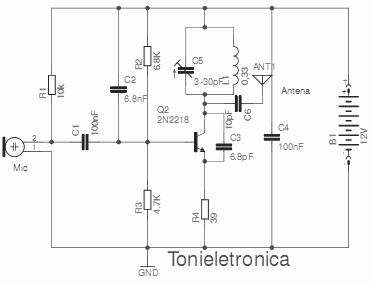
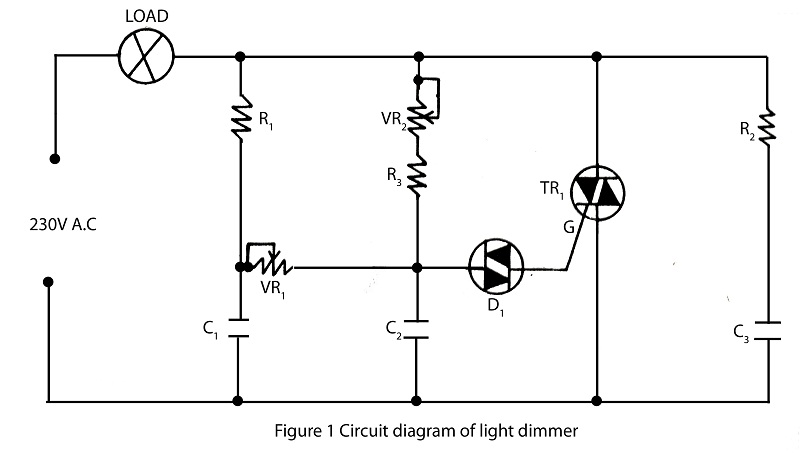
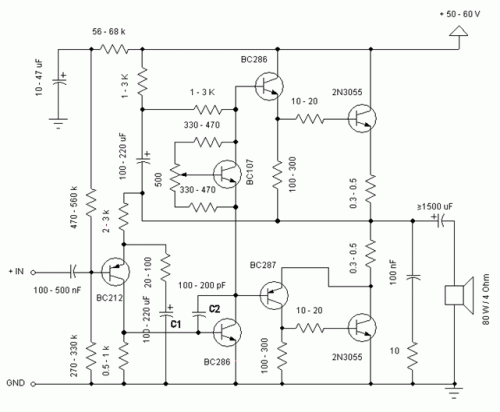
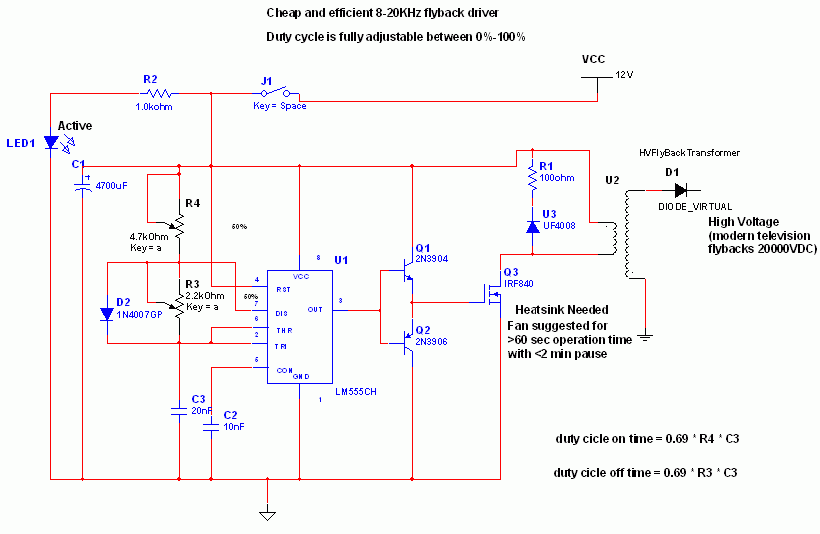
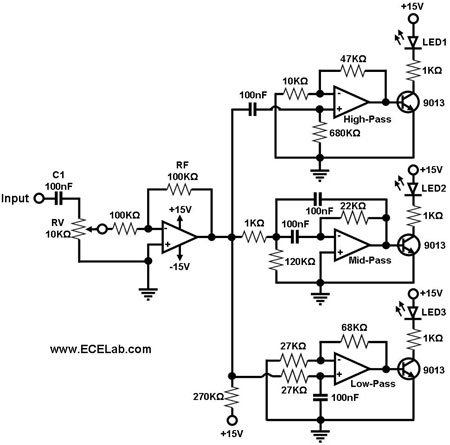
Transistor DC Transformer
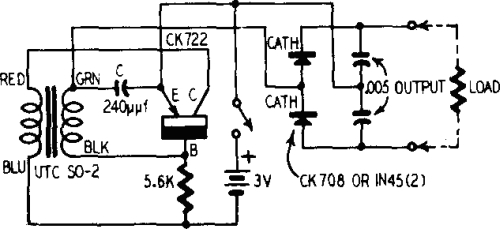
A battery is a low-impedance power source. It operates most efficiently and economically when providing low voltage at high current.
Batteries serve as essential components in various electronic circuits, functioning as a reliable source of energy. Their low-impedance characteristic allows for minimal energy loss during power delivery, which is particularly advantageous in applications requiring high current output. This feature enables batteries to efficiently power devices such as electric motors, portable electronics, and various sensors.
When designing circuits that incorporate batteries, several factors must be considered to optimize performance. The selection of battery type—such as lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, or lead-acid—will influence the voltage and current capabilities, as well as the overall efficiency of the system. Furthermore, the circuit design should include appropriate voltage regulation and current limiting components to ensure that the battery operates within its specified parameters, thus prolonging its lifespan and maintaining safety.
In addition, the configuration of the battery in the circuit can be critical. For instance, connecting multiple batteries in parallel can increase the total current capacity while maintaining the same voltage level. Conversely, connecting batteries in series increases the overall voltage, which may be necessary for certain applications.
The integration of battery management systems (BMS) is also crucial in more complex designs. A BMS monitors the state of charge, temperature, and health of the battery, ensuring that it operates optimally and safely. It can prevent overcharging, deep discharging, and other conditions that could lead to battery failure or hazards.
Overall, the efficient use of batteries in electronic circuits requires careful consideration of their characteristics, applications, and integration with other circuit elements to achieve optimal performance.A battery is a low-impedence source of power. It is most efficient and economical when supplying low voltage at high current 🔗 External reference
Batteries serve as essential components in various electronic circuits, functioning as a reliable source of energy. Their low-impedance characteristic allows for minimal energy loss during power delivery, which is particularly advantageous in applications requiring high current output. This feature enables batteries to efficiently power devices such as electric motors, portable electronics, and various sensors.
When designing circuits that incorporate batteries, several factors must be considered to optimize performance. The selection of battery type—such as lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, or lead-acid—will influence the voltage and current capabilities, as well as the overall efficiency of the system. Furthermore, the circuit design should include appropriate voltage regulation and current limiting components to ensure that the battery operates within its specified parameters, thus prolonging its lifespan and maintaining safety.
In addition, the configuration of the battery in the circuit can be critical. For instance, connecting multiple batteries in parallel can increase the total current capacity while maintaining the same voltage level. Conversely, connecting batteries in series increases the overall voltage, which may be necessary for certain applications.
The integration of battery management systems (BMS) is also crucial in more complex designs. A BMS monitors the state of charge, temperature, and health of the battery, ensuring that it operates optimally and safely. It can prevent overcharging, deep discharging, and other conditions that could lead to battery failure or hazards.
Overall, the efficient use of batteries in electronic circuits requires careful consideration of their characteristics, applications, and integration with other circuit elements to achieve optimal performance.A battery is a low-impedence source of power. It is most efficient and economical when supplying low voltage at high current 🔗 External reference