low cost precision light control dimmer
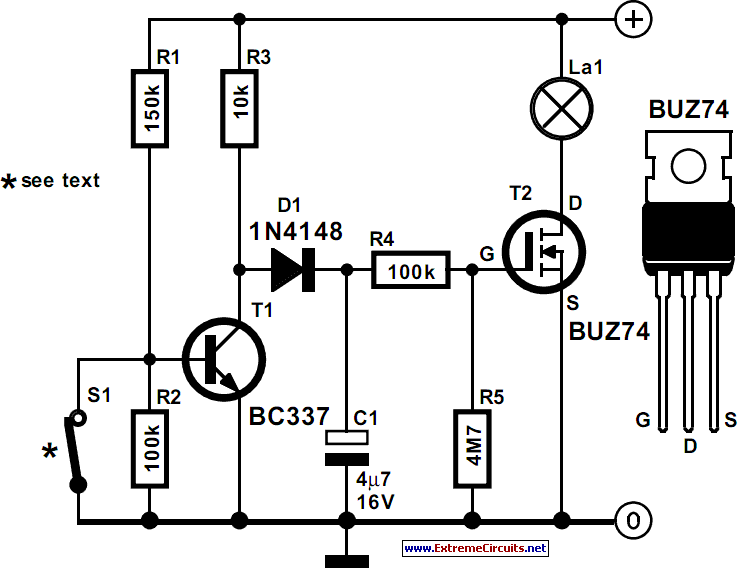
This circuit utilizes a controlled half-plus fixed half-wave phase control method to regulate an 860-watt lamp load, allowing for power adjustment from half to full capacity. The circuit controls the light output of the lamp, enabling a range from 30% to 100% brightness, as half power applied to an incandescent lamp results in approximately 30% of full light output.
The controlled half-plus fixed half-wave phase control method is an effective technique for dimming incandescent lamps by adjusting the phase angle of the AC waveform. In this circuit, a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) is employed to switch the load on and off during specific portions of the AC cycle. The phase control is achieved by delaying the triggering of the TRIAC, which allows for a portion of the AC waveform to be cut off, thereby reducing the effective voltage and power delivered to the lamp.
The circuit typically consists of a phase control circuit, a TRIAC, and a load (the lamp). The phase control circuit includes a variable resistor (potentiometer) that allows the user to adjust the delay in the TRIAC's triggering. This adjustment directly influences the amount of power delivered to the lamp. For instance, at a delay of zero degrees, the TRIAC conducts for the entire half-cycle, delivering full power to the lamp. Conversely, as the delay increases, the conduction angle decreases, resulting in lower power and dimmer light output.
In practical applications, this circuit can be used in various lighting scenarios, such as home lighting systems, theatrical lighting, and decorative lighting, where adjustable brightness is desired. The implementation of this phase control method not only enhances user comfort by providing customizable lighting levels but also contributes to energy savings by reducing power consumption when full brightness is not required.
The design should also incorporate necessary safety features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, to protect against overload conditions, and heat sinks may be required for the TRIAC to dissipate heat generated during operation. Proper selection of components, including the TRIAC rating and the load characteristics, is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of the circuit.Using a the controlled-half-plus-fixed-half-wave phase control method, this circuit can regulate an 860 a watt lamp load from half to full power. This circuit control the light output of the lamp from 30% to 100% because Half power applied to an incandescent lamp gives 30% of full light output.
This is the figure of the circuit; 🔗 External reference
The controlled half-plus fixed half-wave phase control method is an effective technique for dimming incandescent lamps by adjusting the phase angle of the AC waveform. In this circuit, a TRIAC (Triode for Alternating Current) is employed to switch the load on and off during specific portions of the AC cycle. The phase control is achieved by delaying the triggering of the TRIAC, which allows for a portion of the AC waveform to be cut off, thereby reducing the effective voltage and power delivered to the lamp.
The circuit typically consists of a phase control circuit, a TRIAC, and a load (the lamp). The phase control circuit includes a variable resistor (potentiometer) that allows the user to adjust the delay in the TRIAC's triggering. This adjustment directly influences the amount of power delivered to the lamp. For instance, at a delay of zero degrees, the TRIAC conducts for the entire half-cycle, delivering full power to the lamp. Conversely, as the delay increases, the conduction angle decreases, resulting in lower power and dimmer light output.
In practical applications, this circuit can be used in various lighting scenarios, such as home lighting systems, theatrical lighting, and decorative lighting, where adjustable brightness is desired. The implementation of this phase control method not only enhances user comfort by providing customizable lighting levels but also contributes to energy savings by reducing power consumption when full brightness is not required.
The design should also incorporate necessary safety features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, to protect against overload conditions, and heat sinks may be required for the TRIAC to dissipate heat generated during operation. Proper selection of components, including the TRIAC rating and the load characteristics, is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of the circuit.Using a the controlled-half-plus-fixed-half-wave phase control method, this circuit can regulate an 860 a watt lamp load from half to full power. This circuit control the light output of the lamp from 30% to 100% because Half power applied to an incandescent lamp gives 30% of full light output.
This is the figure of the circuit; 🔗 External reference