555 LED flasher
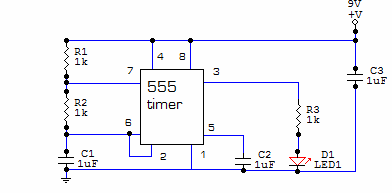
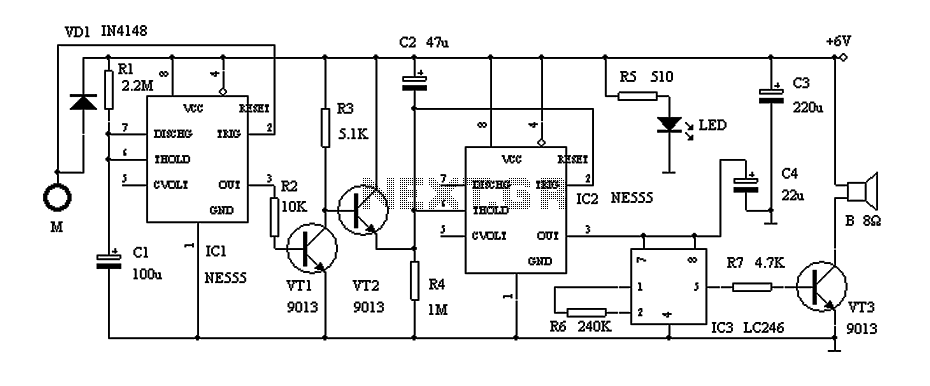
This circuit is built around one of the most popular timer integrated circuits, the 555 timer. It will flash the LED on and off at regular intervals. From left to right, the two resistors and the capacitor set the time it takes to turn the LED on or off, by changing the time it takes to charge the capacitor to trigger the timer. Next is the 555 timer, this is where all the work gets done to determine the time the LED stays on and off. It contains a complicated circuit inside, but since it is packaged in the IC, it can be used as a simple component. The two capacitors that are right of the timer are just accessories, so to speak, but are needed for the timer to work correctly. The last part is the resistor and the LED; the resistor is there to limit the current on the LED so that it won't burn.
The circuit utilizes the 555 timer in astable mode, which allows it to continuously switch between high and low states, thereby causing the LED to flash. The timing of this oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors (R1 and R2) and the capacitor (C1) connected to the timer. The formula used to calculate the frequency of the oscillation is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C1} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency in hertz,
- \( R1 \) is the resistance of the first resistor,
- \( R2 \) is the resistance of the second resistor,
- \( C1 \) is the capacitance in farads.
In this configuration, the charge and discharge times of the capacitor dictate how long the LED remains lit and how long it is off. The two additional capacitors connected to the timer (C2 and C3) may serve as decoupling capacitors to stabilize the power supply and filter out any noise that may affect the performance of the timer.
The current-limiting resistor (R3) connected in series with the LED ensures that the LED operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, considering the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
In summary, this circuit effectively demonstrates the versatility and functionality of the 555 timer in creating a simple LED flasher, with careful consideration given to the timing components and current limiting to ensure reliable operation.This circuit is built around one of the most popular timer integrated circuits, the 555 timer. It will flash the led on and of at regular intervals. From left to right, the two resistors and the capacitor set the time it takes to turn the led on or off, by changing the time it takes to charge the capacitor to trigger the timer. Next is the 555 timer, this is where all the work gets done to determine the time the led stays on and off.
It contains a complicated circuit inside, but since it is packaged in the IC it can be used as a simple component. The two capacitors that are right of the timer are just accessories so to speak, but are needed for the timer to work correctly. The last part is the resistor and the led, the resistor is there to limit the current on the led so that it won't burn.
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the 555 timer in astable mode, which allows it to continuously switch between high and low states, thereby causing the LED to flash. The timing of this oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors (R1 and R2) and the capacitor (C1) connected to the timer. The formula used to calculate the frequency of the oscillation is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C1} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the frequency in hertz,
- \( R1 \) is the resistance of the first resistor,
- \( R2 \) is the resistance of the second resistor,
- \( C1 \) is the capacitance in farads.
In this configuration, the charge and discharge times of the capacitor dictate how long the LED remains lit and how long it is off. The two additional capacitors connected to the timer (C2 and C3) may serve as decoupling capacitors to stabilize the power supply and filter out any noise that may affect the performance of the timer.
The current-limiting resistor (R3) connected in series with the LED ensures that the LED operates within its specified current range, preventing damage due to excessive current. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, considering the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
In summary, this circuit effectively demonstrates the versatility and functionality of the 555 timer in creating a simple LED flasher, with careful consideration given to the timing components and current limiting to ensure reliable operation.This circuit is built around one of the most popular timer integrated circuits, the 555 timer. It will flash the led on and of at regular intervals. From left to right, the two resistors and the capacitor set the time it takes to turn the led on or off, by changing the time it takes to charge the capacitor to trigger the timer. Next is the 555 timer, this is where all the work gets done to determine the time the led stays on and off.
It contains a complicated circuit inside, but since it is packaged in the IC it can be used as a simple component. The two capacitors that are right of the timer are just accessories so to speak, but are needed for the timer to work correctly. The last part is the resistor and the led, the resistor is there to limit the current on the led so that it won't burn.
🔗 External reference