Self oscillating flyback converter
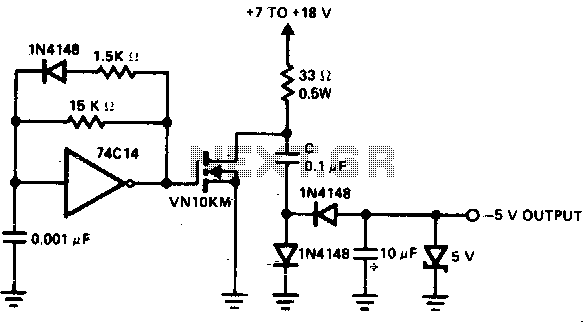
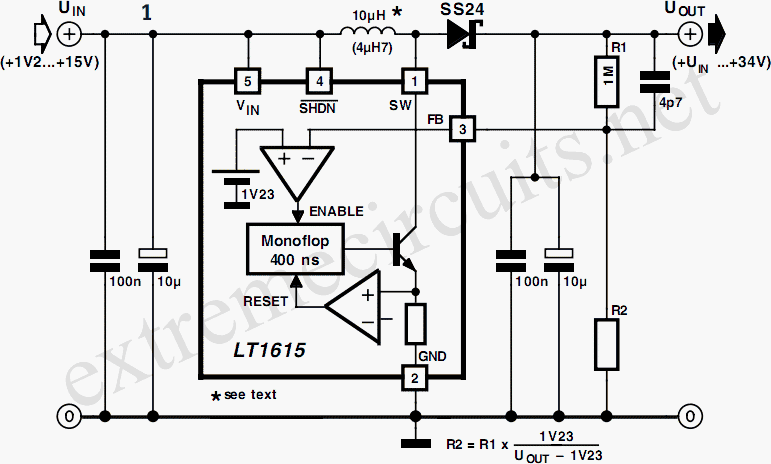
A low-power converter designed to derive a higher voltage from a main system rail in an on-board application. The operating frequency with the transformer depicted is 250 kHz. Z1 functions as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and limits the drain voltage to a value below the rated VMOS breakdown voltage.
The low-power converter is engineered to efficiently step up the voltage from a primary system rail, making it suitable for use in various on-board applications, such as in electronic devices and automotive systems where space and power efficiency are critical. The converter operates at a frequency of 250 kHz, which is optimal for balancing performance and efficiency while minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The core component of this converter is a transformer, which is utilized to increase the voltage level. The transformer design should be carefully selected to handle the required power levels and ensure minimal losses during operation. The winding ratios are crucial, as they dictate the output voltage based on the input voltage. Additionally, the transformer must be rated for the operating frequency to prevent saturation and ensure efficient energy transfer.
Z1, functioning as a dissipative voltage regulator, plays a vital role in stabilizing the output voltage. It prevents voltage spikes and maintains the output within a specified range, ensuring reliable operation of downstream components. By clipping the drain voltage, Z1 protects the VMOS transistor from exceeding its breakdown voltage, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the circuit and preventing catastrophic failures.
The overall design must also consider thermal management, as the converter may generate heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or thermal dissipation methods should be implemented to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
In summary, this low-power converter is an essential component for applications requiring voltage step-up capabilities, with an emphasis on reliability, efficiency, and protection against voltage transients. The integration of a transformer and a voltage regulator like Z1 ensures that the converter operates within safe parameters while delivering the necessary power to the load.A low-power converter suitable for deriving a higher voltage from a main system rail in an on-board application. With the transformer shown, the operating frequency is 250 kHz Z1 serves as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and also clips the drain voltage to a level below the rated VMOS breakdown voltage. 🔗 External reference
The low-power converter is engineered to efficiently step up the voltage from a primary system rail, making it suitable for use in various on-board applications, such as in electronic devices and automotive systems where space and power efficiency are critical. The converter operates at a frequency of 250 kHz, which is optimal for balancing performance and efficiency while minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The core component of this converter is a transformer, which is utilized to increase the voltage level. The transformer design should be carefully selected to handle the required power levels and ensure minimal losses during operation. The winding ratios are crucial, as they dictate the output voltage based on the input voltage. Additionally, the transformer must be rated for the operating frequency to prevent saturation and ensure efficient energy transfer.
Z1, functioning as a dissipative voltage regulator, plays a vital role in stabilizing the output voltage. It prevents voltage spikes and maintains the output within a specified range, ensuring reliable operation of downstream components. By clipping the drain voltage, Z1 protects the VMOS transistor from exceeding its breakdown voltage, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of the circuit and preventing catastrophic failures.
The overall design must also consider thermal management, as the converter may generate heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or thermal dissipation methods should be implemented to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
In summary, this low-power converter is an essential component for applications requiring voltage step-up capabilities, with an emphasis on reliability, efficiency, and protection against voltage transients. The integration of a transformer and a voltage regulator like Z1 ensures that the converter operates within safe parameters while delivering the necessary power to the load.A low-power converter suitable for deriving a higher voltage from a main system rail in an on-board application. With the transformer shown, the operating frequency is 250 kHz Z1 serves as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and also clips the drain voltage to a level below the rated VMOS breakdown voltage. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713