Disinfection cabinet electronic control circuit diagram
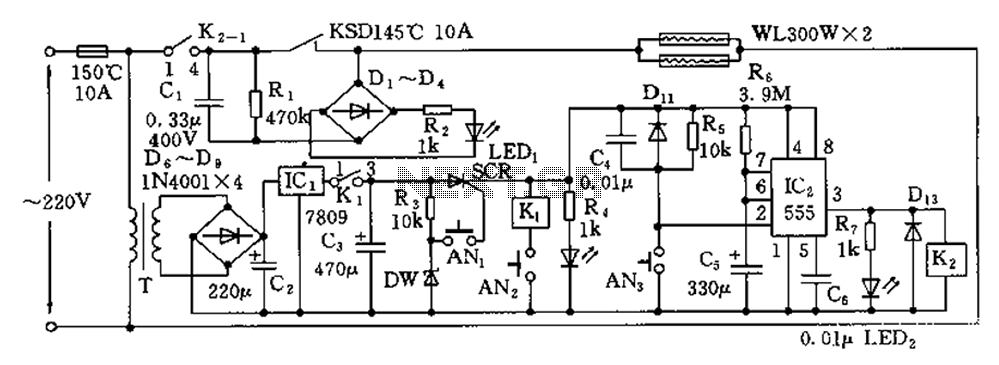
The disinfection cabinet circuit operates on the principle of using infrared heating within a closed cabinet to create a high-temperature environment for disinfecting tableware. The circuit includes an AC buck regulator, an infrared heating circuit, and a timing control circuit. Single-phase AC power is supplied through a temperature limit fuse (FU) rated at 10A and 150 degrees Celsius, which connects to the primary side of transformer T. The circuit then utilizes a buck converter, rectifier, and regulator to output 9V DC. The normally closed contact (1-3) of relay K1 is connected to the anode of a single SCR. The power control key (AN1) is used to trigger the SCR, enabling power control. The infrared heating is initiated by pressing button AN3, which triggers a low-level signal at pin 2 of the 555 timer IC. The 555 timer, along with resistors R5, R6, and capacitors C4, C5, forms a stability circuit, which maintains a transient stability time of approximately 24 minutes, with the high output duration lasting around 24 minutes.
The disinfection cabinet circuit is designed to ensure effective sterilization of tableware by leveraging infrared heating technology. The primary component, the AC buck regulator, reduces the input AC voltage to a manageable level suitable for the subsequent stages of the circuit. The temperature limit fuse (FU) serves as a safety mechanism, preventing overheating by disconnecting the circuit if the temperature exceeds 150 degrees Celsius.
The transformer (T) steps down the voltage further, allowing the circuit to operate safely at 9V DC. The relay (K1) plays a crucial role in controlling the power to the infrared heating elements by utilizing a single SCR, which acts as a switch that can be triggered to allow current flow when necessary. The SCR is triggered by the power control key (AN1), which must be pressed to initiate the disinfection process.
The infrared heating is activated by pressing the start button (AN3). This action sends a low-level trigger to pin 2 of the 555 timer IC, which is configured in a monostable mode. The timing components, including R5, R6, C4, and C5, define the duration of the output signal generated by the 555 timer. The transient stability time of approximately 24 minutes is critical, as it determines how long the heating elements will operate at high output, ensuring sufficient time for effective disinfection.
Overall, the circuit is engineered to provide a reliable and efficient method for disinfecting tableware, with built-in safety features and precise timing controls to enhance user experience and operational safety.Disinfection cabinet circuit principle is the use of infrared heating, in a closed cabinet to create a high-temperature environment, tableware disinfection. Circuit shown in FI G. The control circuit includes an AC buck regulator circuit, infrared heating circuit and the timing control circuit. Single-phase AC power by the temperature limit fuse FU (10A, 150 degrees C) was added to the primary of the transformer T, through the buck, rectifier, regulator, the output voltage of 9V DC, the K1 normally closed contact (1-3) to a single SCR SCR anode to.
AN1 is the power control key, pressing, SCR trigger turn-on, power-on control. AN3 is infrared heating start button, press it, a low level of 2 feet 555 555 trigger set .555 and R5, R6, C4, C5 and other components single stabilizing circuit, when it temporarily stable td 1.1R6C5. FIG. the parameters shown transient stability time of 24 minutes, the duration of 3 feet high output is 555 about 24 minutes.
The disinfection cabinet circuit is designed to ensure effective sterilization of tableware by leveraging infrared heating technology. The primary component, the AC buck regulator, reduces the input AC voltage to a manageable level suitable for the subsequent stages of the circuit. The temperature limit fuse (FU) serves as a safety mechanism, preventing overheating by disconnecting the circuit if the temperature exceeds 150 degrees Celsius.
The transformer (T) steps down the voltage further, allowing the circuit to operate safely at 9V DC. The relay (K1) plays a crucial role in controlling the power to the infrared heating elements by utilizing a single SCR, which acts as a switch that can be triggered to allow current flow when necessary. The SCR is triggered by the power control key (AN1), which must be pressed to initiate the disinfection process.
The infrared heating is activated by pressing the start button (AN3). This action sends a low-level trigger to pin 2 of the 555 timer IC, which is configured in a monostable mode. The timing components, including R5, R6, C4, and C5, define the duration of the output signal generated by the 555 timer. The transient stability time of approximately 24 minutes is critical, as it determines how long the heating elements will operate at high output, ensuring sufficient time for effective disinfection.
Overall, the circuit is engineered to provide a reliable and efficient method for disinfecting tableware, with built-in safety features and precise timing controls to enhance user experience and operational safety.Disinfection cabinet circuit principle is the use of infrared heating, in a closed cabinet to create a high-temperature environment, tableware disinfection. Circuit shown in FI G. The control circuit includes an AC buck regulator circuit, infrared heating circuit and the timing control circuit. Single-phase AC power by the temperature limit fuse FU (10A, 150 degrees C) was added to the primary of the transformer T, through the buck, rectifier, regulator, the output voltage of 9V DC, the K1 normally closed contact (1-3) to a single SCR SCR anode to.
AN1 is the power control key, pressing, SCR trigger turn-on, power-on control. AN3 is infrared heating start button, press it, a low level of 2 feet 555 555 trigger set .555 and R5, R6, C4, C5 and other components single stabilizing circuit, when it temporarily stable td 1.1R6C5. FIG. the parameters shown transient stability time of 24 minutes, the duration of 3 feet high output is 555 about 24 minutes.