NE555 circuit diagram of a divider circuit
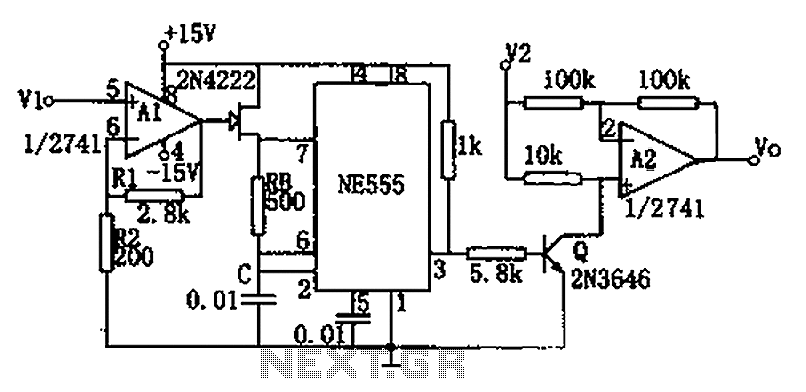
The circuit depicted in the figure consists of a voltage-frequency converter and an amplitude modulator. The input voltage V1, processed by operational amplifier A1, controls the FET 2N4222's internal resistance, which in turn alters the oscillation frequency of the astable multivibrator. Operational amplifier A2 functions as the amplitude modulator, utilizing the input signal V2 for modulation. The pinch-off voltage of the FET is defined as Vp,Tt (1 + R1/R2) Vp. The relationship between the output and input voltages is expressed as Vo - V2/V1, where the required voltage range for V1 and V2 is 0 to 10V. The average output Vo can be obtained through a filter, and a damped voltmeter can be used for readout.
The circuit integrates a voltage-to-frequency conversion mechanism with an amplitude modulation capability, facilitating the transformation of an input voltage signal into a frequency-modulated output. The operational amplifier A1 serves a crucial role in regulating the internal resistance of the FET 2N4222, which is essential for adjusting the frequency of the astable multivibrator. This configuration allows for precise control over the oscillation frequency based on the input voltage V1.
Operational amplifier A2 is tasked with amplitude modulation, where it processes the input signal V2 to produce a modulated output. The modulation depth and characteristics can be fine-tuned by adjusting the circuit components, particularly R1 and R2, which influence the pinch-off voltage of the FET. The relationship defined by Vo - V2/V1 indicates that the output voltage Vo is directly influenced by the ratio of the input voltages, emphasizing the need for careful calibration within the specified range of 0 to 10V.
To obtain the average output voltage Vo, a filtering stage is included, which smooths out the variations in the modulated signal. This filtered output can then be accurately measured using a damped voltmeter, providing a reliable means of monitoring the circuit's performance. The design demonstrates versatility and applicability in various electronic applications, particularly in signal processing where frequency and amplitude modulation are required. As shown in FIG circuit by the voltage - frequency converter and an amplitude modulator. Input voltage V1 by the operational amplifier A1 control FET 2N4222 internal resistance , thereby changing the astable multivibrator oscillation frequency. A2 is the amplitude modulator, modulated by the input signal V2 output. Let FET pinch-off voltage Vp,Tt (1 + R1/R2) Vp, the output and input of the relationship: Vo -V2/V1 V1 and V2 required range is 0 ~ 10V. Vo is the average output can be obtained through the filter, you can also use damped voltmeter readout.
The circuit integrates a voltage-to-frequency conversion mechanism with an amplitude modulation capability, facilitating the transformation of an input voltage signal into a frequency-modulated output. The operational amplifier A1 serves a crucial role in regulating the internal resistance of the FET 2N4222, which is essential for adjusting the frequency of the astable multivibrator. This configuration allows for precise control over the oscillation frequency based on the input voltage V1.
Operational amplifier A2 is tasked with amplitude modulation, where it processes the input signal V2 to produce a modulated output. The modulation depth and characteristics can be fine-tuned by adjusting the circuit components, particularly R1 and R2, which influence the pinch-off voltage of the FET. The relationship defined by Vo - V2/V1 indicates that the output voltage Vo is directly influenced by the ratio of the input voltages, emphasizing the need for careful calibration within the specified range of 0 to 10V.
To obtain the average output voltage Vo, a filtering stage is included, which smooths out the variations in the modulated signal. This filtered output can then be accurately measured using a damped voltmeter, providing a reliable means of monitoring the circuit's performance. The design demonstrates versatility and applicability in various electronic applications, particularly in signal processing where frequency and amplitude modulation are required. As shown in FIG circuit by the voltage - frequency converter and an amplitude modulator. Input voltage V1 by the operational amplifier A1 control FET 2N4222 internal resistance , thereby changing the astable multivibrator oscillation frequency. A2 is the amplitude modulator, modulated by the input signal V2 output. Let FET pinch-off voltage Vp,Tt (1 + R1/R2) Vp, the output and input of the relationship: Vo -V2/V1 V1 and V2 required range is 0 ~ 10V. Vo is the average output can be obtained through the filter, you can also use damped voltmeter readout.