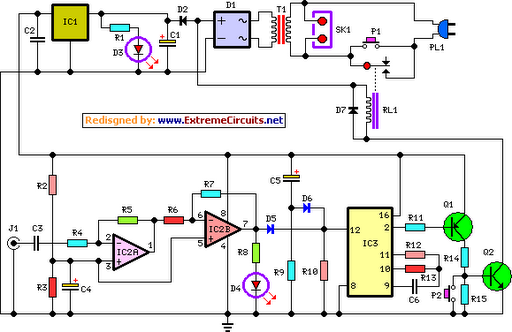
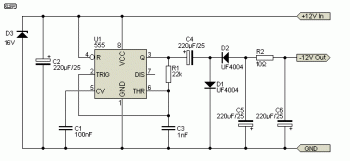
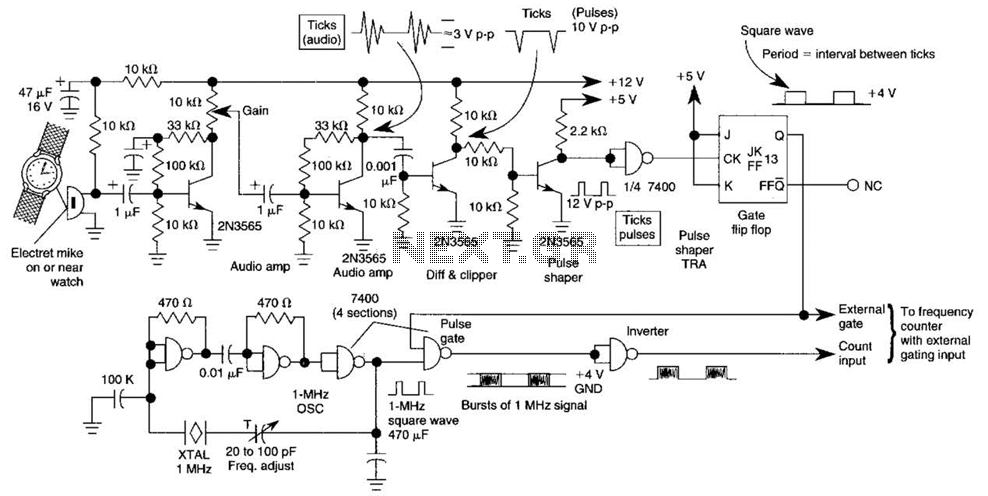
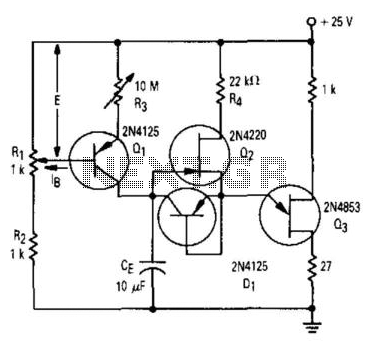
This circuit utilizes the FET 2N3819, which functions as a switch, operating in both conduction and non-conduction states. This behavior is in contrast to that of a bipolar transistor.
The 2N3819 is a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it suitable for various switching applications. In this circuit, the FET operates by controlling the flow of current through its channel based on the voltage applied to its gate terminal. When a sufficient voltage is applied to the gate, the FET enters the conduction state, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source. Conversely, when the gate voltage is removed or reduced below a certain threshold, the FET switches to the non-conduction state, effectively interrupting the flow of current.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected to the gate to establish the necessary biasing conditions. The drain is connected to the load, which could be any device requiring control, such as an LED or a relay. The source is usually connected to ground or a common reference point in the circuit.
In practical applications, the 2N3819 can be employed in digital switching circuits, amplifiers, and signal modulation systems. Its ability to switch rapidly and operate efficiently makes it a valuable component in modern electronic designs. Additionally, it is important to consider the maximum ratings specified in the datasheet for the 2N3819, including gate-source voltage, drain current, and power dissipation, to ensure reliable operation within safe limits.
Overall, the 2N3819 serves as a versatile switch in electronic circuits, demonstrating unique characteristics that distinguish it from traditional bipolar transistors.This circuit is a basic function of the FET 2N3819, which acts as a switch. In the conduction and not conduction. It runs contrary to the transistor. The.. 🔗 External reference
The 2N3819 is a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) known for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it suitable for various switching applications. In this circuit, the FET operates by controlling the flow of current through its channel based on the voltage applied to its gate terminal. When a sufficient voltage is applied to the gate, the FET enters the conduction state, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source. Conversely, when the gate voltage is removed or reduced below a certain threshold, the FET switches to the non-conduction state, effectively interrupting the flow of current.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected to the gate to establish the necessary biasing conditions. The drain is connected to the load, which could be any device requiring control, such as an LED or a relay. The source is usually connected to ground or a common reference point in the circuit.
In practical applications, the 2N3819 can be employed in digital switching circuits, amplifiers, and signal modulation systems. Its ability to switch rapidly and operate efficiently makes it a valuable component in modern electronic designs. Additionally, it is important to consider the maximum ratings specified in the datasheet for the 2N3819, including gate-source voltage, drain current, and power dissipation, to ensure reliable operation within safe limits.
Overall, the 2N3819 serves as a versatile switch in electronic circuits, demonstrating unique characteristics that distinguish it from traditional bipolar transistors.This circuit is a basic function of the FET 2N3819, which acts as a switch. In the conduction and not conduction. It runs contrary to the transistor. The.. 🔗 External reference