Precision full wave rectifier
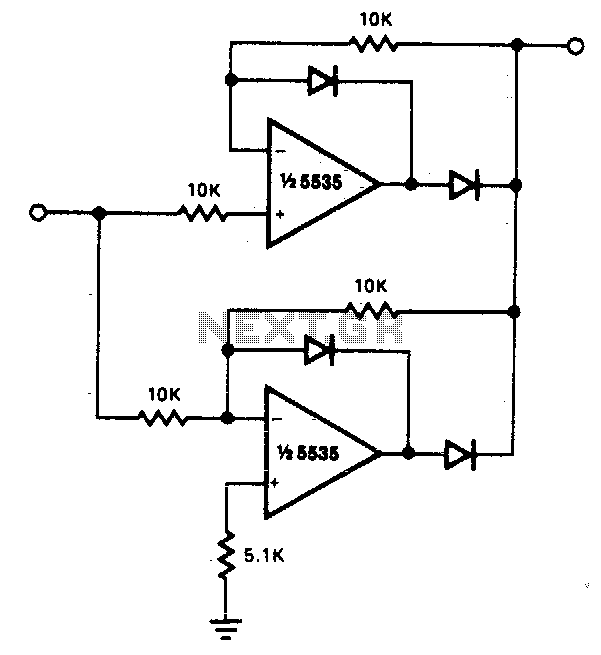
The circuit facilitates precise full-wave rectification. It exhibits low output impedance for both input polarities, and the error rates remain minimal across all signal levels. It is important to note that the output will not be capable of sinking significant current, except for a small amount through the 10K resistors. Consequently, any load connected should be referenced to ground or a negative voltage. Reversing the polarities of all diodes will result in an inversion of the output polarity. Additionally, since the outputs of the amplifiers must transition through two diode drops when the input polarity changes, 741 type devices produce a distortion of 5% at approximately 300 Hz.
The circuit in question is designed for full-wave rectification, which is a process that converts both halves of an AC waveform into a usable DC signal. The low output impedance characteristic is advantageous as it allows for efficient power transfer to the load, minimizing voltage drop and ensuring that the rectified output maintains integrity across varying signal levels.
The inclusion of 10K resistors serves a dual purpose: they limit the current that can be drawn from the output and help stabilize the output voltage. This design consideration ensures that the circuit operates within safe parameters, preventing damage to the diodes or the connected load. The recommendation to reference the load to ground or a negative voltage is crucial to maintain proper operation and prevent erroneous readings or damage to the circuit.
The mention of diode polarity is significant in full-wave rectification. By reversing the polarity of the diodes, the output voltage will also reverse, which can be useful in certain applications where the output needs to be inverted. This characteristic allows for flexibility in circuit design, enabling the same circuit to be adapted for different requirements without extensive redesign.
Furthermore, the performance of the circuit can be influenced by the choice of operational amplifiers used in conjunction with the rectification process. The 741 operational amplifier, while widely used, has limitations, particularly regarding distortion at lower frequencies. The noted 5% distortion at 300 Hz indicates that care must be taken when selecting components for applications that require high fidelity, especially in audio or precision measurement contexts.
Overall, this circuit serves as a reliable solution for applications requiring efficient full-wave rectification, with careful consideration given to component selection and load management to ensure optimal performance.The circuit provides accurate full wave rectification. The output impedance is low for both input polarities, and the errors are small at all signal levels. Note that the output will not sink heavy current, except a small amount through the 10K resistors. Therefore, the load applied should be referenced to ground or a negative voltage. Reversal of all diode polarities will reverse the polarity of the output Since the outputs of the amplifiers must slew through two diode drops when the input polarity changes, 741 type devices give 5% distortion at about 300 Hz. 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question is designed for full-wave rectification, which is a process that converts both halves of an AC waveform into a usable DC signal. The low output impedance characteristic is advantageous as it allows for efficient power transfer to the load, minimizing voltage drop and ensuring that the rectified output maintains integrity across varying signal levels.
The inclusion of 10K resistors serves a dual purpose: they limit the current that can be drawn from the output and help stabilize the output voltage. This design consideration ensures that the circuit operates within safe parameters, preventing damage to the diodes or the connected load. The recommendation to reference the load to ground or a negative voltage is crucial to maintain proper operation and prevent erroneous readings or damage to the circuit.
The mention of diode polarity is significant in full-wave rectification. By reversing the polarity of the diodes, the output voltage will also reverse, which can be useful in certain applications where the output needs to be inverted. This characteristic allows for flexibility in circuit design, enabling the same circuit to be adapted for different requirements without extensive redesign.
Furthermore, the performance of the circuit can be influenced by the choice of operational amplifiers used in conjunction with the rectification process. The 741 operational amplifier, while widely used, has limitations, particularly regarding distortion at lower frequencies. The noted 5% distortion at 300 Hz indicates that care must be taken when selecting components for applications that require high fidelity, especially in audio or precision measurement contexts.
Overall, this circuit serves as a reliable solution for applications requiring efficient full-wave rectification, with careful consideration given to component selection and load management to ensure optimal performance.The circuit provides accurate full wave rectification. The output impedance is low for both input polarities, and the errors are small at all signal levels. Note that the output will not sink heavy current, except a small amount through the 10K resistors. Therefore, the load applied should be referenced to ground or a negative voltage. Reversal of all diode polarities will reverse the polarity of the output Since the outputs of the amplifiers must slew through two diode drops when the input polarity changes, 741 type devices give 5% distortion at about 300 Hz. 🔗 External reference