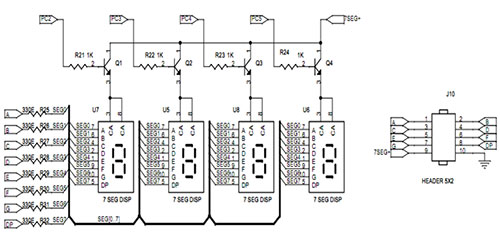
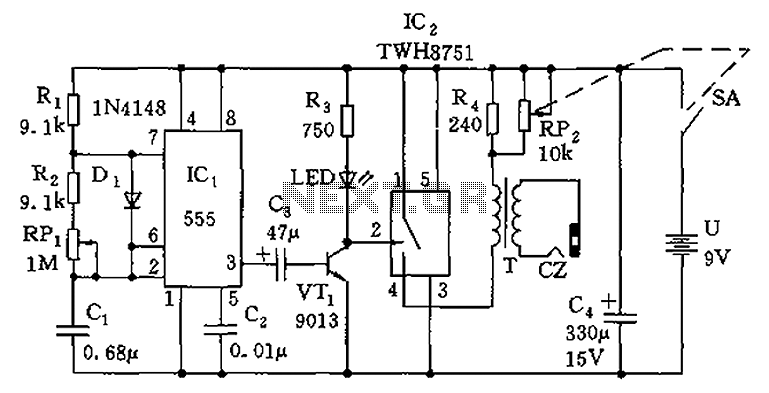
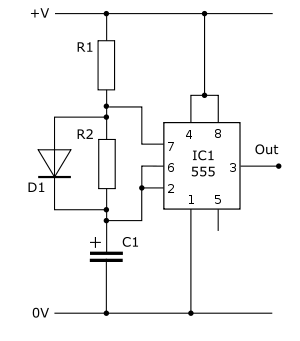
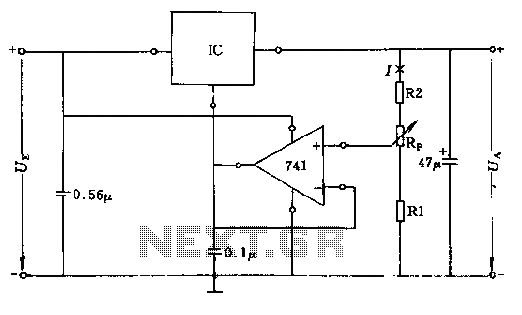
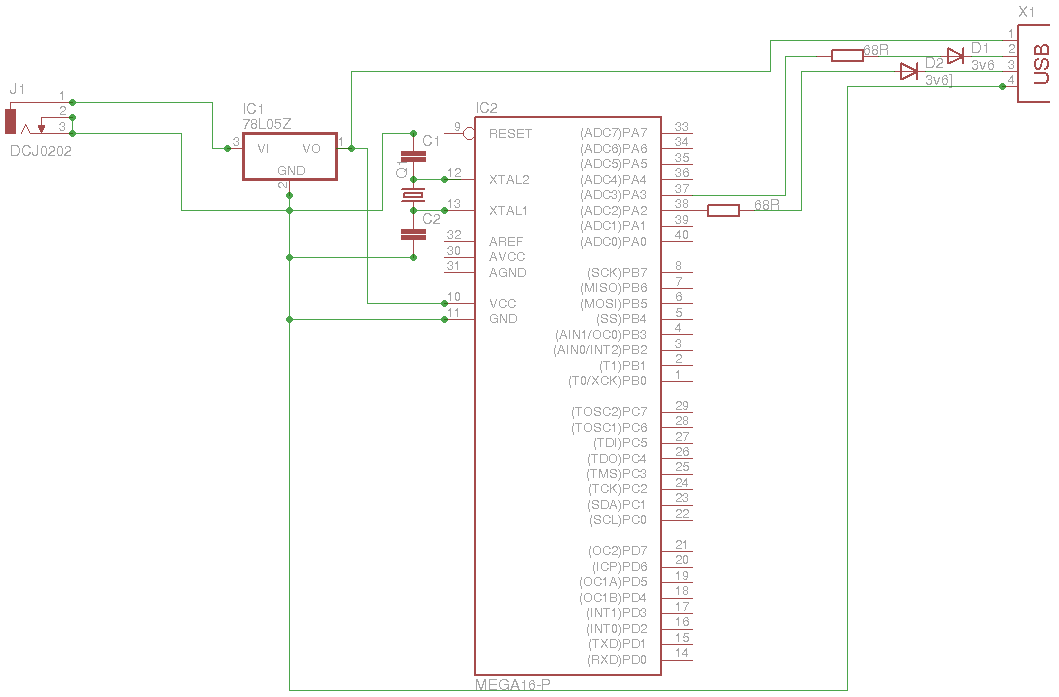
Wiring diagram check up for usb interfaced avr
The 5 V from USB appears to be powering the LED on the laptop power brick. Therefore, even when the power brick is turned off at the wall outlet, the LED remains illuminated. When the USB is unplugged, the LED turns off, but it lights up again as soon as the USB is reconnected. Is it sufficient to just add a diode?
In this scenario, the LED indicator on the laptop power brick is receiving power from the USB port, which provides a constant 5 V supply. This can occur due to the design of the power brick, where the LED is connected to the USB power line, allowing it to remain lit even when the main power supply is turned off.
To address the issue of the LED remaining on when the power brick is switched off, the implementation of a diode could be a viable solution. A diode allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. By placing a diode in series with the LED, the current flow from the USB to the LED can be prevented when the power brick is off.
The diode should be selected based on the current and voltage ratings that are appropriate for the circuit. A common choice for such applications is the 1N4148 or 1N4001 diode, which can handle the typical current levels provided by USB ports. The cathode of the diode should be connected to the LED, while the anode connects to the USB power supply. This configuration ensures that when the USB is connected, the diode will allow current to flow to the LED, illuminating it. Conversely, when the power brick is switched off, the diode will block any reverse current, thus keeping the LED off.
It is important to consider the forward voltage drop of the diode, which may slightly reduce the brightness of the LED when it is on. This drop is typically around 0.7 V for silicon diodes, so it may be necessary to adjust the circuit design accordingly to ensure the LED operates within its desired brightness range.
In conclusion, adding a diode in series with the LED can effectively resolve the issue of the LED being powered by the USB connection when the power brick is off, providing a simple and effective solution to the problem.The 5 V from USB seems to be powering the led on my laptop power brick. Hence even when I switched the power brick off at the wall outlet, the led is still on. When I unplug the USB it goes off but comes back on again as soon as I plug it in. Do Ijust but a diode in 🔗 External reference
In this scenario, the LED indicator on the laptop power brick is receiving power from the USB port, which provides a constant 5 V supply. This can occur due to the design of the power brick, where the LED is connected to the USB power line, allowing it to remain lit even when the main power supply is turned off.
To address the issue of the LED remaining on when the power brick is switched off, the implementation of a diode could be a viable solution. A diode allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. By placing a diode in series with the LED, the current flow from the USB to the LED can be prevented when the power brick is off.
The diode should be selected based on the current and voltage ratings that are appropriate for the circuit. A common choice for such applications is the 1N4148 or 1N4001 diode, which can handle the typical current levels provided by USB ports. The cathode of the diode should be connected to the LED, while the anode connects to the USB power supply. This configuration ensures that when the USB is connected, the diode will allow current to flow to the LED, illuminating it. Conversely, when the power brick is switched off, the diode will block any reverse current, thus keeping the LED off.
It is important to consider the forward voltage drop of the diode, which may slightly reduce the brightness of the LED when it is on. This drop is typically around 0.7 V for silicon diodes, so it may be necessary to adjust the circuit design accordingly to ensure the LED operates within its desired brightness range.
In conclusion, adding a diode in series with the LED can effectively resolve the issue of the LED being powered by the USB connection when the power brick is off, providing a simple and effective solution to the problem.The 5 V from USB seems to be powering the led on my laptop power brick. Hence even when I switched the power brick off at the wall outlet, the led is still on. When I unplug the USB it goes off but comes back on again as soon as I plug it in. Do Ijust but a diode in 🔗 External reference