Phase Delay Network for 3D Audio Enhancement

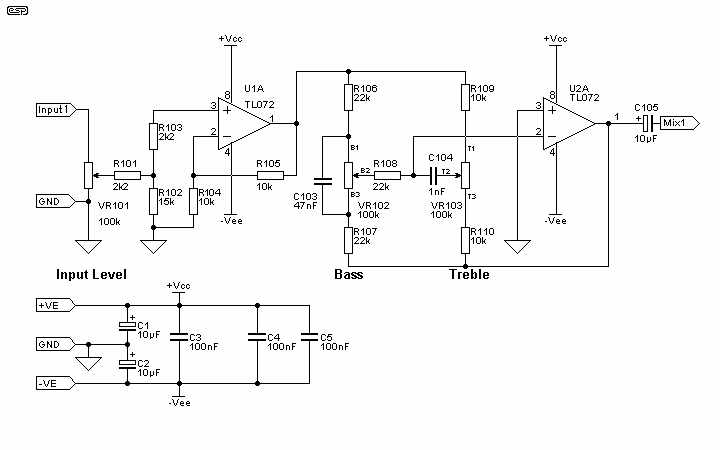
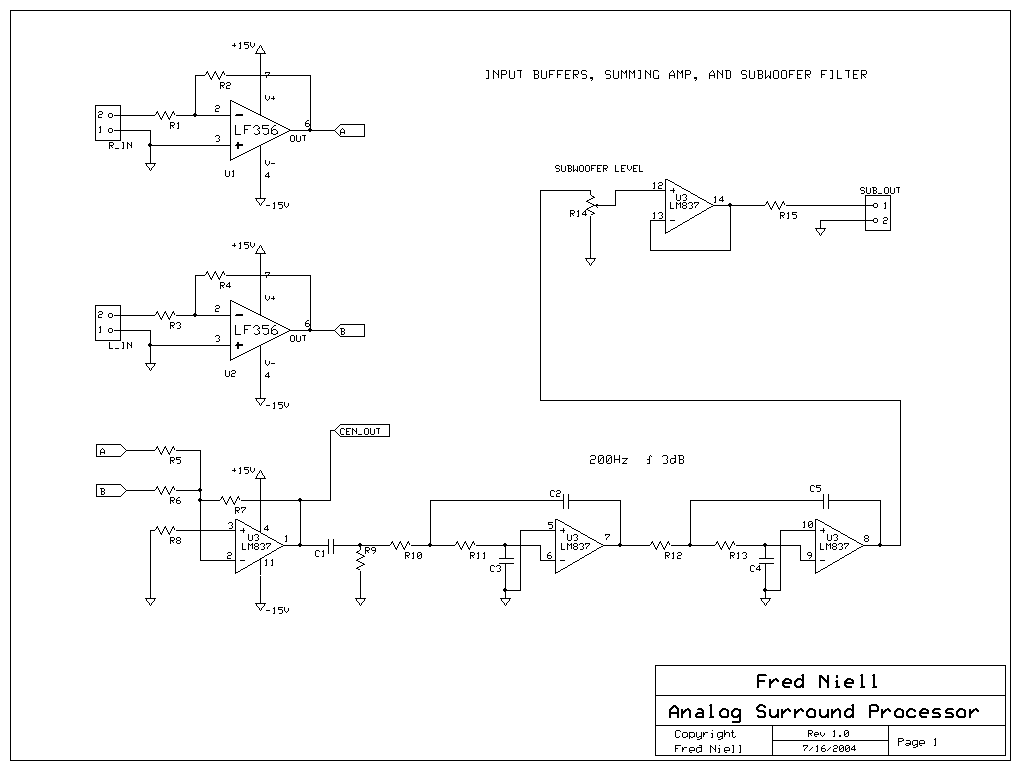
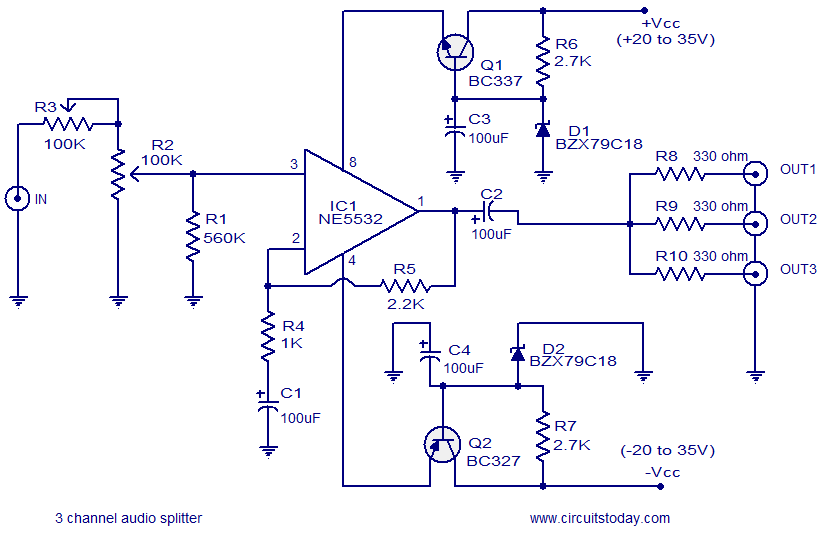
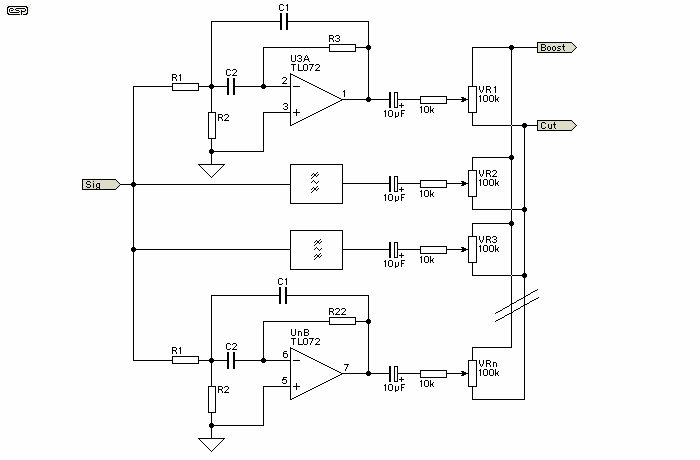
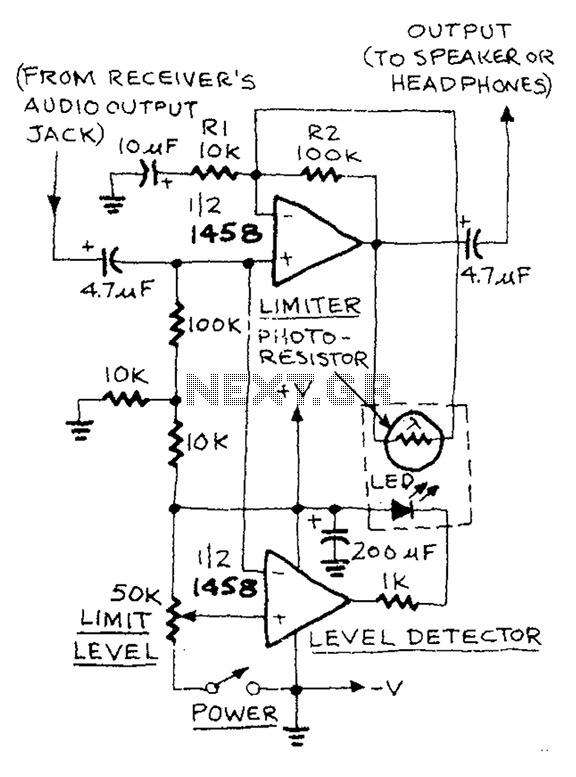
A 3D enhancement is required to achieve a fully three-dimensional sound experience for most stereo multimedia products. Typically, simple phase-delay circuits are utilized to create a widening effect on the perceived sound field. However, this approach can lead to the transaural acoustic crosstalk effect. The following figure illustrates the transaural acoustic crosstalk effect along with the schematic diagram.
More: Simple phase-delay circuits are active circuits that employ a first-order section to implement a phase-shift filter with a cutoff frequency (ft) of 1 kHz for the quadrature signal and a cutoff frequency of 10 kHz for the linear signal. This configuration produces a 90° phase shift between the quadrature and linear signals across the audio bandwidth of 1 kHz to 10 kHz.
The implementation of a 3D audio enhancement circuit involves the careful design of phase-delay circuits that significantly contribute to the perception of spatial audio. The circuit typically consists of a combination of operational amplifiers configured to create the necessary phase shifts for both quadrature and linear signals.
The first-order phase-shift filter is crucial in this design, as it allows the audio signals to be manipulated effectively within the specified frequency range. The choice of cutoff frequencies—1 kHz for the quadrature signal and 10 kHz for the linear signal—ensures that the circuit can handle the typical audio bandwidth while maintaining clarity and fidelity.
The output of the phase-delay circuit is then combined to produce a stereo output that enhances the spatial characteristics of the audio. By introducing a 90° phase shift, the circuit effectively widens the sound field, creating an immersive listening experience that simulates a three-dimensional sound environment.
However, careful consideration must be given to the transaural acoustic crosstalk effect, which can occur when audio signals intended for one ear are inadvertently heard by the other ear. This phenomenon can detract from the desired 3D effect and requires additional measures, such as crosstalk cancellation techniques or advanced filtering, to mitigate its impact.
Overall, the design of a 3D enhancement circuit using simple phase-delay circuits is a sophisticated endeavor that combines principles of audio engineering and psychoacoustics to deliver a compelling auditory experience.3D enhancement is needed to create a fully 3-dimensional sound for most stereo multimedia products. Usually, simple phase-delay circuits is used to produce a widening effect on the perceived sound field. However, there is transaural acoustic crosstalk effect. The following figure shows transaural acoustic crosstalk effect and schematic diagram of simple phase-delay circuits : This is an active circuit that uses first-order section to present a phase-shift filter with ft of 1kHz for the quadrature signal and ft = 10kHz for the linear signal. It will produce 90 ° phase shift between the quadrature and linear signals over the audio bandwidth of 1kHz to 10kHz.
[Source: maxim-ic. com] 🔗 External reference
More: Simple phase-delay circuits are active circuits that employ a first-order section to implement a phase-shift filter with a cutoff frequency (ft) of 1 kHz for the quadrature signal and a cutoff frequency of 10 kHz for the linear signal. This configuration produces a 90° phase shift between the quadrature and linear signals across the audio bandwidth of 1 kHz to 10 kHz.
The implementation of a 3D audio enhancement circuit involves the careful design of phase-delay circuits that significantly contribute to the perception of spatial audio. The circuit typically consists of a combination of operational amplifiers configured to create the necessary phase shifts for both quadrature and linear signals.
The first-order phase-shift filter is crucial in this design, as it allows the audio signals to be manipulated effectively within the specified frequency range. The choice of cutoff frequencies—1 kHz for the quadrature signal and 10 kHz for the linear signal—ensures that the circuit can handle the typical audio bandwidth while maintaining clarity and fidelity.
The output of the phase-delay circuit is then combined to produce a stereo output that enhances the spatial characteristics of the audio. By introducing a 90° phase shift, the circuit effectively widens the sound field, creating an immersive listening experience that simulates a three-dimensional sound environment.
However, careful consideration must be given to the transaural acoustic crosstalk effect, which can occur when audio signals intended for one ear are inadvertently heard by the other ear. This phenomenon can detract from the desired 3D effect and requires additional measures, such as crosstalk cancellation techniques or advanced filtering, to mitigate its impact.
Overall, the design of a 3D enhancement circuit using simple phase-delay circuits is a sophisticated endeavor that combines principles of audio engineering and psychoacoustics to deliver a compelling auditory experience.3D enhancement is needed to create a fully 3-dimensional sound for most stereo multimedia products. Usually, simple phase-delay circuits is used to produce a widening effect on the perceived sound field. However, there is transaural acoustic crosstalk effect. The following figure shows transaural acoustic crosstalk effect and schematic diagram of simple phase-delay circuits : This is an active circuit that uses first-order section to present a phase-shift filter with ft of 1kHz for the quadrature signal and ft = 10kHz for the linear signal. It will produce 90 ° phase shift between the quadrature and linear signals over the audio bandwidth of 1kHz to 10kHz.
[Source: maxim-ic. com] 🔗 External reference