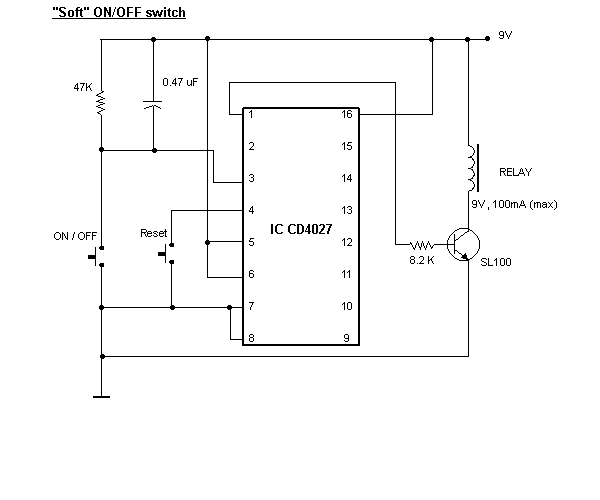
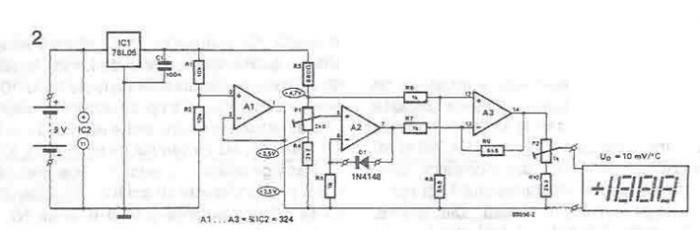
Triac lights automatically switch schematic
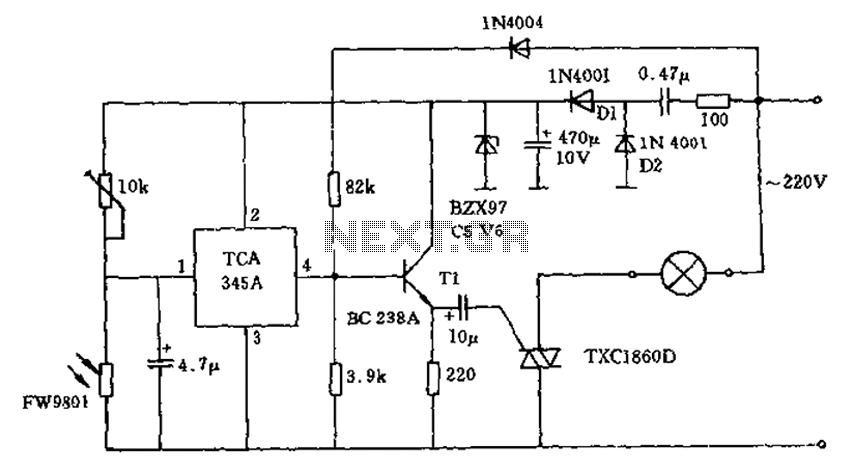
A 200W lamp switch control operates at a power supply voltage of 220V. It automatically turns the light on or off based on ambient illumination levels, specifically activating at approximately 100 lux. In low light conditions, a time-sensitive resistor exhibits high resistance, resulting in a switch input voltage that exceeds 0.7 times the threshold. Consequently, the output also demonstrates high resistance. As a result, the grid voltage, divided by resistors, allows the positive half-cycle of the AC signal to turn on a transistor. This action generates a trigger pulse at the emitter electrode during each half cycle, energizing the load. Conversely, when the ambient light exceeds 100 lux, the threshold switch output terminal becomes negative, leading to no current flow to the transistor and triac gate, thereby disabling the circuit. The circuit requires a DC voltage, which is obtained after rectification through diodes D1 and D2, with the current control circuit necessitating approximately 15mA.
The 200W lamp switch control circuit is designed to automatically manage lighting based on ambient light intensity. The system incorporates a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a similar photoresistor as the primary sensing element. When the light level falls below the defined threshold of 100 lux, the resistance of the LDR increases, allowing a voltage divider configuration to produce a voltage that exceeds the threshold required to activate the transistor.
The circuit employs a standard NPN transistor, which acts as a switch to control the current flow to the load, represented by the lamp. The transistor is configured to turn on when the input voltage reaches approximately 0.7V, which is the typical base-emitter turn-on voltage for silicon transistors. The emitter of the transistor is connected to the load, allowing the flow of current to energize the lamp during the low light condition.
The triac is utilized in conjunction with the transistor to handle the AC load. The gate of the triac is connected to the collector of the transistor, ensuring that when the transistor is activated, it provides a gate pulse to the triac, allowing it to conduct and power the lamp. When ambient light exceeds 100 lux, the output of the threshold switch becomes negative, cutting off the gate current to the triac, which in turn deactivates the lamp.
Power for the circuit is derived from the AC mains supply, which is rectified by diodes D1 and D2 to produce a smooth DC voltage necessary for the operation of the control circuit. The rectification process ensures that the circuit operates safely and effectively without exposure to high AC voltages. The design also incorporates filtering capacitors to stabilize the voltage and reduce ripple, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this circuit serves as an efficient solution for automatically controlling lighting based on environmental conditions, enhancing energy savings and convenience in various applications such as outdoor lighting, security lights, and garden illumination.200W lamp switch control, power supply voltage is 220V, is about 100lx illumination light automatically turned on or off. In the ambient light is dark time sensitive resistor w as high resistance, the voltage threshold switch input voltage of about 2 feet higher than 0.7 times, its output also showed a high resistance, so the grid voltage by dividing resistors followed by the positive half cycle transistor is turned on, and at the emitter electrode of each half cycle to form a trigger pulse, the load is energized. When strong light (more than 100lx), the threshold switch output terminal becomes negative, the transistor and the triac gate no current, the circuit fails.
Circuit required by the DC voltage obtained after rectification diodes D1 and D2. Current control circuit requires about 15mA.
The 200W lamp switch control circuit is designed to automatically manage lighting based on ambient light intensity. The system incorporates a light-dependent resistor (LDR) or a similar photoresistor as the primary sensing element. When the light level falls below the defined threshold of 100 lux, the resistance of the LDR increases, allowing a voltage divider configuration to produce a voltage that exceeds the threshold required to activate the transistor.
The circuit employs a standard NPN transistor, which acts as a switch to control the current flow to the load, represented by the lamp. The transistor is configured to turn on when the input voltage reaches approximately 0.7V, which is the typical base-emitter turn-on voltage for silicon transistors. The emitter of the transistor is connected to the load, allowing the flow of current to energize the lamp during the low light condition.
The triac is utilized in conjunction with the transistor to handle the AC load. The gate of the triac is connected to the collector of the transistor, ensuring that when the transistor is activated, it provides a gate pulse to the triac, allowing it to conduct and power the lamp. When ambient light exceeds 100 lux, the output of the threshold switch becomes negative, cutting off the gate current to the triac, which in turn deactivates the lamp.
Power for the circuit is derived from the AC mains supply, which is rectified by diodes D1 and D2 to produce a smooth DC voltage necessary for the operation of the control circuit. The rectification process ensures that the circuit operates safely and effectively without exposure to high AC voltages. The design also incorporates filtering capacitors to stabilize the voltage and reduce ripple, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this circuit serves as an efficient solution for automatically controlling lighting based on environmental conditions, enhancing energy savings and convenience in various applications such as outdoor lighting, security lights, and garden illumination.200W lamp switch control, power supply voltage is 220V, is about 100lx illumination light automatically turned on or off. In the ambient light is dark time sensitive resistor w as high resistance, the voltage threshold switch input voltage of about 2 feet higher than 0.7 times, its output also showed a high resistance, so the grid voltage by dividing resistors followed by the positive half cycle transistor is turned on, and at the emitter electrode of each half cycle to form a trigger pulse, the load is energized. When strong light (more than 100lx), the threshold switch output terminal becomes negative, the transistor and the triac gate no current, the circuit fails.
Circuit required by the DC voltage obtained after rectification diodes D1 and D2. Current control circuit requires about 15mA.