Simple Safety Circuit Circuit
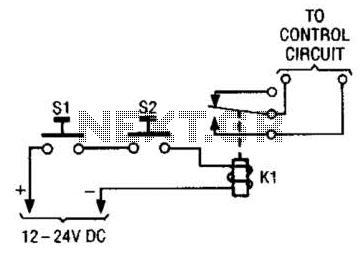
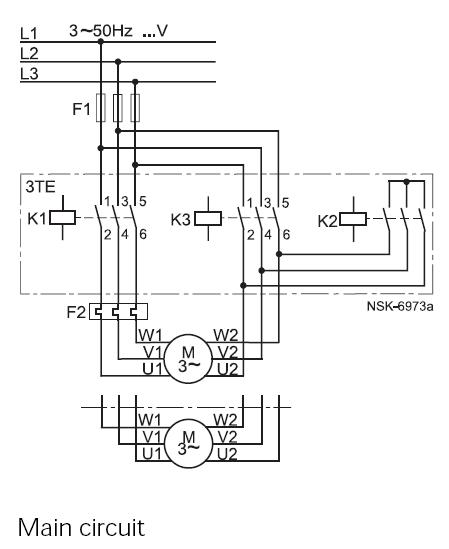
The simple two-hand safety control switch consists of two pushbutton switches connected in series; both must be depressed to energize the relay.
The two-hand safety control switch is designed to enhance safety in applications where the operation of machinery or equipment could pose a risk to the operator. By requiring both pushbutton switches to be activated simultaneously, the system ensures that the operator maintains a safe distance from the moving parts or hazardous areas.
In this configuration, each pushbutton switch is connected in series, meaning that the circuit is only completed when both switches are pressed. The switches are typically momentary contact types, which means they return to their default position when released. This design prevents accidental activation of the relay and ensures that the machinery remains in a safe state when the operator's hands are not in the correct position.
The relay, which is energized when both switches are pressed, can control larger loads or more complex machinery, acting as an interface between the low-power control circuit and the high-power operational circuit. It is essential to select a relay that is rated for the load it will control, ensuring reliability and safety in operation.
In addition, it is advisable to implement additional safety measures such as emergency stop buttons and visual indicators to further enhance the safety of the system. Proper labeling and training for operators are also critical to ensure that the two-hand control mechanism is used correctly, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents. The simple two-hand safety-control switch shown here is little more than two pushbutton switches connected in series; both must be depressed in order to energize the relay. 🔗 External reference
The two-hand safety control switch is designed to enhance safety in applications where the operation of machinery or equipment could pose a risk to the operator. By requiring both pushbutton switches to be activated simultaneously, the system ensures that the operator maintains a safe distance from the moving parts or hazardous areas.
In this configuration, each pushbutton switch is connected in series, meaning that the circuit is only completed when both switches are pressed. The switches are typically momentary contact types, which means they return to their default position when released. This design prevents accidental activation of the relay and ensures that the machinery remains in a safe state when the operator's hands are not in the correct position.
The relay, which is energized when both switches are pressed, can control larger loads or more complex machinery, acting as an interface between the low-power control circuit and the high-power operational circuit. It is essential to select a relay that is rated for the load it will control, ensuring reliability and safety in operation.
In addition, it is advisable to implement additional safety measures such as emergency stop buttons and visual indicators to further enhance the safety of the system. Proper labeling and training for operators are also critical to ensure that the two-hand control mechanism is used correctly, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents. The simple two-hand safety-control switch shown here is little more than two pushbutton switches connected in series; both must be depressed in order to energize the relay. 🔗 External reference