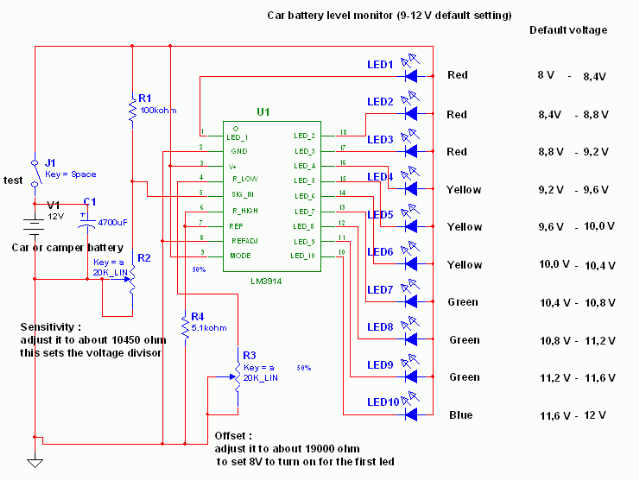
Pot plant water tester
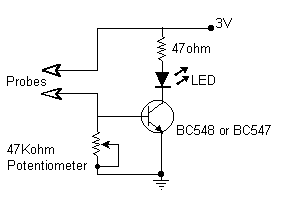
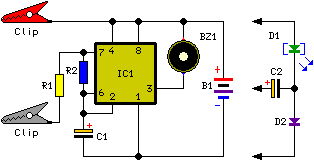
This simple device checks if there is water in a pot plant. You stick the two probes (paperclips) into the pot plant and if the LED lights, it means there is water in the pot plant.
The described device operates as a basic moisture sensor for plants, utilizing two conductive probes to detect the presence of water in the soil. The design consists of a simple circuit that includes a power source, the probes, a resistor, and an LED indicator.
The probes, which can be made from paperclips, are inserted into the soil of the pot plant. When the soil is moist, it conducts electricity between the two probes. This conductivity completes the circuit, allowing current to flow from the power source through a resistor and into the LED. The LED will light up, providing a visual indication that there is sufficient moisture in the soil.
In terms of circuit design, the power source can be a small battery, such as a 9V battery or a pair of AA batteries, depending on the desired voltage and current requirements. The resistor is crucial as it limits the current flowing through the LED to prevent damage. A typical value for this resistor could be around 220 ohms, depending on the specific LED characteristics.
To enhance the reliability of the moisture detection, it may be beneficial to implement a simple comparator circuit using an operational amplifier. This would allow for adjustable sensitivity and the ability to set a threshold for moisture detection. Additionally, incorporating a buzzer or a more sophisticated display could provide alternative indications of moisture levels, making the device more user-friendly.
Overall, this moisture sensing device is an effective and straightforward solution for monitoring the water content in potted plants, ensuring that they receive adequate hydration without the need for constant manual checks.This simple device checks if their is water in a pot plant. You stick the two probes(paperclips)into the pot plant and if the LED lights, it means there is water in the pot plant. 🔗 External reference
The described device operates as a basic moisture sensor for plants, utilizing two conductive probes to detect the presence of water in the soil. The design consists of a simple circuit that includes a power source, the probes, a resistor, and an LED indicator.
The probes, which can be made from paperclips, are inserted into the soil of the pot plant. When the soil is moist, it conducts electricity between the two probes. This conductivity completes the circuit, allowing current to flow from the power source through a resistor and into the LED. The LED will light up, providing a visual indication that there is sufficient moisture in the soil.
In terms of circuit design, the power source can be a small battery, such as a 9V battery or a pair of AA batteries, depending on the desired voltage and current requirements. The resistor is crucial as it limits the current flowing through the LED to prevent damage. A typical value for this resistor could be around 220 ohms, depending on the specific LED characteristics.
To enhance the reliability of the moisture detection, it may be beneficial to implement a simple comparator circuit using an operational amplifier. This would allow for adjustable sensitivity and the ability to set a threshold for moisture detection. Additionally, incorporating a buzzer or a more sophisticated display could provide alternative indications of moisture levels, making the device more user-friendly.
Overall, this moisture sensing device is an effective and straightforward solution for monitoring the water content in potted plants, ensuring that they receive adequate hydration without the need for constant manual checks.This simple device checks if their is water in a pot plant. You stick the two probes(paperclips)into the pot plant and if the LED lights, it means there is water in the pot plant. 🔗 External reference