Infrared Remote Control Tester Circuit
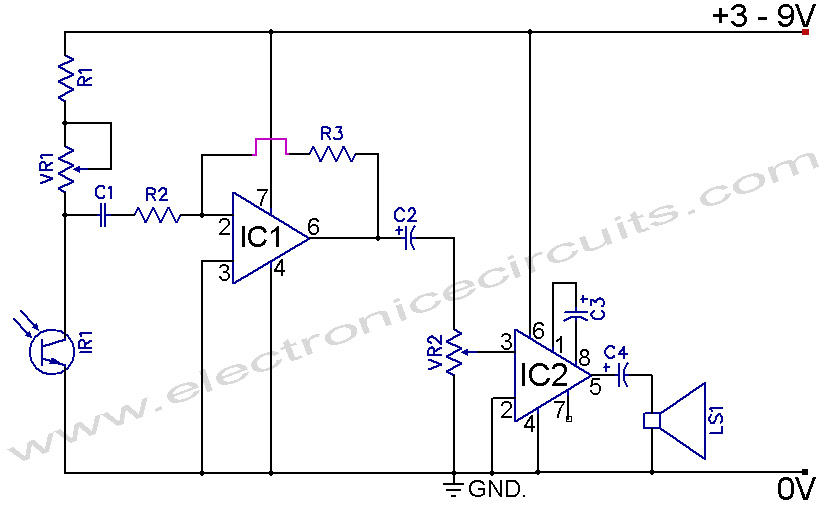
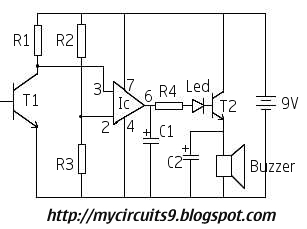
Infrared Remote Control Tester Circuit. This is a simple circuit that can be built to test infrared remote controls. The circuit utilizes an...
This infrared remote control tester circuit is designed to verify the functionality of infrared remote controls commonly used with various electronic devices. The primary components of the circuit include a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects infrared signals emitted by the remote control, and a simple LED indicator that lights up when an infrared signal is detected.
The circuit operates by placing the photodiode or phototransistor in close proximity to the infrared remote control. When a button on the remote is pressed, it emits infrared light, which is picked up by the photodiode or phototransistor. The output from the photodiode or phototransistor is then fed into a resistor and connected to an LED. The LED illuminates in response to the detected infrared signal, providing a visual indication that the remote is functioning properly.
To construct this circuit, the following components are typically required:
- A photodiode or phototransistor (such as a TSOP series receiver)
- An LED (light-emitting diode)
- A resistor (typically in the range of 220 to 1k ohms)
- A power supply (such as a 9V battery)
- A breadboard or PCB for assembly
The circuit can be easily assembled on a breadboard for prototyping. The photodiode or phototransistor should be oriented to face the infrared source, while the LED should be connected in such a way that it illuminates when the photodiode or phototransistor receives sufficient infrared light. Proper orientation and alignment are crucial for accurate testing.
This simple yet effective circuit serves as a valuable tool for troubleshooting and verifying the operation of infrared remote controls, making it an essential project for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike.Infrared Remote Control Tester Circuit This is a simple circuit you can build in order to test infrared remote controls. The circuit uses an.. 🔗 External reference
This infrared remote control tester circuit is designed to verify the functionality of infrared remote controls commonly used with various electronic devices. The primary components of the circuit include a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects infrared signals emitted by the remote control, and a simple LED indicator that lights up when an infrared signal is detected.
The circuit operates by placing the photodiode or phototransistor in close proximity to the infrared remote control. When a button on the remote is pressed, it emits infrared light, which is picked up by the photodiode or phototransistor. The output from the photodiode or phototransistor is then fed into a resistor and connected to an LED. The LED illuminates in response to the detected infrared signal, providing a visual indication that the remote is functioning properly.
To construct this circuit, the following components are typically required:
- A photodiode or phototransistor (such as a TSOP series receiver)
- An LED (light-emitting diode)
- A resistor (typically in the range of 220 to 1k ohms)
- A power supply (such as a 9V battery)
- A breadboard or PCB for assembly
The circuit can be easily assembled on a breadboard for prototyping. The photodiode or phototransistor should be oriented to face the infrared source, while the LED should be connected in such a way that it illuminates when the photodiode or phototransistor receives sufficient infrared light. Proper orientation and alignment are crucial for accurate testing.
This simple yet effective circuit serves as a valuable tool for troubleshooting and verifying the operation of infrared remote controls, making it an essential project for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike.Infrared Remote Control Tester Circuit This is a simple circuit you can build in order to test infrared remote controls. The circuit uses an.. 🔗 External reference