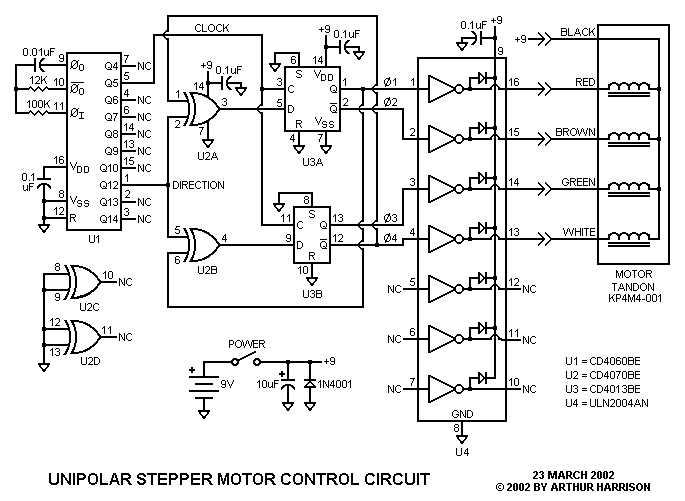
l293d motor driver
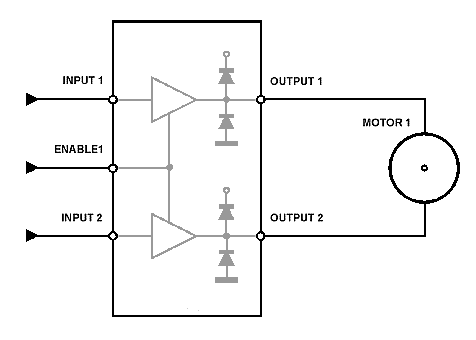
L293D Schematic diagram. The L293D division supplies power to the chip and its controlled motors, enabling the connection of motors with a higher voltage power supply than the chip itself. The separation of power circuits and electric motors may also be essential to minimize interference caused by surges associated with motor operation.
The L293D is an integrated circuit designed for driving DC motors and stepper motors, providing a convenient interface between low-power control signals and high-power motor operations. The chip features dual H-bridge outputs, allowing for bidirectional control of two motors or control of a single motor at different speeds and directions.
In the schematic, the L293D is typically represented with its power pins connected to a suitable power supply, which can be higher than the logic level voltage. The Vcc pin connects to the motor power supply, while the Vss pin connects to the logic supply, typically +5V. The enable pins (1 and 9) must be activated to allow the motor outputs to function, usually connected to the logic high level.
The input pins (2, 7, 10, and 15) receive control signals from a microcontroller or other logic devices, determining the direction and speed of the motors. When one of the input pins is set high while the corresponding enable pin is activated, the associated output pin drives the motor in one direction. Conversely, driving the opposite input pin high reverses the motor's direction.
Decoupling capacitors are often placed close to the power pins to filter out noise and prevent voltage spikes from affecting the performance of the L293D. Additionally, flyback diodes may be included in the schematic to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the motors are switched off, which could otherwise damage the L293D.
For applications requiring multiple motors or higher current ratings, multiple L293D chips can be paralleled, ensuring that each motor receives sufficient power while maintaining operational integrity. Proper thermal management, such as heat sinks, may be necessary due to the power dissipation in the chip, particularly under heavy load conditions.
In summary, the L293D schematic provides a robust framework for motor control applications, balancing power requirements and control flexibility while mitigating potential interference and ensuring reliable operation.L293D Schematic diagram. L293D division provides power for the chip and its controlled motors, allowing you to connect motors with high-voltage power supply than the chip. The separation of power circuits and electric motors may also be necessary to reduce interference caused by the Surge, work-related motors.
🔗 External reference
The L293D is an integrated circuit designed for driving DC motors and stepper motors, providing a convenient interface between low-power control signals and high-power motor operations. The chip features dual H-bridge outputs, allowing for bidirectional control of two motors or control of a single motor at different speeds and directions.
In the schematic, the L293D is typically represented with its power pins connected to a suitable power supply, which can be higher than the logic level voltage. The Vcc pin connects to the motor power supply, while the Vss pin connects to the logic supply, typically +5V. The enable pins (1 and 9) must be activated to allow the motor outputs to function, usually connected to the logic high level.
The input pins (2, 7, 10, and 15) receive control signals from a microcontroller or other logic devices, determining the direction and speed of the motors. When one of the input pins is set high while the corresponding enable pin is activated, the associated output pin drives the motor in one direction. Conversely, driving the opposite input pin high reverses the motor's direction.
Decoupling capacitors are often placed close to the power pins to filter out noise and prevent voltage spikes from affecting the performance of the L293D. Additionally, flyback diodes may be included in the schematic to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the motors are switched off, which could otherwise damage the L293D.
For applications requiring multiple motors or higher current ratings, multiple L293D chips can be paralleled, ensuring that each motor receives sufficient power while maintaining operational integrity. Proper thermal management, such as heat sinks, may be necessary due to the power dissipation in the chip, particularly under heavy load conditions.
In summary, the L293D schematic provides a robust framework for motor control applications, balancing power requirements and control flexibility while mitigating potential interference and ensuring reliable operation.L293D Schematic diagram. L293D division provides power for the chip and its controlled motors, allowing you to connect motors with high-voltage power supply than the chip. The separation of power circuits and electric motors may also be necessary to reduce interference caused by the Surge, work-related motors.
🔗 External reference