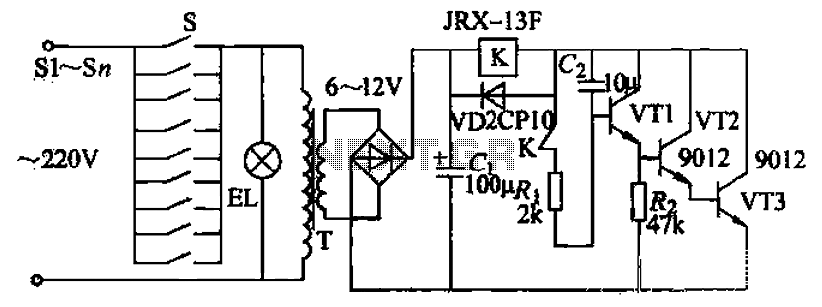
Charge Limiter circuit
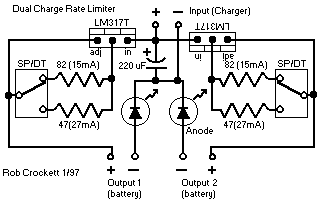
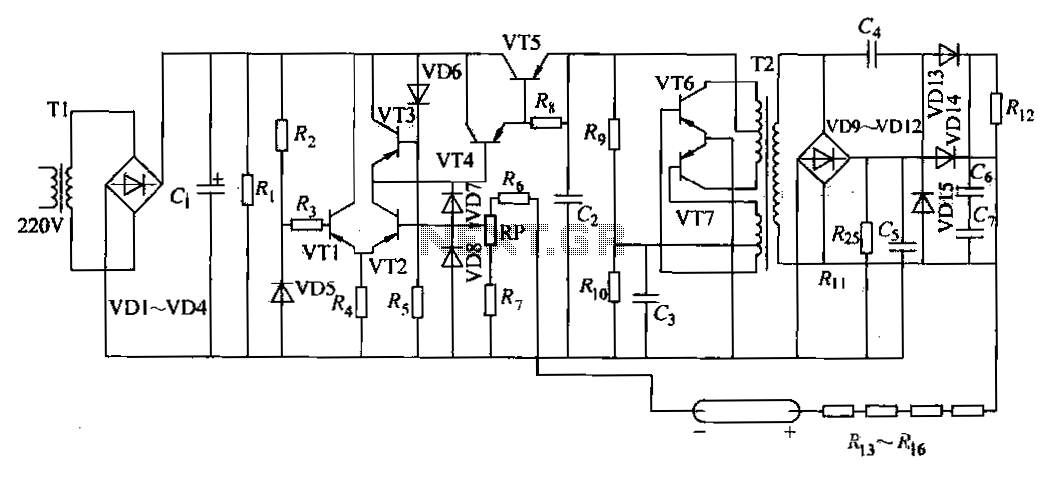
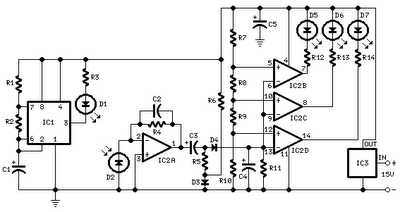
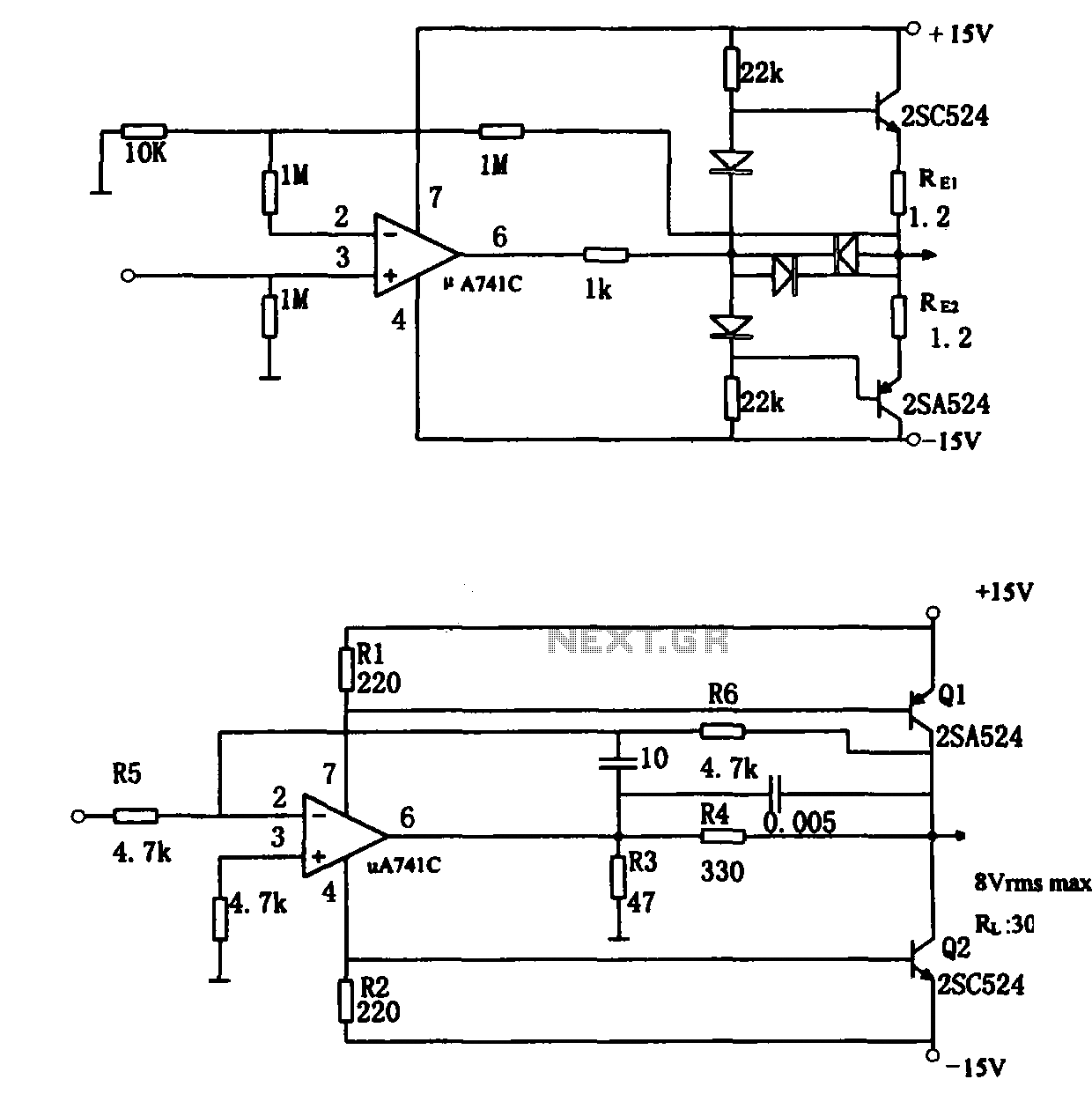
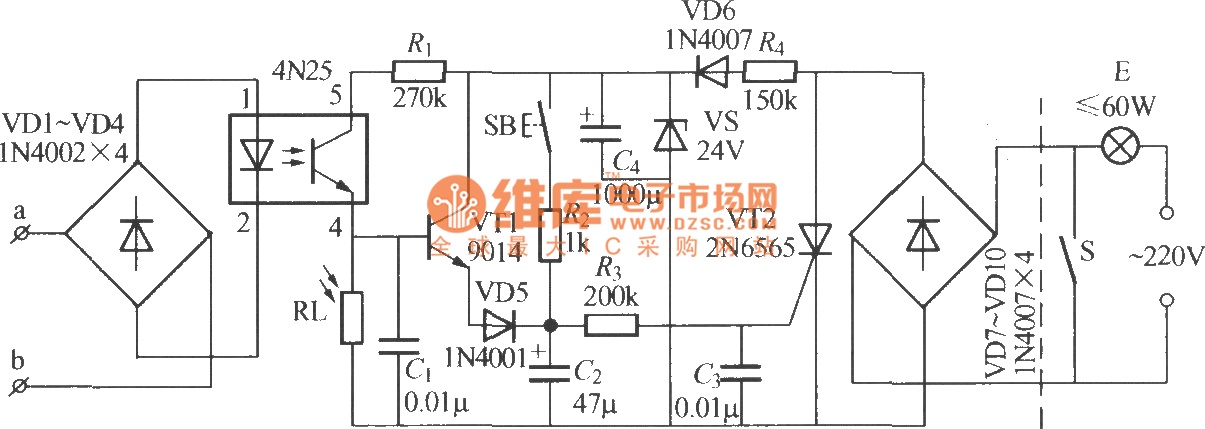
Here is a deluxe version of the simple charge rate limiter, using the same idea but with the ability to charge two packs simultaneously from a single wall charger. For circuit description and parts list, see the simple charger page. Since wall chargers provide about 55 mA, you should not use this dual circuit to charge batteries at rates greater than 27 mA (for a total of 54 mA).
The deluxe charge rate limiter circuit is designed to efficiently manage the charging process of two battery packs simultaneously while ensuring that the total current drawn from the wall charger does not exceed its rated output. The circuit employs a dual-channel architecture, allowing each battery pack to be charged independently but with a common power source.
Key components of the circuit include two charge rate limiting resistors, which are crucial in controlling the charging current to each battery pack. These resistors are selected to allow a maximum charging current of 27 mA per pack, ensuring that the total current remains within the 55 mA limit of the wall charger. Additionally, the circuit may utilize diodes to prevent backflow of current between the two battery packs, ensuring that each pack maintains its charge level without interference from the other.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize resistance and potential voltage drops, which can affect charging efficiency. A PCB design that allows for short traces and adequate grounding is recommended to enhance performance. Furthermore, it is advisable to incorporate suitable connectors for the battery packs and the wall charger, ensuring secure connections and ease of use.
Thermal considerations must also be taken into account, as the resistors may dissipate heat during operation. Proper heat sinking or spacing may be necessary to prevent overheating, especially during prolonged charging sessions.
In summary, the deluxe charge rate limiter circuit provides a practical solution for charging two battery packs from a single power source while maintaining safe operating conditions and preventing overcurrent situations. Careful selection of components and layout design will ensure optimal performance and reliability of the charging system.Here is a deluxe version of the simple charge rate limiter, using the same idea but with the ability to charge two packs simultaneously from a single wall charger. For circuit description and parts list, see the simple charger page. Since wall chargers provide about 55 mA, you should not use this dual circuit to charge batteries at rates greater than 27 mA (for a total of 54 mA).
🔗 External reference
The deluxe charge rate limiter circuit is designed to efficiently manage the charging process of two battery packs simultaneously while ensuring that the total current drawn from the wall charger does not exceed its rated output. The circuit employs a dual-channel architecture, allowing each battery pack to be charged independently but with a common power source.
Key components of the circuit include two charge rate limiting resistors, which are crucial in controlling the charging current to each battery pack. These resistors are selected to allow a maximum charging current of 27 mA per pack, ensuring that the total current remains within the 55 mA limit of the wall charger. Additionally, the circuit may utilize diodes to prevent backflow of current between the two battery packs, ensuring that each pack maintains its charge level without interference from the other.
The circuit layout should be carefully designed to minimize resistance and potential voltage drops, which can affect charging efficiency. A PCB design that allows for short traces and adequate grounding is recommended to enhance performance. Furthermore, it is advisable to incorporate suitable connectors for the battery packs and the wall charger, ensuring secure connections and ease of use.
Thermal considerations must also be taken into account, as the resistors may dissipate heat during operation. Proper heat sinking or spacing may be necessary to prevent overheating, especially during prolonged charging sessions.
In summary, the deluxe charge rate limiter circuit provides a practical solution for charging two battery packs from a single power source while maintaining safe operating conditions and preventing overcurrent situations. Careful selection of components and layout design will ensure optimal performance and reliability of the charging system.Here is a deluxe version of the simple charge rate limiter, using the same idea but with the ability to charge two packs simultaneously from a single wall charger. For circuit description and parts list, see the simple charger page. Since wall chargers provide about 55 mA, you should not use this dual circuit to charge batteries at rates greater than 27 mA (for a total of 54 mA).
🔗 External reference