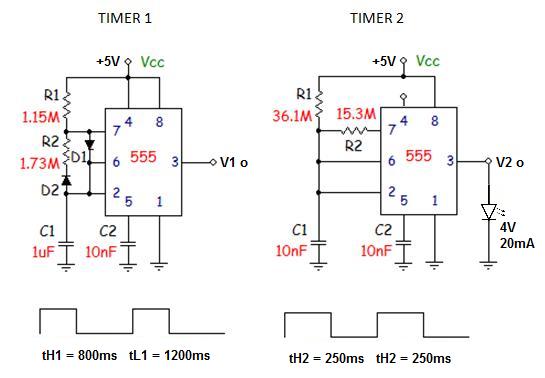
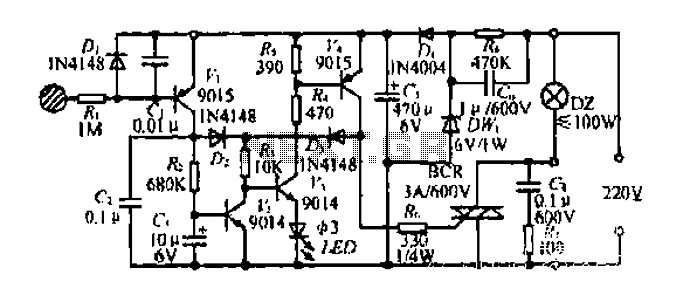
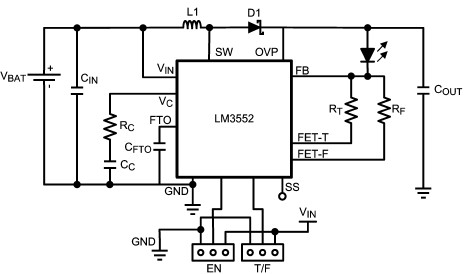
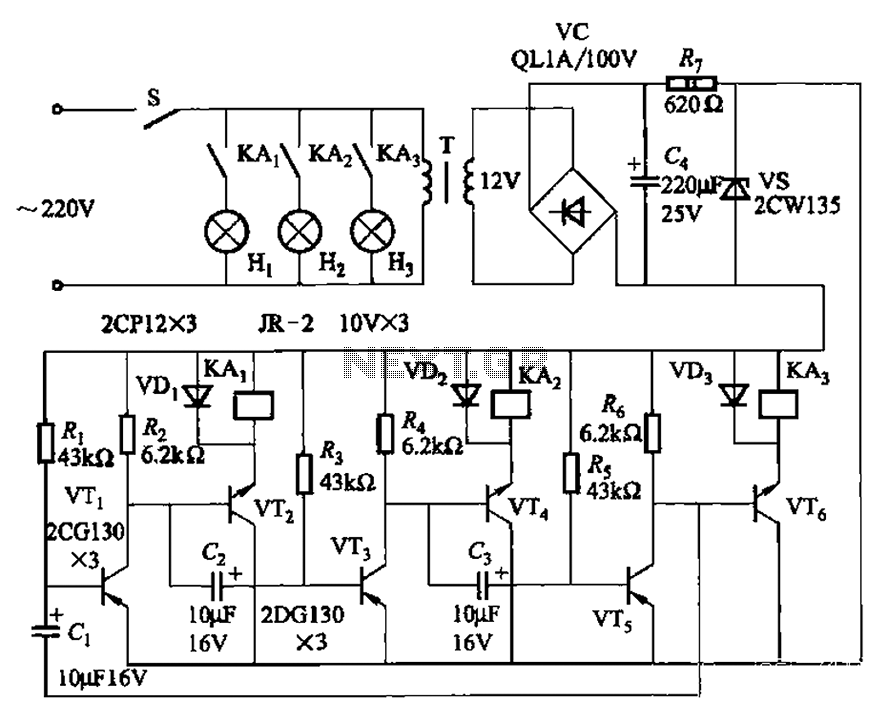
A single pulse signal generating circuit
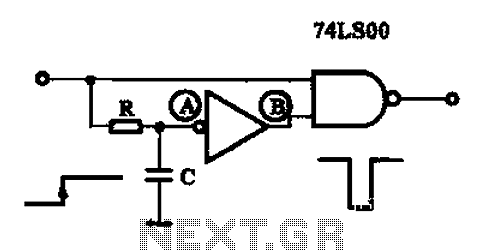
A single pulse signal generating circuit is designed to produce a one-shot pulse output. This circuit can be utilized in applications requiring a digital reset signal or to halt a signal. It operates as a non-synchronous differential circuit.
The single pulse signal generating circuit, commonly referred to as a one-shot pulse generator, is essential in various electronic applications where precise timing and control of signal pulses are required. This circuit typically employs a combination of resistors, capacitors, and active components such as operational amplifiers or timers (e.g., 555 timer IC) to achieve its function.
In operation, the circuit is triggered by a specific input signal, which initiates the generation of a single output pulse of predetermined duration. The pulse width can be adjusted by modifying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing network, allowing for flexibility in different applications. The non-synchronous aspect of this circuit means that it does not rely on a clock signal for operation; instead, it responds directly to the input trigger.
The output pulse can be used in various scenarios, such as resetting digital counters, generating clock signals for sequential logic circuits, or controlling the timing of other electronic devices. Additionally, the circuit can include features such as output buffering to drive larger loads or integration with microcontroller systems for enhanced control and functionality.
Overall, the single pulse signal generating circuit is a versatile tool in digital electronics, providing reliable and precise pulse generation for a wide range of applications.A single pulse signal generating circuit Shown as a single pulse signal generating circuit, switch contacts such as the use of such a digital signal reset signal or the stop si gnal is to be formed, this one-shot pulse generating circuit can be used. This circuit is a non-synchronous differential circuit.
The single pulse signal generating circuit, commonly referred to as a one-shot pulse generator, is essential in various electronic applications where precise timing and control of signal pulses are required. This circuit typically employs a combination of resistors, capacitors, and active components such as operational amplifiers or timers (e.g., 555 timer IC) to achieve its function.
In operation, the circuit is triggered by a specific input signal, which initiates the generation of a single output pulse of predetermined duration. The pulse width can be adjusted by modifying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing network, allowing for flexibility in different applications. The non-synchronous aspect of this circuit means that it does not rely on a clock signal for operation; instead, it responds directly to the input trigger.
The output pulse can be used in various scenarios, such as resetting digital counters, generating clock signals for sequential logic circuits, or controlling the timing of other electronic devices. Additionally, the circuit can include features such as output buffering to drive larger loads or integration with microcontroller systems for enhanced control and functionality.
Overall, the single pulse signal generating circuit is a versatile tool in digital electronics, providing reliable and precise pulse generation for a wide range of applications.A single pulse signal generating circuit Shown as a single pulse signal generating circuit, switch contacts such as the use of such a digital signal reset signal or the stop si gnal is to be formed, this one-shot pulse generating circuit can be used. This circuit is a non-synchronous differential circuit.