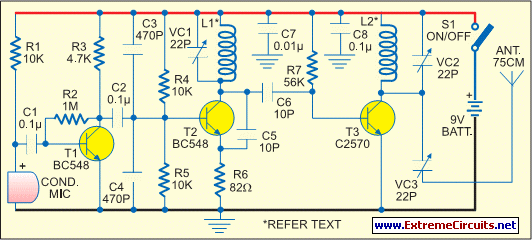
switching power supply circuit diagram
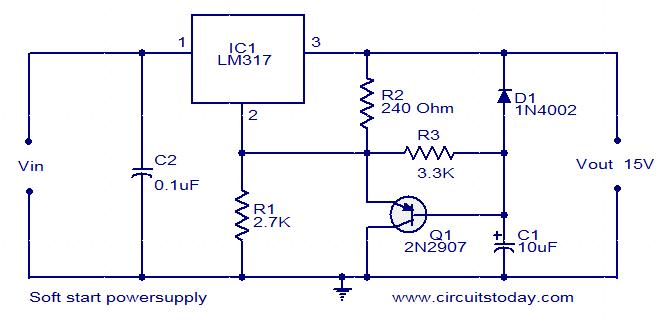
This post presents an interesting topic about switching power supply circuit diagrams for those who wish to learn more.
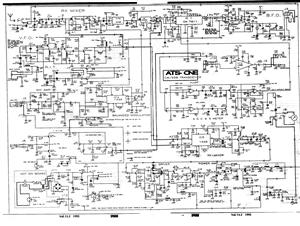
A switching power supply is a type of power supply that uses a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Unlike linear power supplies, which dissipate excess voltage as heat, switching power supplies operate by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, allowing for greater efficiency and reduced heat generation.
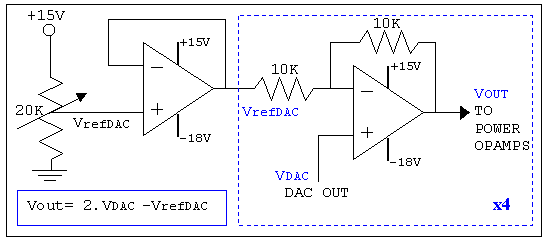
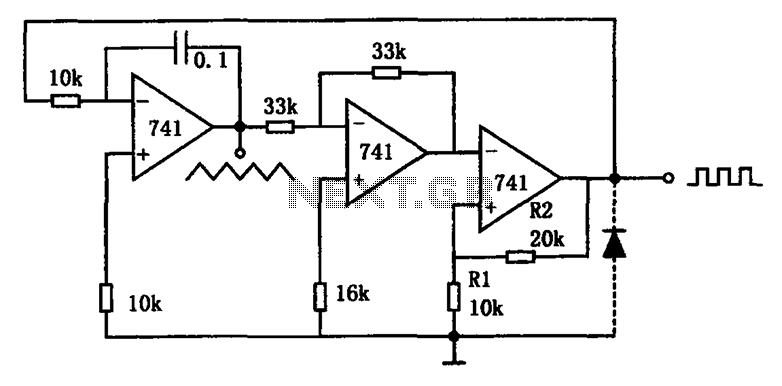
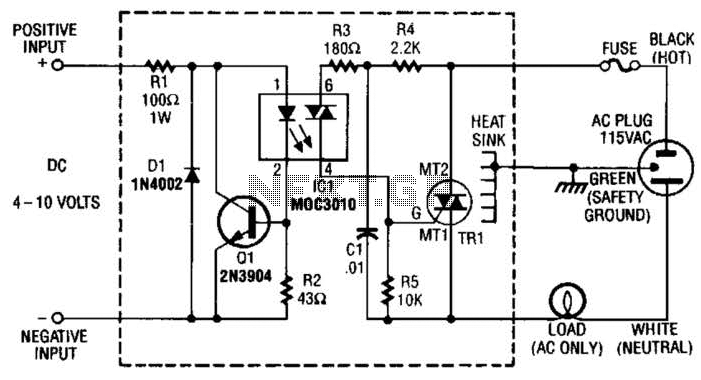
The basic components of a switching power supply circuit include a transformer, a switching element (such as a MOSFET), a diode, an inductor, and capacitors. The switching element is driven by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller, which adjusts the duty cycle of the switching signal to regulate the output voltage.
In a typical schematic, the input voltage is connected to the switching element, which alternates the current flow through the transformer. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage as required, and the output is rectified by the diode, smoothing the output with capacitors and inductors to reduce ripple voltage. Feedback mechanisms are often incorporated to ensure stable output under varying load conditions, enhancing the reliability of the power supply.
Overall, switching power supply circuits are widely used in various applications due to their compact size, high efficiency, and ability to handle a wide range of input voltages.Welcome folks, today I want post interesting topic about switching power supply circuit diagram for you who want to learn more you can search.. 🔗 External reference
A switching power supply is a type of power supply that uses a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Unlike linear power supplies, which dissipate excess voltage as heat, switching power supplies operate by rapidly switching the input voltage on and off, allowing for greater efficiency and reduced heat generation.
The basic components of a switching power supply circuit include a transformer, a switching element (such as a MOSFET), a diode, an inductor, and capacitors. The switching element is driven by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller, which adjusts the duty cycle of the switching signal to regulate the output voltage.
In a typical schematic, the input voltage is connected to the switching element, which alternates the current flow through the transformer. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage as required, and the output is rectified by the diode, smoothing the output with capacitors and inductors to reduce ripple voltage. Feedback mechanisms are often incorporated to ensure stable output under varying load conditions, enhancing the reliability of the power supply.
Overall, switching power supply circuits are widely used in various applications due to their compact size, high efficiency, and ability to handle a wide range of input voltages.Welcome folks, today I want post interesting topic about switching power supply circuit diagram for you who want to learn more you can search.. 🔗 External reference