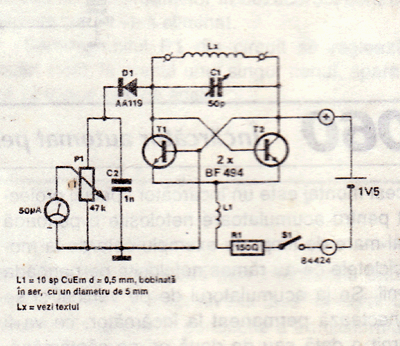
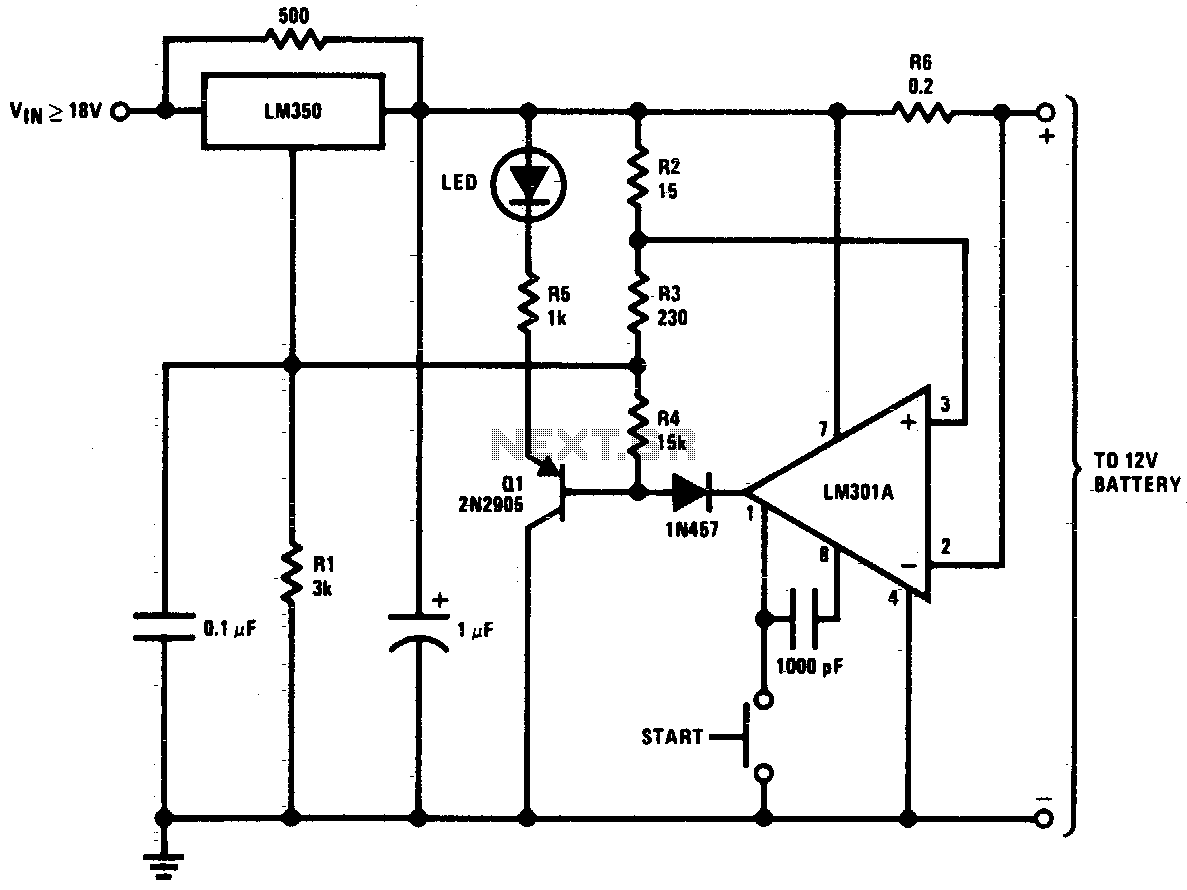
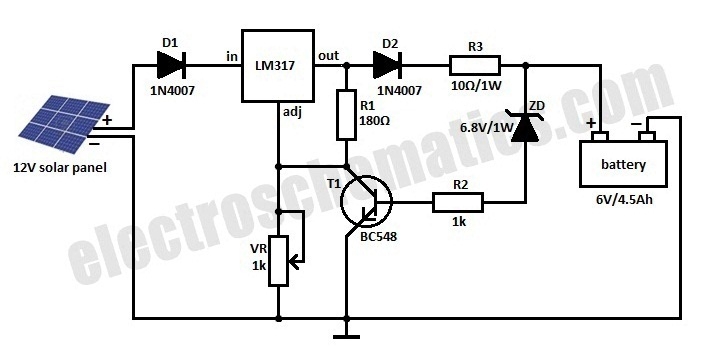
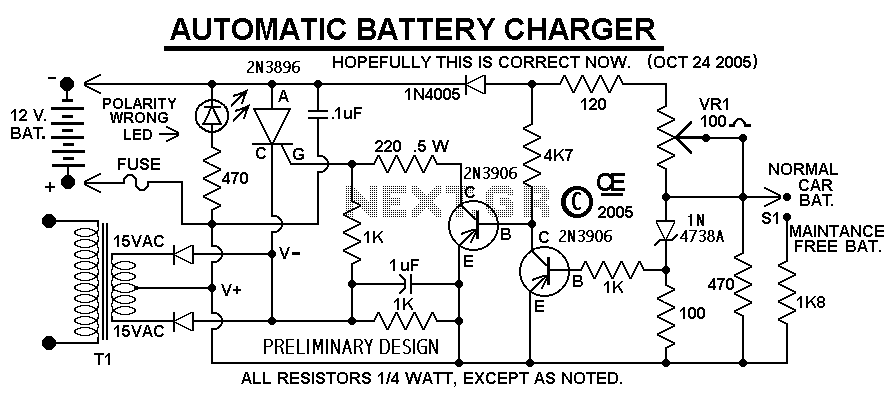
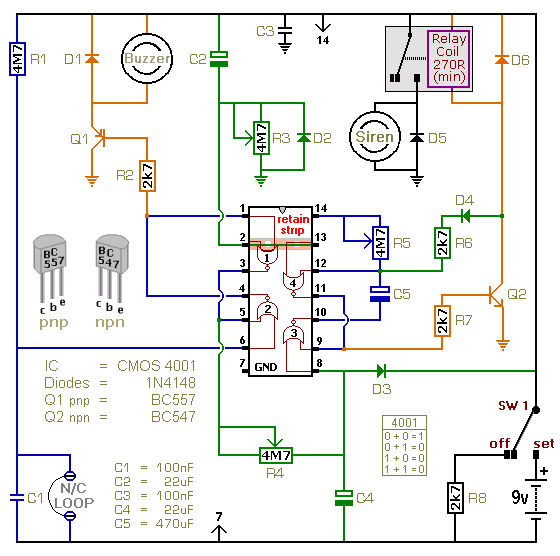
Battery indicator
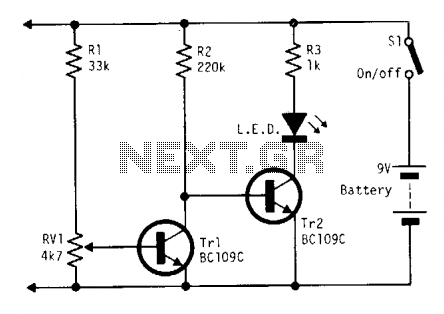
Continuously monitors battery voltage during use and consumes only about 250 microamperes until the end point is reached. Near the end point, transistor Tr1 turns off, allowing transistor Tr2 to illuminate the LED, which increases current drain further, leading to a distinct turn-off point. A low current LED diode is utilized.
This circuit is designed to monitor battery voltage levels while ensuring minimal power consumption. The primary component, Tr1, is a transistor that operates in a low-power state, drawing approximately 250 microamperes. This low consumption is crucial for applications where battery life is a priority.
As the battery voltage approaches a predefined threshold, Tr1 ceases operation, which triggers Tr2 to activate. Tr2 is responsible for driving a low current LED diode. The LED serves not only as an indicator of the circuit's status but also increases the current draw from the battery. This additional load assists in reaching a clear and distinct turn-off point for the circuit, ensuring that the battery is not over-discharged, which could lead to damage.
The use of a low current LED diode is essential in this design, as it allows for visual feedback without significantly impacting the overall power consumption. The circuit can be applied in various battery-operated devices where monitoring battery status is critical, such as portable electronics or remote sensors.
In summary, this battery monitoring circuit effectively balances low power consumption with functionality, leveraging transistors for control and an LED for user indication, thereby enhancing the reliability and longevity of battery-powered applications.Continually monitors battery voltage during use and consumes only about 250 ? A (until the end point is reached). Near the end point Trl turns off, allowing Tr2 to illuminate the LED to increase current drain further leading to a distinct turn off point. Use a low current LED diode. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to monitor battery voltage levels while ensuring minimal power consumption. The primary component, Tr1, is a transistor that operates in a low-power state, drawing approximately 250 microamperes. This low consumption is crucial for applications where battery life is a priority.
As the battery voltage approaches a predefined threshold, Tr1 ceases operation, which triggers Tr2 to activate. Tr2 is responsible for driving a low current LED diode. The LED serves not only as an indicator of the circuit's status but also increases the current draw from the battery. This additional load assists in reaching a clear and distinct turn-off point for the circuit, ensuring that the battery is not over-discharged, which could lead to damage.
The use of a low current LED diode is essential in this design, as it allows for visual feedback without significantly impacting the overall power consumption. The circuit can be applied in various battery-operated devices where monitoring battery status is critical, such as portable electronics or remote sensors.
In summary, this battery monitoring circuit effectively balances low power consumption with functionality, leveraging transistors for control and an LED for user indication, thereby enhancing the reliability and longevity of battery-powered applications.Continually monitors battery voltage during use and consumes only about 250 ? A (until the end point is reached). Near the end point Trl turns off, allowing Tr2 to illuminate the LED to increase current drain further leading to a distinct turn off point. Use a low current LED diode. 🔗 External reference