transistors Having difficulties using a darlington (BD681) to drive a 12V fan from an Arduino
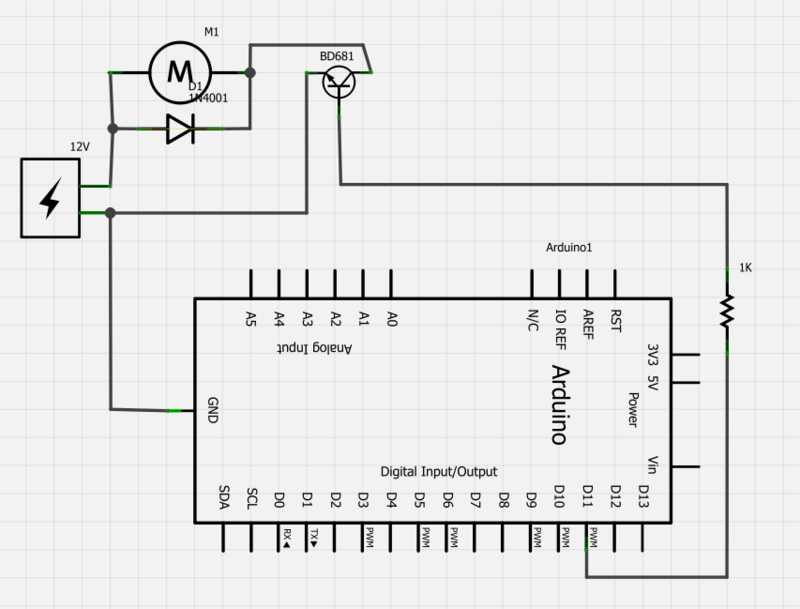
Power a 12V fan using a Darlington transistor to control the speed from an Arduino. When wired as described, nothing happens even though a PWM signal is being sent. It is suggested to edit the question and ensure the current image is readable. Additionally, check the breadboard as many rows along the side may have interruptions halfway, particularly the Arduino's GND connection. Including a picture of the setup is also recommended.
To power a 12V fan using a Darlington transistor for speed control via an Arduino, the following circuit configuration is advised. The Darlington transistor, which consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected together, provides high current gain and is suitable for switching applications.
The circuit should include an NPN Darlington transistor, such as the TIP120, which is capable of handling the required current for the fan. The Arduino will output a PWM signal to control the fan speed. Connect one of the PWM-capable digital pins of the Arduino (for example, pin 9) to the base of the Darlington transistor through a current-limiting resistor (typically 1kΩ). This resistor is essential to protect the Arduino from excess current.
The collector of the Darlington transistor should be connected to the positive terminal of the 12V power supply, while the emitter connects to one terminal of the fan. The other terminal of the fan should be connected to the ground of the power supply. It is crucial to ensure that the ground of the Arduino is also connected to the ground of the 12V power supply to establish a common reference point.
For additional protection, a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4001) should be placed in parallel with the fan terminals to prevent back EMF generated by the inductive load when the fan is switched off. The cathode of the diode connects to the positive terminal of the fan, while the anode connects to the ground side.
In summary, the circuit consists of an Arduino sending a PWM signal to a resistor connected to the base of a Darlington transistor, which in turn controls the fan powered by a 12V supply. Proper connections and component selection are critical to ensure functionality and prevent damage to the components.Power a 12v fan using a darlington so I can control the speed from an Arduino. When I wire up as below nothing happens, even though I`m sending a PWM signal: Please draw a proper circuit. Edit your question and hit Ctrl+M, the current image is unreadable. Check your breadboard, most rows along the side are have one or two interruptio ns half way (Arduino`s GND connection). Possibly add a picture of your setup aswell. jippie Apr 13 `13 at 20:16 🔗 External reference
To power a 12V fan using a Darlington transistor for speed control via an Arduino, the following circuit configuration is advised. The Darlington transistor, which consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected together, provides high current gain and is suitable for switching applications.
The circuit should include an NPN Darlington transistor, such as the TIP120, which is capable of handling the required current for the fan. The Arduino will output a PWM signal to control the fan speed. Connect one of the PWM-capable digital pins of the Arduino (for example, pin 9) to the base of the Darlington transistor through a current-limiting resistor (typically 1kΩ). This resistor is essential to protect the Arduino from excess current.
The collector of the Darlington transistor should be connected to the positive terminal of the 12V power supply, while the emitter connects to one terminal of the fan. The other terminal of the fan should be connected to the ground of the power supply. It is crucial to ensure that the ground of the Arduino is also connected to the ground of the 12V power supply to establish a common reference point.
For additional protection, a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4001) should be placed in parallel with the fan terminals to prevent back EMF generated by the inductive load when the fan is switched off. The cathode of the diode connects to the positive terminal of the fan, while the anode connects to the ground side.
In summary, the circuit consists of an Arduino sending a PWM signal to a resistor connected to the base of a Darlington transistor, which in turn controls the fan powered by a 12V supply. Proper connections and component selection are critical to ensure functionality and prevent damage to the components.Power a 12v fan using a darlington so I can control the speed from an Arduino. When I wire up as below nothing happens, even though I`m sending a PWM signal: Please draw a proper circuit. Edit your question and hit Ctrl+M, the current image is unreadable. Check your breadboard, most rows along the side are have one or two interruptio ns half way (Arduino`s GND connection). Possibly add a picture of your setup aswell. jippie Apr 13 `13 at 20:16 🔗 External reference