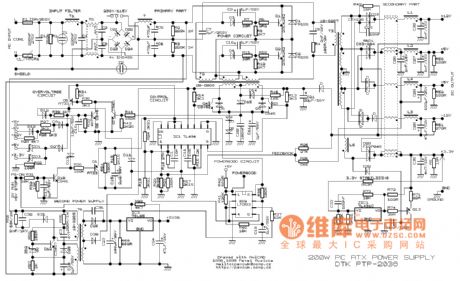
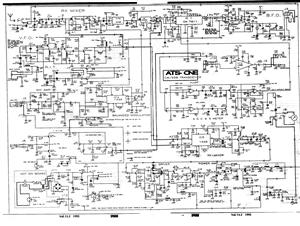
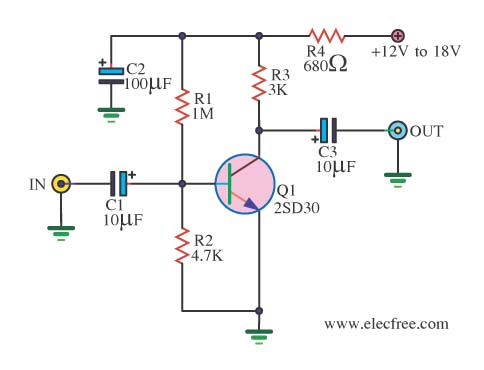
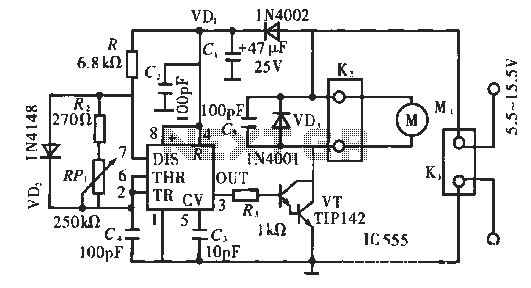
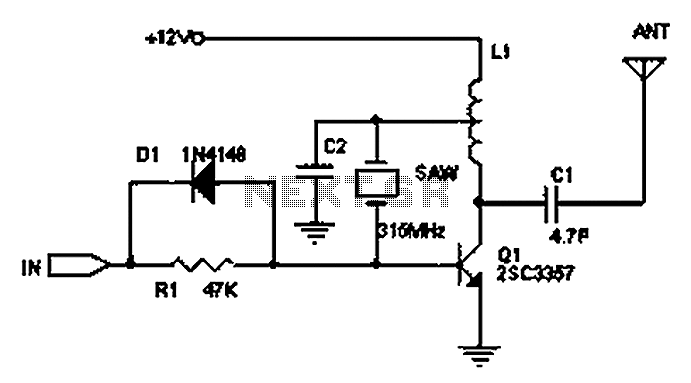
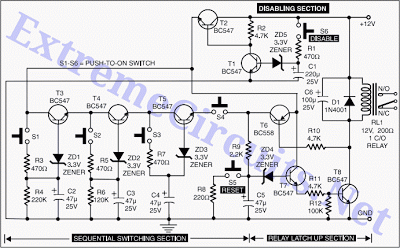
A circuit diagram of a wireless hands-free telephone device
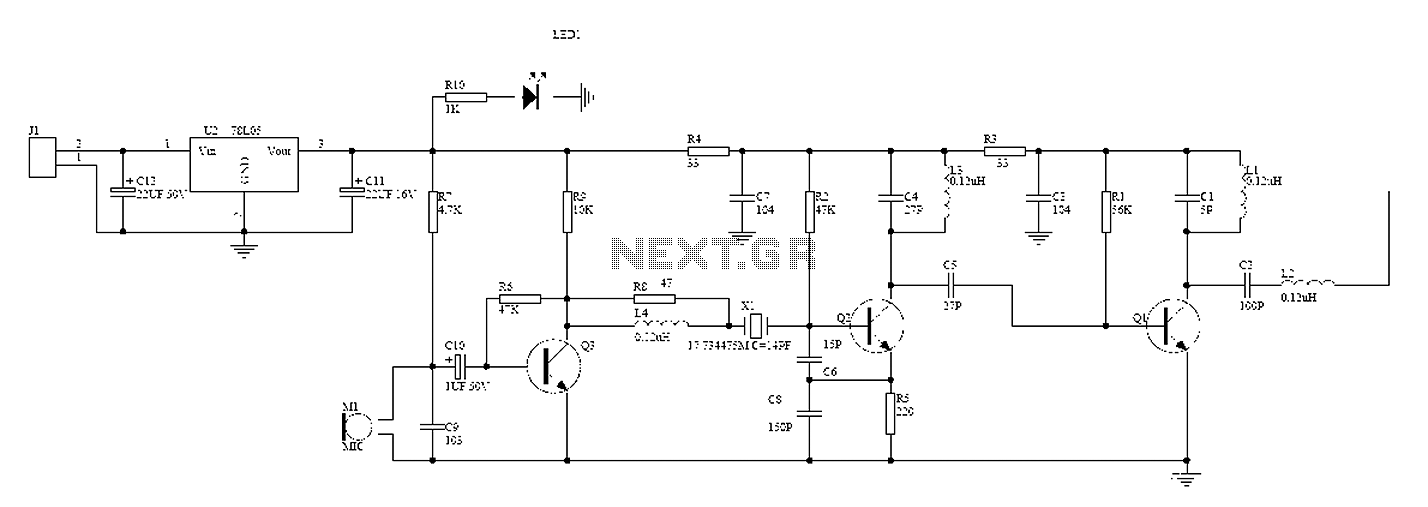
A wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram is presented below.
The wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram typically comprises several key components that work together to enable hands-free communication. The primary components include a microphone, speaker, Bluetooth module, power supply, and control circuitry.
The microphone captures the user's voice and converts it into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the control circuitry, which may include an operational amplifier for signal conditioning. The processed audio signal is transmitted wirelessly via the Bluetooth module, which allows for connectivity with a compatible mobile phone or other communication devices.
On the receiving end, the Bluetooth module decodes the incoming audio signal and sends it to the speaker, which converts the electrical signal back into sound waves, allowing the user to hear the other party. The power supply, often a rechargeable battery, provides the necessary voltage and current to power the entire circuit, ensuring that all components operate effectively.
Additional features may include volume control, LED indicators for connection status, and noise cancellation circuitry to enhance audio clarity. The layout of the circuit should be designed to minimize interference and optimize performance, ensuring reliable hands-free communication in various environments. Overall, the wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram illustrates a sophisticated integration of components that facilitate convenient and efficient communication.A wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram as follows:
The wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram typically comprises several key components that work together to enable hands-free communication. The primary components include a microphone, speaker, Bluetooth module, power supply, and control circuitry.
The microphone captures the user's voice and converts it into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the control circuitry, which may include an operational amplifier for signal conditioning. The processed audio signal is transmitted wirelessly via the Bluetooth module, which allows for connectivity with a compatible mobile phone or other communication devices.
On the receiving end, the Bluetooth module decodes the incoming audio signal and sends it to the speaker, which converts the electrical signal back into sound waves, allowing the user to hear the other party. The power supply, often a rechargeable battery, provides the necessary voltage and current to power the entire circuit, ensuring that all components operate effectively.
Additional features may include volume control, LED indicators for connection status, and noise cancellation circuitry to enhance audio clarity. The layout of the circuit should be designed to minimize interference and optimize performance, ensuring reliable hands-free communication in various environments. Overall, the wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram illustrates a sophisticated integration of components that facilitate convenient and efficient communication.A wireless hands-free telephone device circuit diagram as follows: