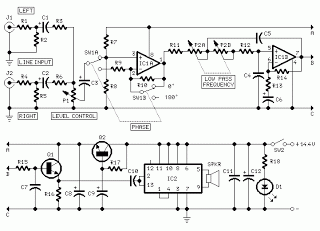
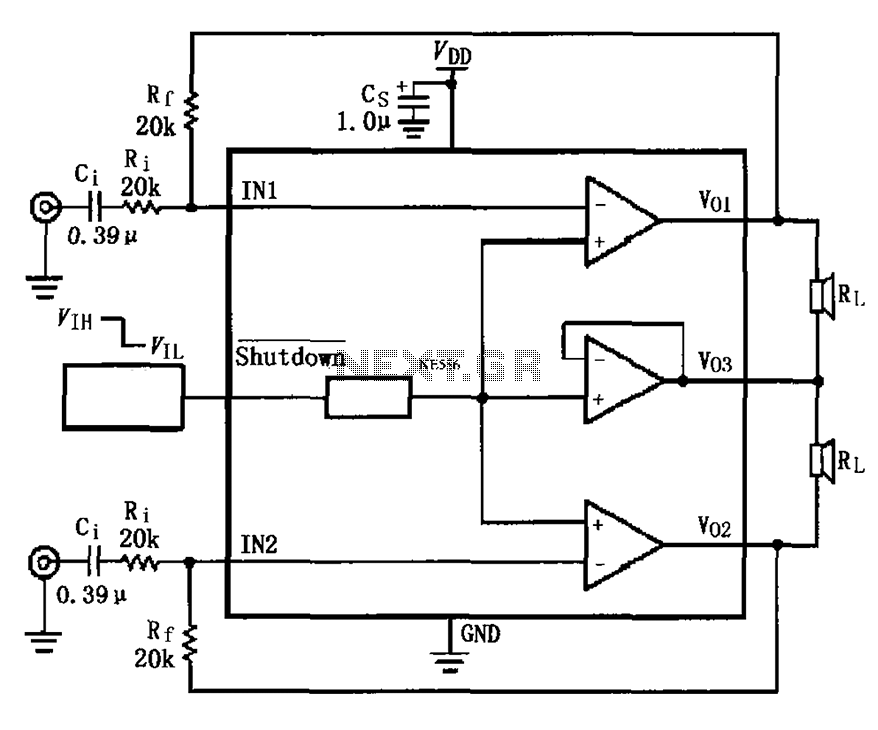
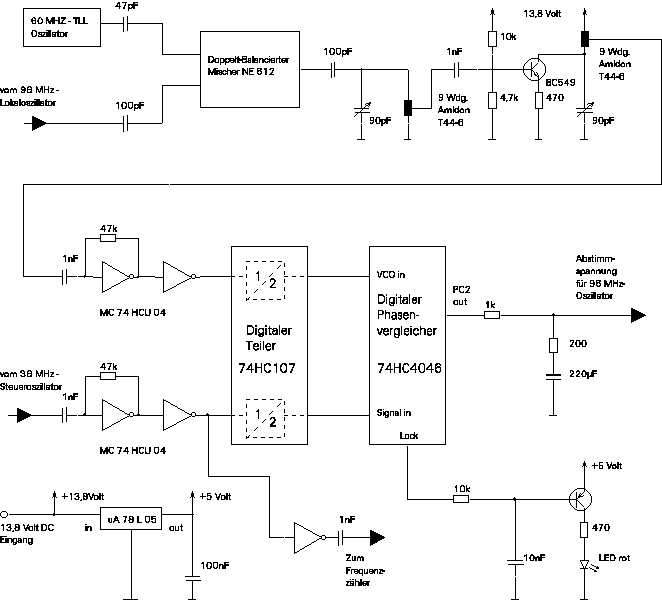
Thermistor lights lighting delay circuit
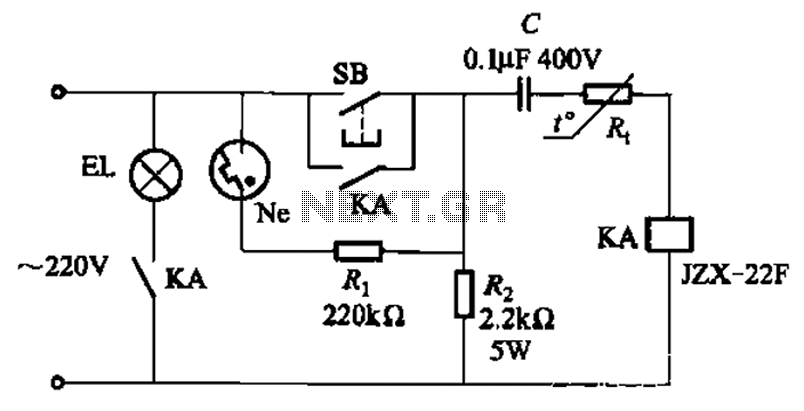
The circuit illustrated in Figure 2-49 is straightforward, featuring a cold Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistor element. It utilizes the thermal resistance characteristics of the lamp to manage the delay time, which typically ranges from 10 to 30 seconds. To modify the delay time, adjustable resistors Rz and the capacitance value C can be altered. The PTC thermistor is selected with a Curie point of approximately 80 degrees Celsius, with a nominal resistance of 1500 ohms at 20 degrees Celsius, which can increase to several thousand ohms, reaching tens of kilohms at 80 degrees Celsius. The resistors Rt and R2 must be in close contact for optimal performance.
The circuit operates based on the thermal characteristics of the PTC thermistor, which exhibits a significant increase in resistance as the temperature approaches its Curie point. Initially, when the circuit is powered on, the thermistor remains cold, allowing current to flow through it and the lamp, resulting in illumination. As the lamp heats up, the temperature of the thermistor rises, leading to an increase in its resistance. This change in resistance effectively reduces the current flowing through the lamp, thereby controlling its brightness and extending the delay time before it turns off.
Adjustable resistor Rz plays a critical role in fine-tuning the delay time. By varying its resistance, the user can change the time it takes for the thermistor to reach its Curie point and thus modify the duration of the lamp's illumination. The value of the capacitor C is also essential, as it influences the charging time and, consequently, the delay time. A larger capacitance will result in a longer delay, while a smaller capacitance will shorten the delay.
The close contact requirement between resistors Rt and R2 ensures that they effectively sense the thermal changes in the circuit. This configuration is vital for accurate temperature measurement and response, allowing the circuit to function reliably under varying operational conditions. The overall design is simple yet effective, providing a practical solution for applications requiring controlled delay timing in lighting systems. Circuit shown in Figure 2-49. The circuit is very simple, cold PTC thermistor element, jump characteristic thermal resistance of the lamp to control delay time. Usually the del ay time is 10 ~ 30s, such as to change the delay time, adjustable Rz, the value of C. R. Adopt a positive temperature coefficient of thermal PTC thermistor, the choice of the Curie point about 80, nominal resistance value at 20 rise when 1500,80 to several thousand Euro to several tens of kilohms. Rt and R2 is required intimate contact.
The circuit operates based on the thermal characteristics of the PTC thermistor, which exhibits a significant increase in resistance as the temperature approaches its Curie point. Initially, when the circuit is powered on, the thermistor remains cold, allowing current to flow through it and the lamp, resulting in illumination. As the lamp heats up, the temperature of the thermistor rises, leading to an increase in its resistance. This change in resistance effectively reduces the current flowing through the lamp, thereby controlling its brightness and extending the delay time before it turns off.
Adjustable resistor Rz plays a critical role in fine-tuning the delay time. By varying its resistance, the user can change the time it takes for the thermistor to reach its Curie point and thus modify the duration of the lamp's illumination. The value of the capacitor C is also essential, as it influences the charging time and, consequently, the delay time. A larger capacitance will result in a longer delay, while a smaller capacitance will shorten the delay.
The close contact requirement between resistors Rt and R2 ensures that they effectively sense the thermal changes in the circuit. This configuration is vital for accurate temperature measurement and response, allowing the circuit to function reliably under varying operational conditions. The overall design is simple yet effective, providing a practical solution for applications requiring controlled delay timing in lighting systems. Circuit shown in Figure 2-49. The circuit is very simple, cold PTC thermistor element, jump characteristic thermal resistance of the lamp to control delay time. Usually the del ay time is 10 ~ 30s, such as to change the delay time, adjustable Rz, the value of C. R. Adopt a positive temperature coefficient of thermal PTC thermistor, the choice of the Curie point about 80, nominal resistance value at 20 rise when 1500,80 to several thousand Euro to several tens of kilohms. Rt and R2 is required intimate contact.