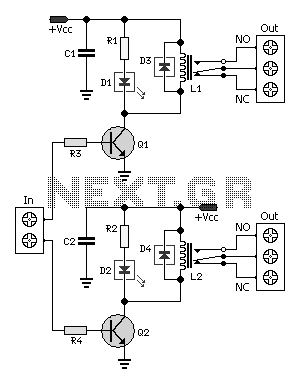
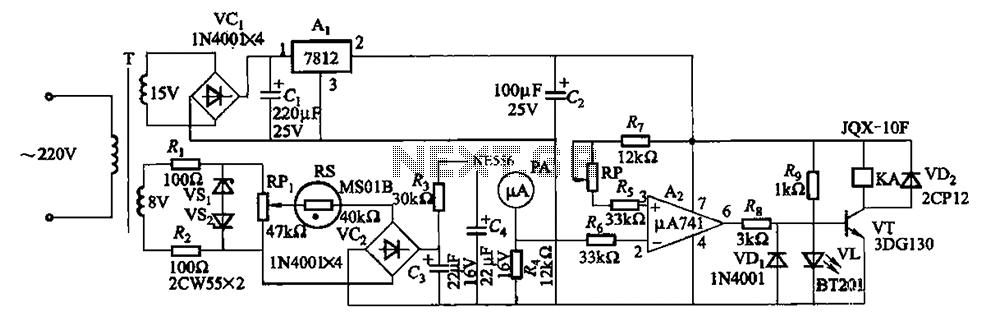
Invisible Infrared Alarm Circuit
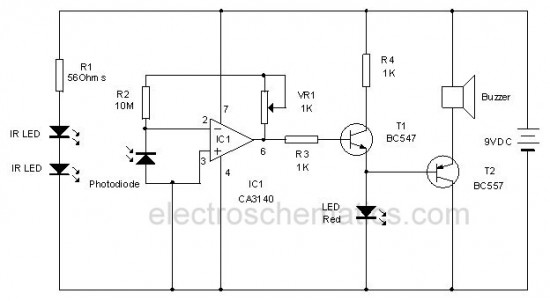
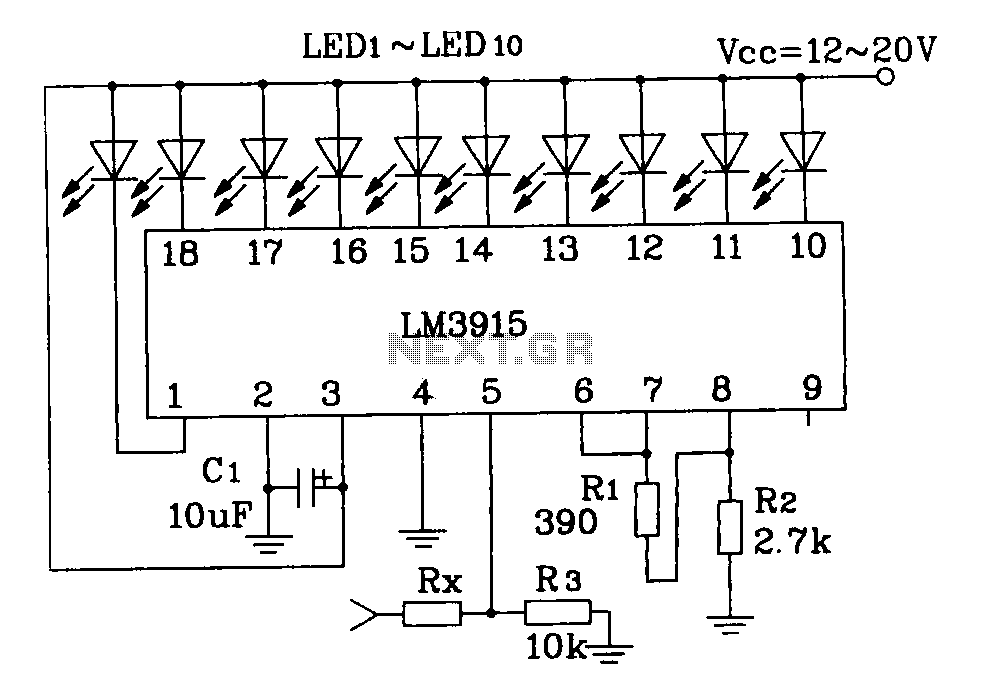
This circuit utilizes invisible infrared light to detect the movement of individuals passing through a doorway. A short beep is produced when the infrared beam is interrupted.
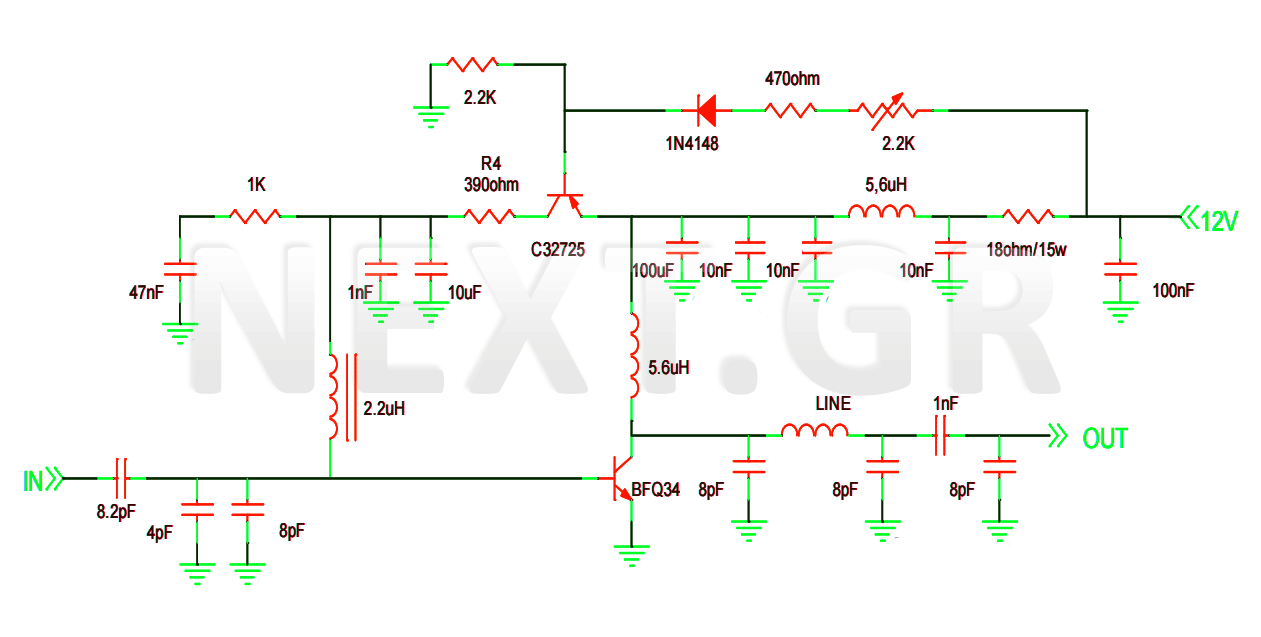
The circuit operates by employing an infrared transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye. This light is directed across the doorway to the receiver located on the opposite side. When an individual walks through the door, they obstruct the infrared beam, causing a disruption in the light signal received by the sensor.
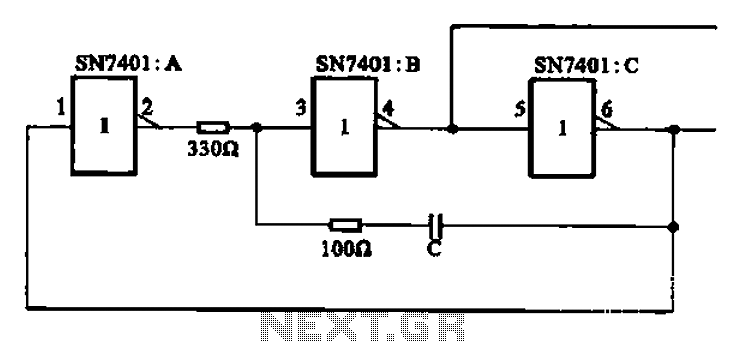
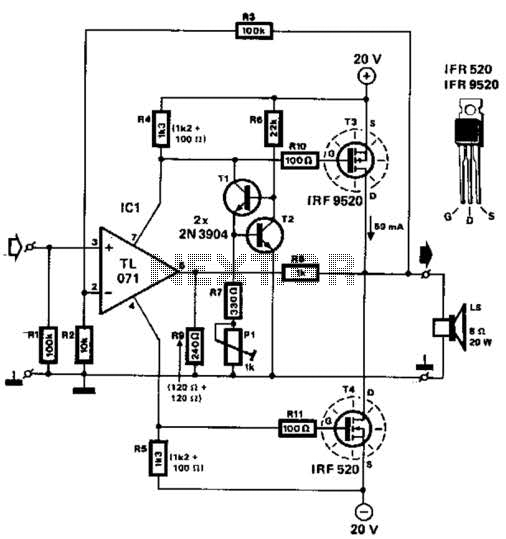
The receiver is often a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects the intensity of the incoming infrared light. When the beam is broken, the output of the photodiode changes, triggering a signal to a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit. This signal is then processed to activate a sound-generating component, such as a piezo buzzer or speaker, which emits a short beep to indicate the presence of movement.
Additionally, the circuit may include components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for signal smoothing, and possibly a microcontroller for more advanced processing and features, such as adjustable sensitivity or delay times. Power supply considerations are also essential; the circuit can be powered by batteries or an external power source depending on the application requirements.
Overall, this infrared motion detection circuit is a practical solution for security and automation applications, providing a simple yet effective means of detecting movement and alerting users accordingly.This circuit uses Invisible Infrared light to detect the movement of people through the door. A short beep will be generated when the infrared beam breaks 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by employing an infrared transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye. This light is directed across the doorway to the receiver located on the opposite side. When an individual walks through the door, they obstruct the infrared beam, causing a disruption in the light signal received by the sensor.
The receiver is often a photodiode or phototransistor, which detects the intensity of the incoming infrared light. When the beam is broken, the output of the photodiode changes, triggering a signal to a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit. This signal is then processed to activate a sound-generating component, such as a piezo buzzer or speaker, which emits a short beep to indicate the presence of movement.
Additionally, the circuit may include components such as resistors to limit current, capacitors for signal smoothing, and possibly a microcontroller for more advanced processing and features, such as adjustable sensitivity or delay times. Power supply considerations are also essential; the circuit can be powered by batteries or an external power source depending on the application requirements.
Overall, this infrared motion detection circuit is a practical solution for security and automation applications, providing a simple yet effective means of detecting movement and alerting users accordingly.This circuit uses Invisible Infrared light to detect the movement of people through the door. A short beep will be generated when the infrared beam breaks 🔗 External reference