Multivibrators including Monostable Astable and Bistable
Electronics tutorial about multivibrators, including monostable multivibrator circuits, astable multivibrators, bistable oscillators, and clocks.
Multivibrators are essential electronic circuits that generate specific output waveforms based on their configuration. They are classified into three primary types: monostable, astable, and bistable multivibrators. Each type serves distinct functions and applications in electronic systems.
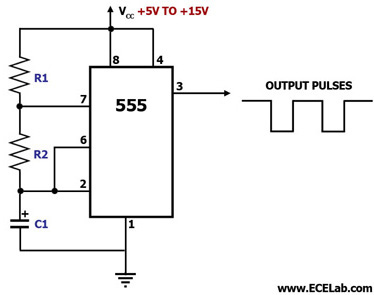
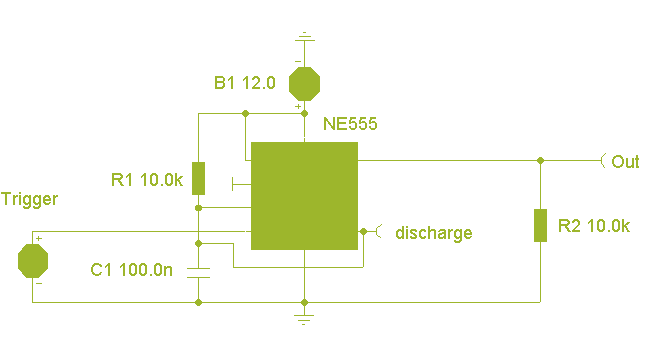
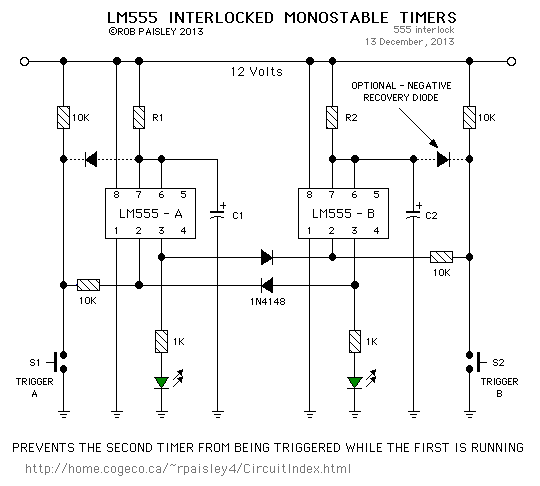
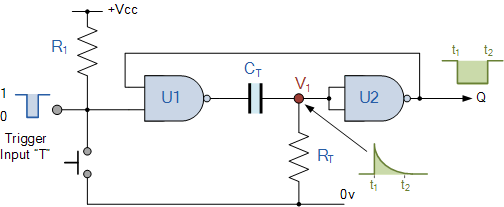
Monostable multivibrators, also known as one-shot circuits, produce a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. The pulse duration is determined by external components, typically a resistor and a capacitor, which define the timing interval. This type of multivibrator is widely used in applications such as timers, pulse-width modulation, and signal conditioning.
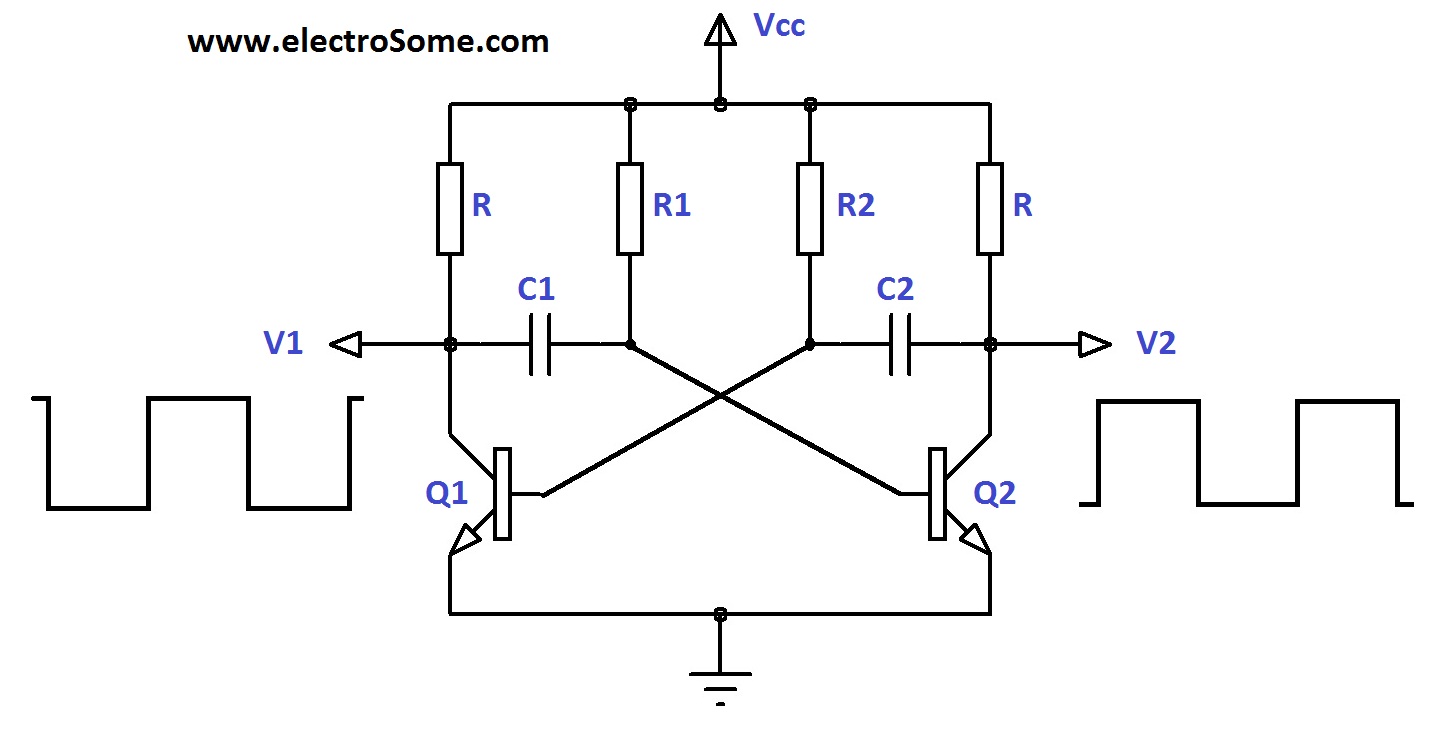
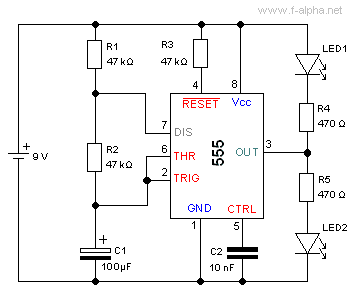
Astable multivibrators operate continuously without requiring an external trigger, generating a square wave output. This circuit alternates between two unstable states, with the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform determined by the values of the timing components. Astable multivibrators are commonly employed in clock pulse generation, frequency modulation, and LED flashers.
Bistable multivibrators, or flip-flops, possess two stable states and can be used to store binary information. They require an input signal to switch between these states, making them fundamental in digital circuits for data storage, memory elements, and state retention in sequential logic devices.
In summary, multivibrators play a crucial role in electronic design, providing versatile solutions for timing, waveform generation, and data storage in various applications. Understanding their operation and characteristics is essential for engineers working with digital and analog systems.Electronics Tutorial about Multivibrators including Monostable Multivibrator Circuits, Astable Multivibrators, Bistable Oscillators and Clocks.. 🔗 External reference
Multivibrators are essential electronic circuits that generate specific output waveforms based on their configuration. They are classified into three primary types: monostable, astable, and bistable multivibrators. Each type serves distinct functions and applications in electronic systems.
Monostable multivibrators, also known as one-shot circuits, produce a single output pulse in response to an input trigger. The pulse duration is determined by external components, typically a resistor and a capacitor, which define the timing interval. This type of multivibrator is widely used in applications such as timers, pulse-width modulation, and signal conditioning.
Astable multivibrators operate continuously without requiring an external trigger, generating a square wave output. This circuit alternates between two unstable states, with the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform determined by the values of the timing components. Astable multivibrators are commonly employed in clock pulse generation, frequency modulation, and LED flashers.
Bistable multivibrators, or flip-flops, possess two stable states and can be used to store binary information. They require an input signal to switch between these states, making them fundamental in digital circuits for data storage, memory elements, and state retention in sequential logic devices.
In summary, multivibrators play a crucial role in electronic design, providing versatile solutions for timing, waveform generation, and data storage in various applications. Understanding their operation and characteristics is essential for engineers working with digital and analog systems.Electronics Tutorial about Multivibrators including Monostable Multivibrator Circuits, Astable Multivibrators, Bistable Oscillators and Clocks.. 🔗 External reference