4541 Timer Relay Circuit 0.3 second to 10 hours
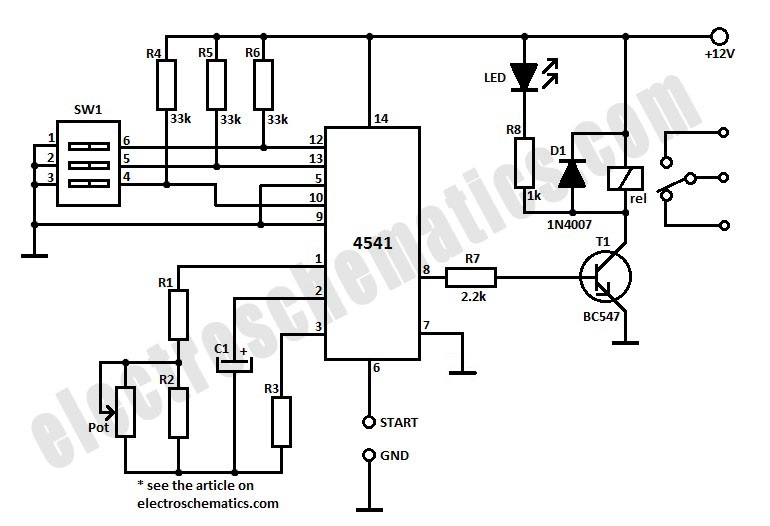
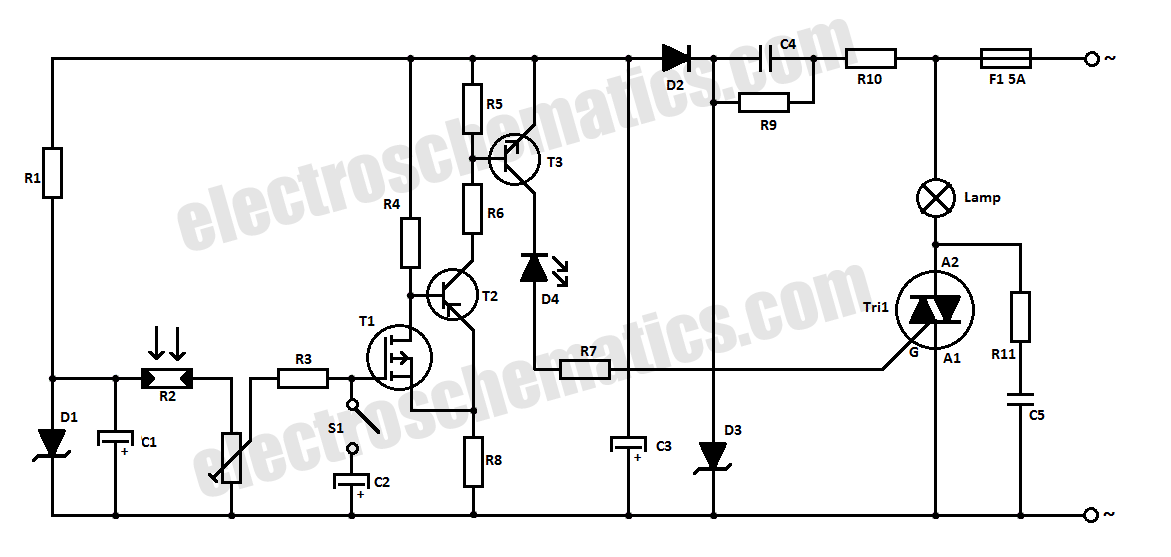
To initiate the timing process, there are two options available: either connect the START point to ground (GND), in which case the timer activates when connected to the voltage supply, or employ a switch to start the timer.
The timing circuit in question operates using two distinct methods for activation, providing flexibility depending on the application requirements. When the START point is connected to ground (GND), the circuit is designed to initiate timing upon receiving a voltage supply. This method is particularly useful in automated systems where grounding can serve as a reliable trigger for the timer.
Alternatively, the use of a switch for activation allows for manual control over the timing process. This approach can be advantageous in scenarios where user intervention is necessary, providing a straightforward means to start the timer on demand. The switch can be a simple toggle or push-button type, which, when engaged, completes the circuit and sends a signal to the timer to commence its operation.
In both configurations, careful attention must be paid to the circuit design to ensure that the timer operates reliably under the intended conditions. Components such as resistors, capacitors, and the timer IC itself must be selected based on the desired timing intervals and the overall voltage levels used in the circuit. Proper layout and grounding practices should also be considered to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.In order to start the timining you have 2 possibilities: you either connect the START point to ground GND and in this case the timer starts when you connect it to the voltage supply or you can place a switch to start it. 🔗 External reference
The timing circuit in question operates using two distinct methods for activation, providing flexibility depending on the application requirements. When the START point is connected to ground (GND), the circuit is designed to initiate timing upon receiving a voltage supply. This method is particularly useful in automated systems where grounding can serve as a reliable trigger for the timer.
Alternatively, the use of a switch for activation allows for manual control over the timing process. This approach can be advantageous in scenarios where user intervention is necessary, providing a straightforward means to start the timer on demand. The switch can be a simple toggle or push-button type, which, when engaged, completes the circuit and sends a signal to the timer to commence its operation.
In both configurations, careful attention must be paid to the circuit design to ensure that the timer operates reliably under the intended conditions. Components such as resistors, capacitors, and the timer IC itself must be selected based on the desired timing intervals and the overall voltage levels used in the circuit. Proper layout and grounding practices should also be considered to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.In order to start the timining you have 2 possibilities: you either connect the START point to ground GND and in this case the timer starts when you connect it to the voltage supply or you can place a switch to start it. 🔗 External reference