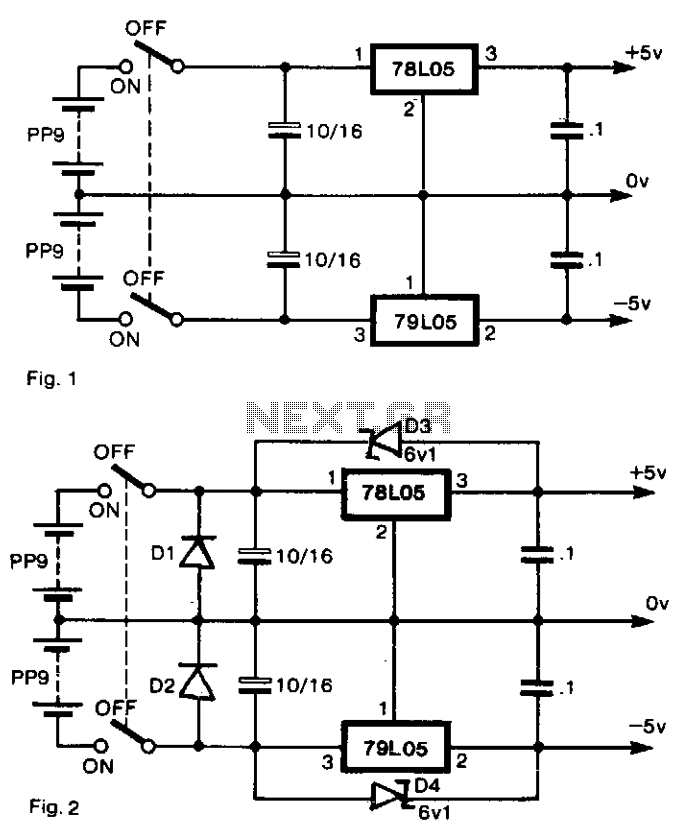
Bipolar Stepper Motor
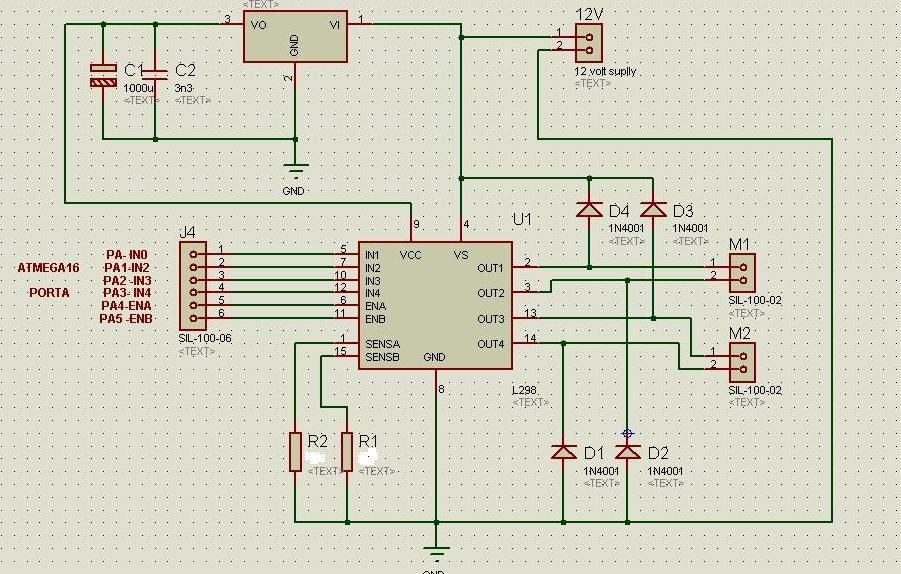
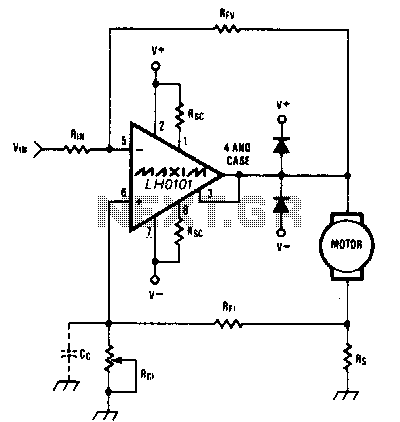
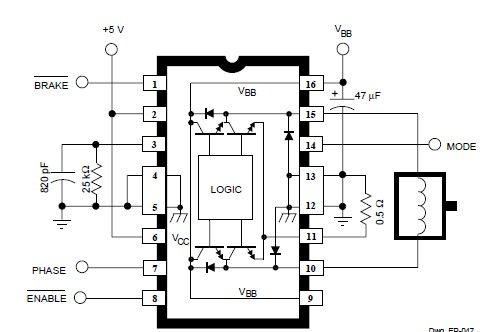
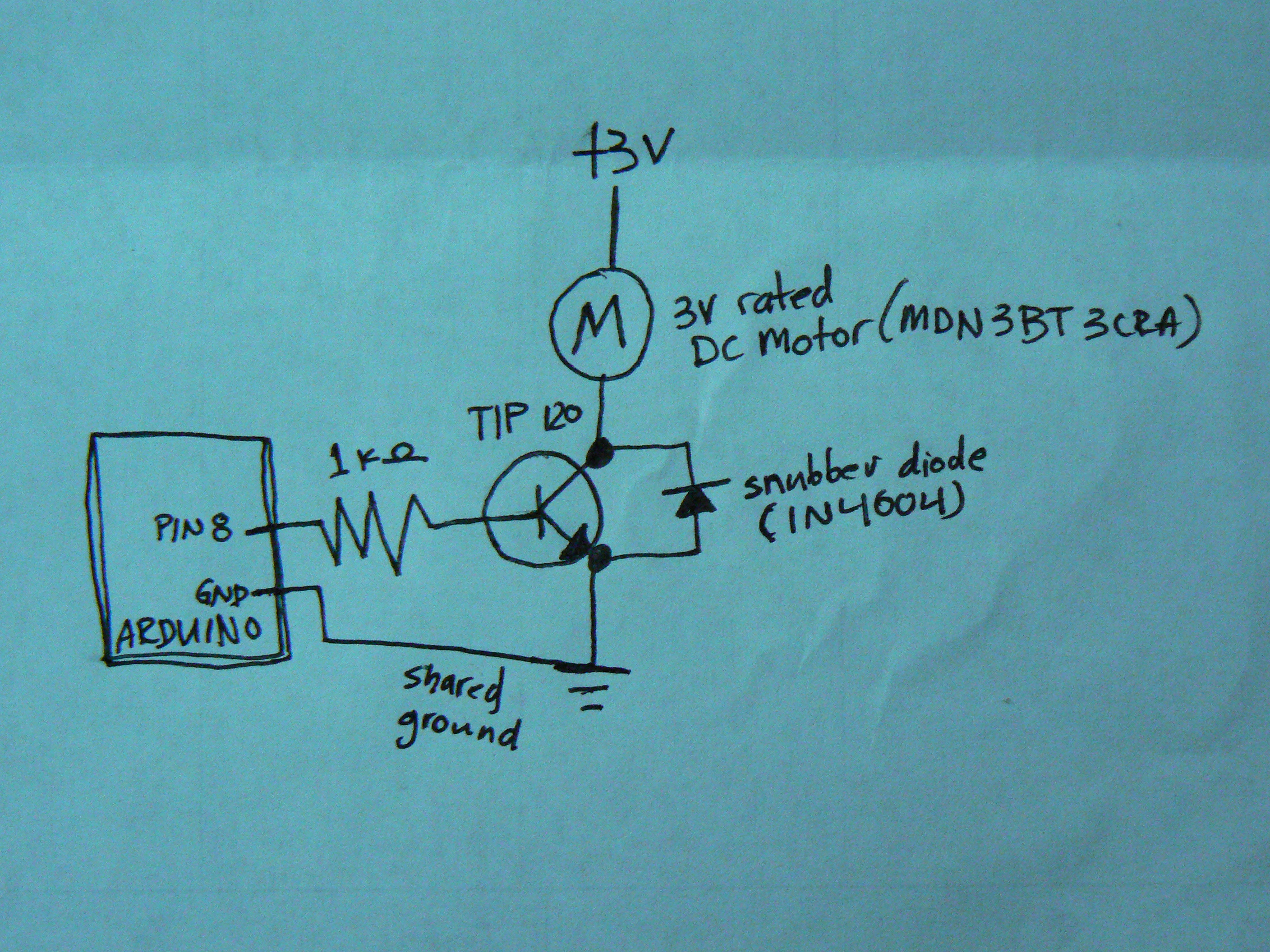
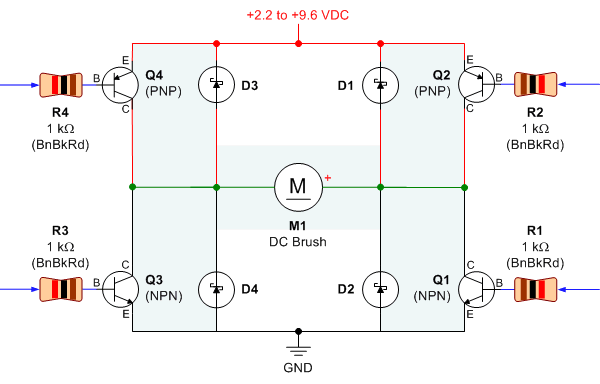
The circuit diagram includes M1 connected to Coil A of a stepper motor and M2 connected to Coil B of the stepper motor. Resistors R1 and R2 are 1 Ohm resistors used for current limiting.
The circuit design involves a stepper motor controlled by two drive circuits, M1 and M2, which are responsible for energizing the respective coils, Coil A and Coil B. The stepper motor operates by sequentially energizing the coils, allowing for precise control over the motor's position and speed.
In this configuration, M1 and M2 may be transistors or MOSFETs, selected based on their ability to handle the required current and voltage levels for the stepper motor. The use of 1 Ohm resistors, R1 and R2, serves a dual purpose: they limit the current flowing through the coils to prevent damage to the motor and the driving circuits, and they also provide a means to monitor the current, as the voltage drop across these resistors can be measured.
It is essential to ensure that the resistors are rated for the power they will dissipate, calculated using the formula P = I²R, where I is the current through the resistor. The choice of a 1 Ohm resistor suggests that the application may involve high currents, thus requiring careful consideration of thermal management.
The circuit may also benefit from additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, which would safeguard the driving transistors from voltage spikes generated when the motor coils are de-energized. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable operation of the stepper motor system.
Overall, the described circuit is a fundamental design for controlling a stepper motor, highlighting the importance of current limiting and protective measures in motor drive applications.For the Circuit diagram M1 connected to Coil A for stepper motor. M2 connected to Coil B for stepper motor. R1 & R2 1 Ohm resistors for current limiti.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design involves a stepper motor controlled by two drive circuits, M1 and M2, which are responsible for energizing the respective coils, Coil A and Coil B. The stepper motor operates by sequentially energizing the coils, allowing for precise control over the motor's position and speed.
In this configuration, M1 and M2 may be transistors or MOSFETs, selected based on their ability to handle the required current and voltage levels for the stepper motor. The use of 1 Ohm resistors, R1 and R2, serves a dual purpose: they limit the current flowing through the coils to prevent damage to the motor and the driving circuits, and they also provide a means to monitor the current, as the voltage drop across these resistors can be measured.
It is essential to ensure that the resistors are rated for the power they will dissipate, calculated using the formula P = I²R, where I is the current through the resistor. The choice of a 1 Ohm resistor suggests that the application may involve high currents, thus requiring careful consideration of thermal management.
The circuit may also benefit from additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, which would safeguard the driving transistors from voltage spikes generated when the motor coils are de-energized. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure reliable operation of the stepper motor system.
Overall, the described circuit is a fundamental design for controlling a stepper motor, highlighting the importance of current limiting and protective measures in motor drive applications.For the Circuit diagram M1 connected to Coil A for stepper motor. M2 connected to Coil B for stepper motor. R1 & R2 1 Ohm resistors for current limiti.. 🔗 External reference