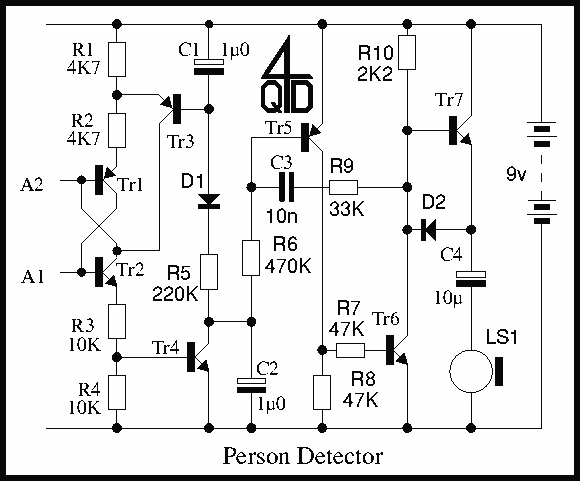
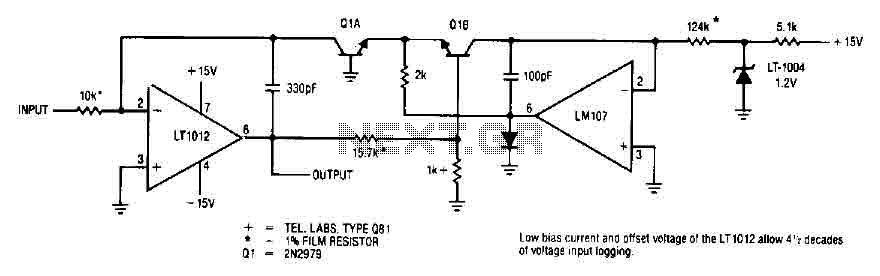
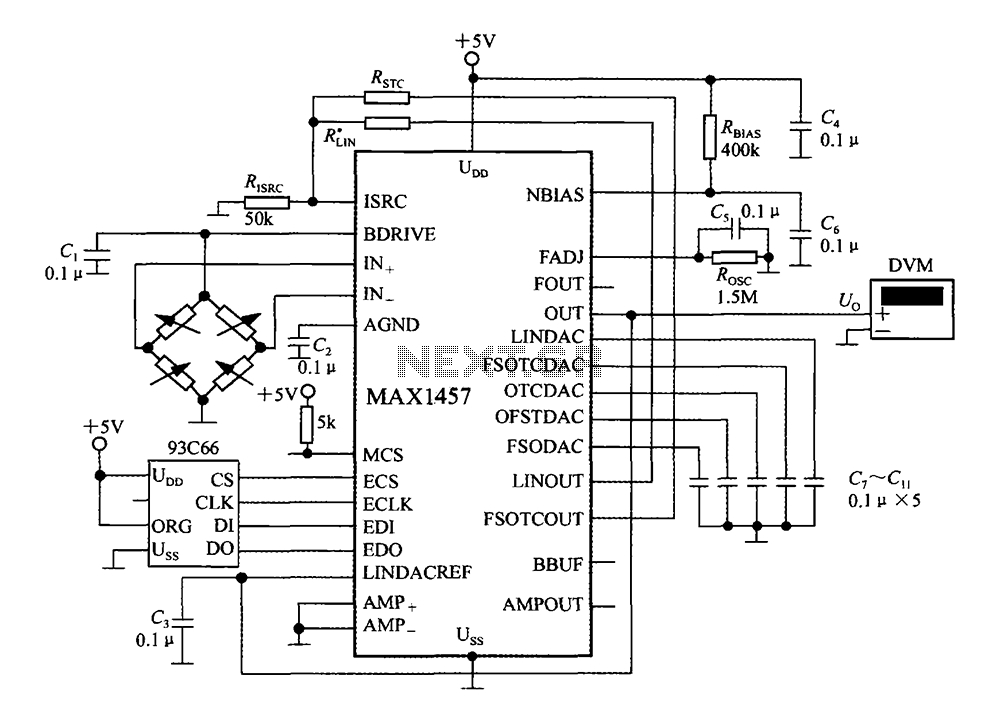
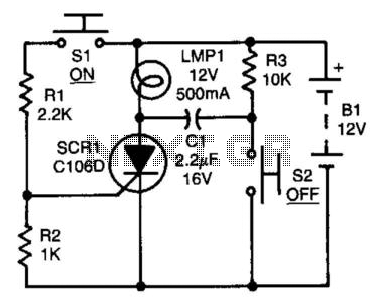
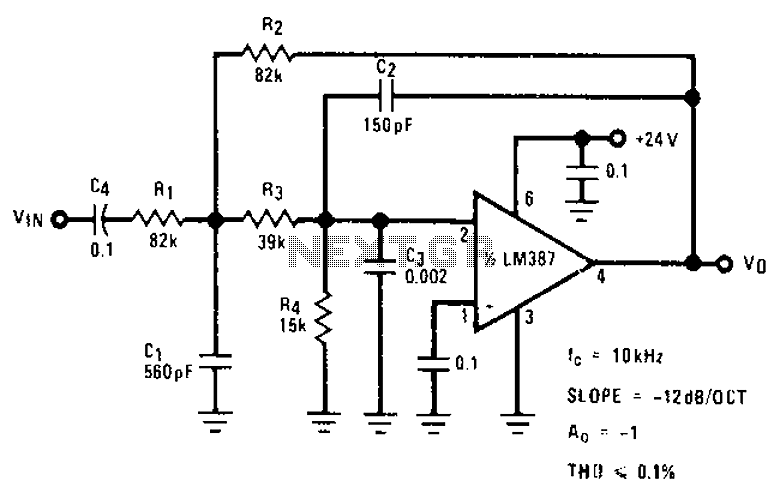
The luminous flux test circuit with optical resistors
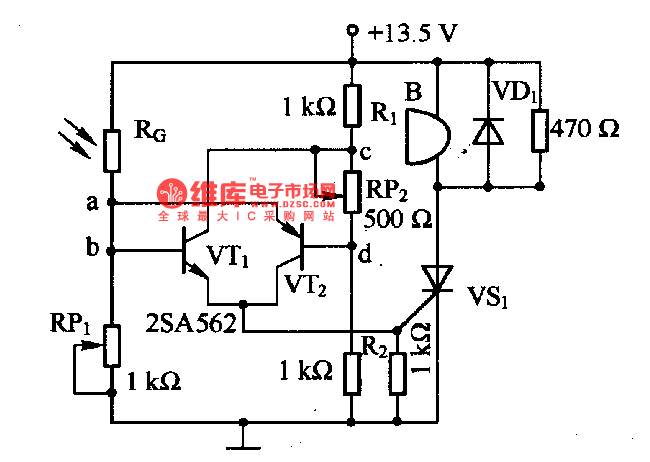
This is a luminous flux test circuit that utilizes optical resistors. In the circuit, the optical resistor RG forms a bridge with resistors RP1, RP2, R1, and R2. RP1 is employed to balance the bridge, while RP2 is used to adjust the circuit's sensitivity. When RP1 is adjusted to equalize the voltages at points a and c, the voltages VT1 and VT2 become zero, resulting in the thyristor in VSI being turned off.
The luminous flux test circuit is designed to measure light intensity using a configuration of optical resistors, which change their resistance based on the amount of light exposure. The core of this circuit is a Wheatstone bridge formed by RG, RP1, RP2, R1, and R2. The optical resistor RG responds to light levels, altering the resistance and thus influencing the balance of the bridge.
Resistor RP1 serves a critical role in fine-tuning the bridge balance. By adjusting RP1, the user can achieve equal voltage levels at nodes a and c, which is essential for accurate measurements. The second variable resistor, RP2, is responsible for adjusting the sensitivity of the entire circuit, allowing the user to calibrate the response to varying light conditions.
When the circuit is balanced—meaning the voltages at points a and c are equal—the output voltages VT1 and VT2 drop to zero. This condition indicates that the thyristor in the VSI section of the circuit is no longer conducting, effectively turning it off. The design ensures that the circuit can operate effectively under different lighting conditions by providing a means to adjust both the balance and sensitivity, making it suitable for applications requiring precise luminous flux measurements.
Overall, this luminous flux test circuit exemplifies the use of optical resistors in a bridge configuration to achieve accurate light intensity readings, with adjustable parameters for fine-tuning performance.This is a luminous flux test circuit with optical resistors. In the circuit, the optical resistor RG forms a bridge with RP1,RP2,R1 and R2; RP1 is used to adjust the balance of the bridge; RP2 is used to adjust the sensitivity of the circuit. If we adjust RP1 to make the voltages on a and c are equal, then VTl and VT2 stop, and the thyristor of VSI is off.
I.. 🔗 External reference
The luminous flux test circuit is designed to measure light intensity using a configuration of optical resistors, which change their resistance based on the amount of light exposure. The core of this circuit is a Wheatstone bridge formed by RG, RP1, RP2, R1, and R2. The optical resistor RG responds to light levels, altering the resistance and thus influencing the balance of the bridge.
Resistor RP1 serves a critical role in fine-tuning the bridge balance. By adjusting RP1, the user can achieve equal voltage levels at nodes a and c, which is essential for accurate measurements. The second variable resistor, RP2, is responsible for adjusting the sensitivity of the entire circuit, allowing the user to calibrate the response to varying light conditions.
When the circuit is balanced—meaning the voltages at points a and c are equal—the output voltages VT1 and VT2 drop to zero. This condition indicates that the thyristor in the VSI section of the circuit is no longer conducting, effectively turning it off. The design ensures that the circuit can operate effectively under different lighting conditions by providing a means to adjust both the balance and sensitivity, making it suitable for applications requiring precise luminous flux measurements.
Overall, this luminous flux test circuit exemplifies the use of optical resistors in a bridge configuration to achieve accurate light intensity readings, with adjustable parameters for fine-tuning performance.This is a luminous flux test circuit with optical resistors. In the circuit, the optical resistor RG forms a bridge with RP1,RP2,R1 and R2; RP1 is used to adjust the balance of the bridge; RP2 is used to adjust the sensitivity of the circuit. If we adjust RP1 to make the voltages on a and c are equal, then VTl and VT2 stop, and the thyristor of VSI is off.
I.. 🔗 External reference