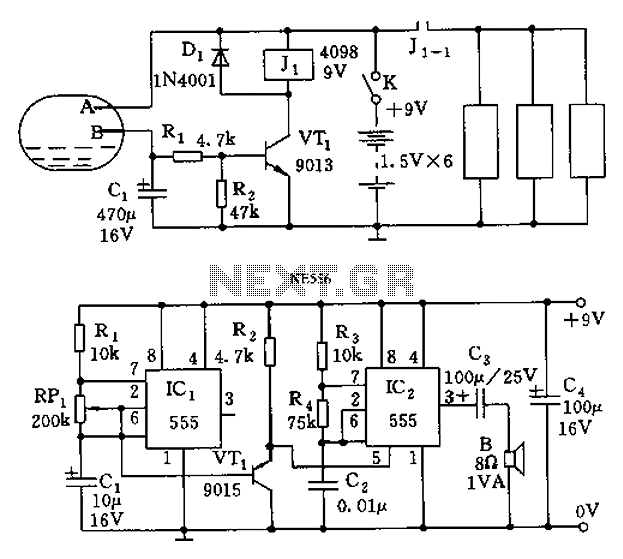
Computer fan speed tacho out circuit
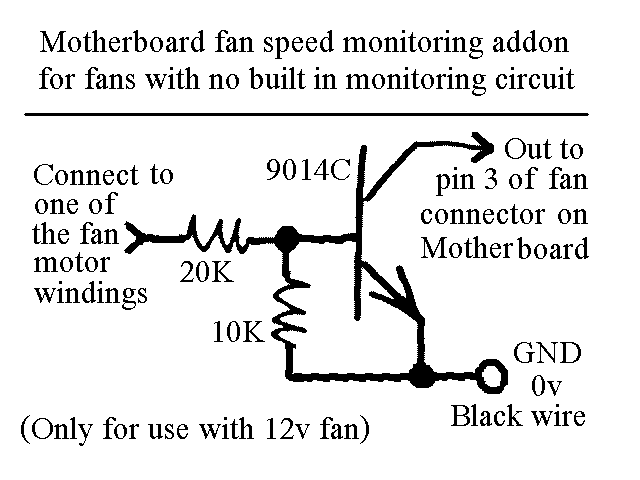
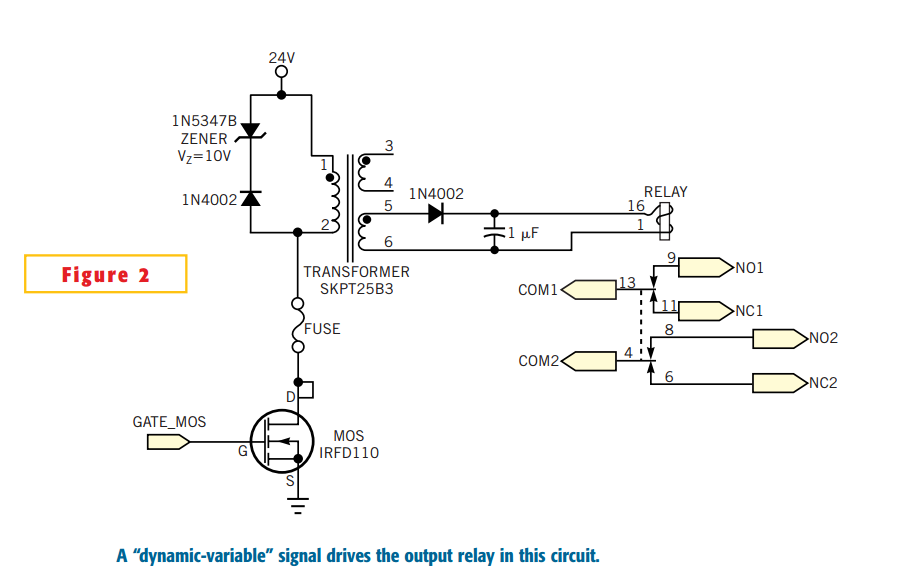
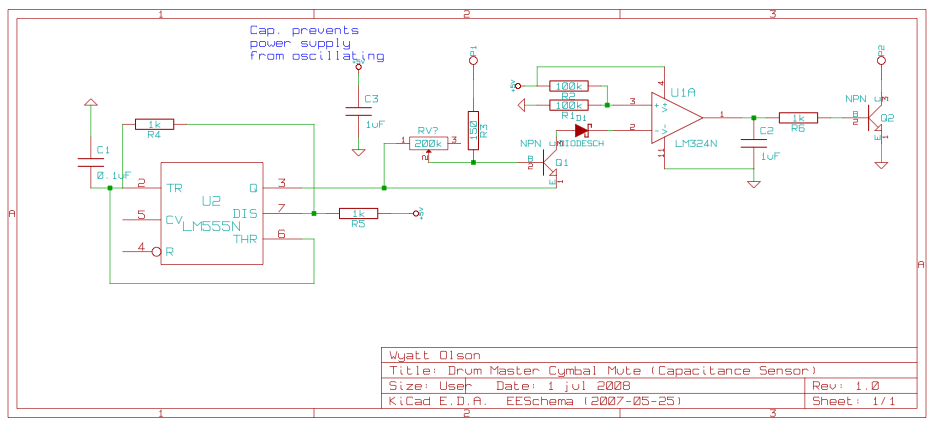
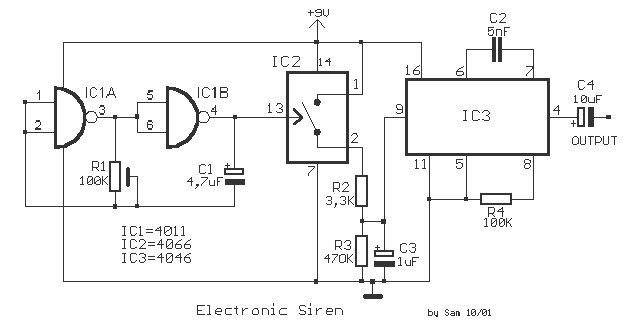
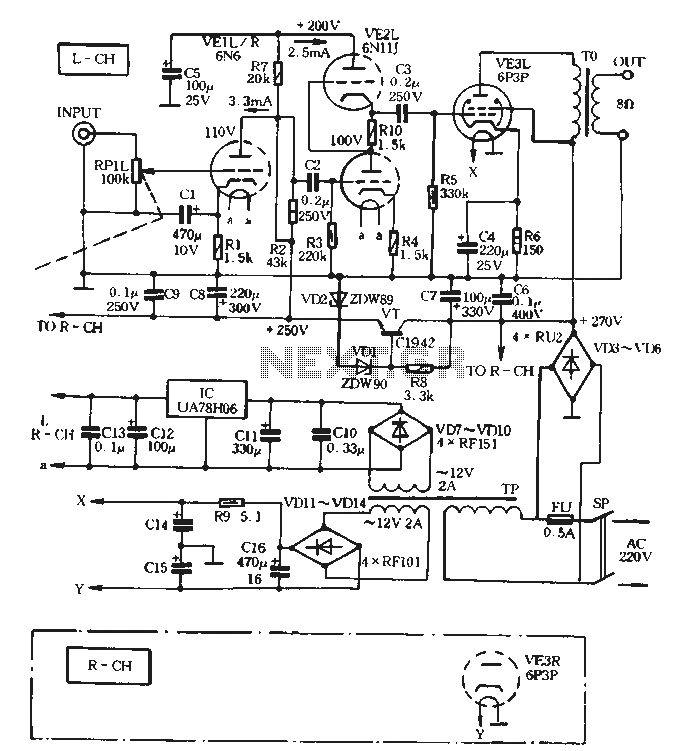
You will find this identical circuit inside most 3 wire computer fans with speed monitoring output to the motherboard. Peel off the sticker from the fan hub in order to access a motor winding pin for connecting up the tacho circuit.
The circuit described is a common configuration found in 3-wire computer fans, which typically consist of three connections: power (VCC), ground (GND), and a tachometer output (TACH). The power and ground wires supply the necessary voltage to operate the fan motor, while the tachometer output provides feedback regarding the fan's rotational speed.
To access the tachometer circuit, it is necessary to peel off a sticker from the fan hub, revealing a pin connected to one of the motor windings. This pin is crucial for measuring the speed of the fan. The fan's internal circuitry generates a pulse signal on the TACH line, which corresponds to the rotation of the fan blades; typically, one pulse is produced for each revolution.
The TACH signal is typically a square wave, where the frequency of the pulses is directly proportional to the fan speed. This signal can be interfaced with a microcontroller or a motherboard fan controller, allowing the system to monitor and adjust the fan speed as needed for thermal management.
In terms of schematic representation, the fan circuit would include a DC motor connected to the power supply, with the TACH output line connected to a microcontroller input pin. Additional components may include a resistor for signal conditioning and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring a clean and stable output signal for accurate speed monitoring. The design allows for efficient operation and effective thermal control in computer systems, enhancing overall performance and reliability.You will find this identical circuit inside most 3 wire computer fans with speed monitoring output to the motherboard. Peel off the sticker from the fan hub in order to access a motor winding pin for connecting up the tacho circuit.
🔗 External reference
The circuit described is a common configuration found in 3-wire computer fans, which typically consist of three connections: power (VCC), ground (GND), and a tachometer output (TACH). The power and ground wires supply the necessary voltage to operate the fan motor, while the tachometer output provides feedback regarding the fan's rotational speed.
To access the tachometer circuit, it is necessary to peel off a sticker from the fan hub, revealing a pin connected to one of the motor windings. This pin is crucial for measuring the speed of the fan. The fan's internal circuitry generates a pulse signal on the TACH line, which corresponds to the rotation of the fan blades; typically, one pulse is produced for each revolution.
The TACH signal is typically a square wave, where the frequency of the pulses is directly proportional to the fan speed. This signal can be interfaced with a microcontroller or a motherboard fan controller, allowing the system to monitor and adjust the fan speed as needed for thermal management.
In terms of schematic representation, the fan circuit would include a DC motor connected to the power supply, with the TACH output line connected to a microcontroller input pin. Additional components may include a resistor for signal conditioning and capacitors for noise filtering, ensuring a clean and stable output signal for accurate speed monitoring. The design allows for efficient operation and effective thermal control in computer systems, enhancing overall performance and reliability.You will find this identical circuit inside most 3 wire computer fans with speed monitoring output to the motherboard. Peel off the sticker from the fan hub in order to access a motor winding pin for connecting up the tacho circuit.
🔗 External reference