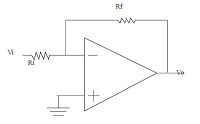
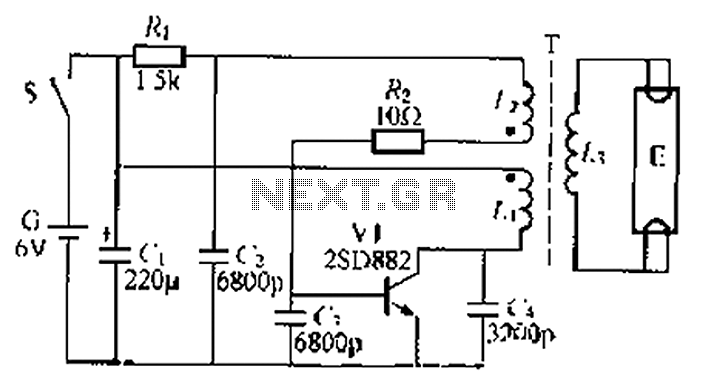
Sawtooth generator circuit II
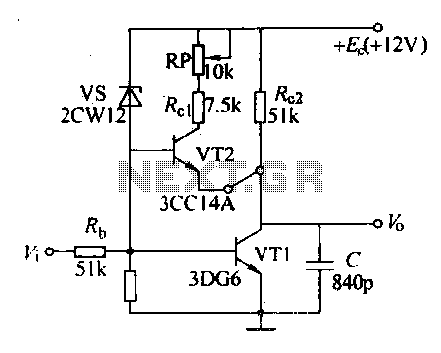
Various sawtooth voltage generators utilize the principle of capacitor charging and discharging to produce sawtooth waveforms in both forward and reverse directions. A simple sawtooth voltage generator circuit is straightforward in design; however, it suffers from poor linearity in output voltage. The amplitude of the voltage changes exponentially over time, deviating significantly from linearity, and the overall power efficiency is low. To achieve a more linear sawtooth voltage, it is essential to maintain a constant current during the capacitor's charging process. This requirement serves as the foundation for a constant current source sawtooth voltage generator. A common approach involves using a transistor in a common base configuration to stabilize the emitter current. The collector current remains relatively unchanged, preserving the capacitor's charging characteristics and enabling a constant current for a linear scan. However, when the constant current circuit is modified, the amplitude of the scanning voltage can saturate, leading to a flattened output waveform. Consequently, the output amplitude is restricted, with a notable limit based on the circuit's parameters. To prevent distortion and flattening of the scanning wave, it is crucial to optimize the scanning period, ensuring that the capacitor is charged adequately during the maximum time allotted for amplitude generation.
The sawtooth voltage generator circuit typically consists of a capacitor, a transistor, and resistive components that help define the charging and discharging paths. The capacitor charges through a resistor connected to the transistor's emitter, which is configured to allow a constant current to flow. The constant current source is vital for maintaining linearity in the output waveform. The transistor operates in a common base configuration, where the base is connected to a fixed voltage, allowing the emitter current to remain stable and thereby controlling the collector current.
In operation, the capacitor charges towards the supply voltage, and once it reaches a predetermined threshold, the transistor switches off, allowing the capacitor to discharge rapidly. The discharge path typically includes a resistor that defines the rate of discharge, which is crucial for establishing the waveform's frequency and duty cycle. By adjusting the values of the resistors and the capacitor, various sawtooth frequencies and amplitudes can be generated.
The circuit's performance can also be influenced by external factors such as temperature and supply voltage variations. Therefore, designing for stability and robustness is essential in practical applications. Feedback mechanisms can be incorporated to further enhance linearity and minimize distortion. Additionally, the use of precision components can significantly improve the overall performance of the sawtooth voltage generator, ensuring that it meets the specific requirements for various electronic applications.Crossing various sawtooth voltage generator, the common denominator is the use of a capacitor charge. Discharge effect to generate a sawtooth voltage of the forward and inverse process. Simple sawtooth voltage generator circuit is simple, but the output voltage linear sawtooth poor voltage amplitude changes exponentially with time, departing from the linear serious, and power efficiency is not high. To get a good linear sawtooth core voltage crossing, the key is to try to make the scan of the capacitor to maintain constant current charging within, which is the basic point of departure for a constant current source sawtooth voltage generator.
Constant is the use of flooded common base connected transistor law in emission current J. Linden Certainly, the collector current is essentially unchanged, maintaining the capacitor charging characteristics to achieve this constant stream of linear scan. But when the constant current circuit with a transistor change after the scan voltage amplitude and is saturated, the scanning voltage will not change, the output voltage waveform appears flattened, therefore, in this circuit, the output amplitude of certain restrictions the most significant v, rhn, only mound -Ut.
To make the scanning wave does not appear flattened and distorted, the best period of the scan (ie, the maximum scan cycle) 1, Li; they should charge the capacitor to the output of the transistor VT1 maximum time required for the amplitude of a million, such as circuit FIG. He was excited by the scanning of a sawtooth generator (Tp), quiescent (z,) and period (n), depending on the telogen, pulse width and period of the input signal, only generator retrace period by the circuit itself parameters decision.
The sawtooth voltage generator circuit typically consists of a capacitor, a transistor, and resistive components that help define the charging and discharging paths. The capacitor charges through a resistor connected to the transistor's emitter, which is configured to allow a constant current to flow. The constant current source is vital for maintaining linearity in the output waveform. The transistor operates in a common base configuration, where the base is connected to a fixed voltage, allowing the emitter current to remain stable and thereby controlling the collector current.
In operation, the capacitor charges towards the supply voltage, and once it reaches a predetermined threshold, the transistor switches off, allowing the capacitor to discharge rapidly. The discharge path typically includes a resistor that defines the rate of discharge, which is crucial for establishing the waveform's frequency and duty cycle. By adjusting the values of the resistors and the capacitor, various sawtooth frequencies and amplitudes can be generated.
The circuit's performance can also be influenced by external factors such as temperature and supply voltage variations. Therefore, designing for stability and robustness is essential in practical applications. Feedback mechanisms can be incorporated to further enhance linearity and minimize distortion. Additionally, the use of precision components can significantly improve the overall performance of the sawtooth voltage generator, ensuring that it meets the specific requirements for various electronic applications.Crossing various sawtooth voltage generator, the common denominator is the use of a capacitor charge. Discharge effect to generate a sawtooth voltage of the forward and inverse process. Simple sawtooth voltage generator circuit is simple, but the output voltage linear sawtooth poor voltage amplitude changes exponentially with time, departing from the linear serious, and power efficiency is not high. To get a good linear sawtooth core voltage crossing, the key is to try to make the scan of the capacitor to maintain constant current charging within, which is the basic point of departure for a constant current source sawtooth voltage generator.
Constant is the use of flooded common base connected transistor law in emission current J. Linden Certainly, the collector current is essentially unchanged, maintaining the capacitor charging characteristics to achieve this constant stream of linear scan. But when the constant current circuit with a transistor change after the scan voltage amplitude and is saturated, the scanning voltage will not change, the output voltage waveform appears flattened, therefore, in this circuit, the output amplitude of certain restrictions the most significant v, rhn, only mound -Ut.
To make the scanning wave does not appear flattened and distorted, the best period of the scan (ie, the maximum scan cycle) 1, Li; they should charge the capacitor to the output of the transistor VT1 maximum time required for the amplitude of a million, such as circuit FIG. He was excited by the scanning of a sawtooth generator (Tp), quiescent (z,) and period (n), depending on the telogen, pulse width and period of the input signal, only generator retrace period by the circuit itself parameters decision.