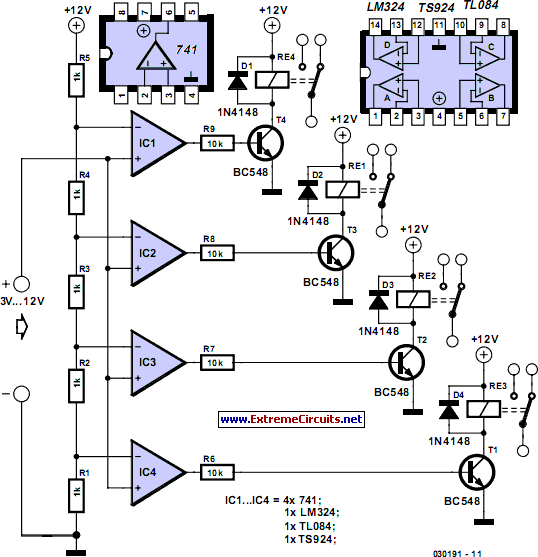
Maximum Minimum Voltage Indicator
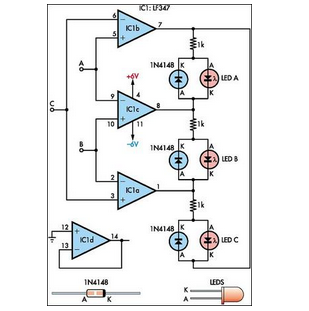
This circuit indicates which of three voltages in the range from approximately -4V to +4V at points A, B, and C is the highest by illuminating one of three indicators.
The circuit is designed to compare three input voltages, labeled A, B, and C, each capable of varying between -4V and +4V. The primary function of this circuit is to determine and visually indicate which of the three input voltages is the greatest by activating one of three indicator lights, typically LEDs.
To achieve this, a series of operational amplifiers (op-amps) can be employed in a comparator configuration. Each op-amp is connected to two of the input voltages, allowing for pairwise comparisons. For instance, one op-amp can compare voltage A with voltage B, while another compares voltage B with voltage C, and the third compares voltage C with voltage A. The outputs of these comparators will indicate which voltage is higher in each pair.
The outputs from the op-amps can be fed into a priority encoder or a simple logic circuit that will determine which voltage is the highest among the three. Based on this logic, the corresponding output will activate one of the three indicator LEDs. Additional circuitry may be included to ensure that only one LED is lit at any given time, preventing conflicts in the outputs.
Power supply considerations must also be taken into account, ensuring that the circuit can operate effectively within the specified voltage range. Proper decoupling capacitors should be used to stabilize the op-amps and prevent oscillations.
In summary, this circuit not only serves the purpose of voltage comparison but also provides a clear visual representation of the highest voltage among the inputs, making it useful in various applications where voltage monitoring is critical.This circuit indicates which of three voltages in the range from about about -4V to about +4V at A, B and C is the highest by lighting one of three in.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to compare three input voltages, labeled A, B, and C, each capable of varying between -4V and +4V. The primary function of this circuit is to determine and visually indicate which of the three input voltages is the greatest by activating one of three indicator lights, typically LEDs.
To achieve this, a series of operational amplifiers (op-amps) can be employed in a comparator configuration. Each op-amp is connected to two of the input voltages, allowing for pairwise comparisons. For instance, one op-amp can compare voltage A with voltage B, while another compares voltage B with voltage C, and the third compares voltage C with voltage A. The outputs of these comparators will indicate which voltage is higher in each pair.
The outputs from the op-amps can be fed into a priority encoder or a simple logic circuit that will determine which voltage is the highest among the three. Based on this logic, the corresponding output will activate one of the three indicator LEDs. Additional circuitry may be included to ensure that only one LED is lit at any given time, preventing conflicts in the outputs.
Power supply considerations must also be taken into account, ensuring that the circuit can operate effectively within the specified voltage range. Proper decoupling capacitors should be used to stabilize the op-amps and prevent oscillations.
In summary, this circuit not only serves the purpose of voltage comparison but also provides a clear visual representation of the highest voltage among the inputs, making it useful in various applications where voltage monitoring is critical.This circuit indicates which of three voltages in the range from about about -4V to about +4V at A, B and C is the highest by lighting one of three in.. 🔗 External reference