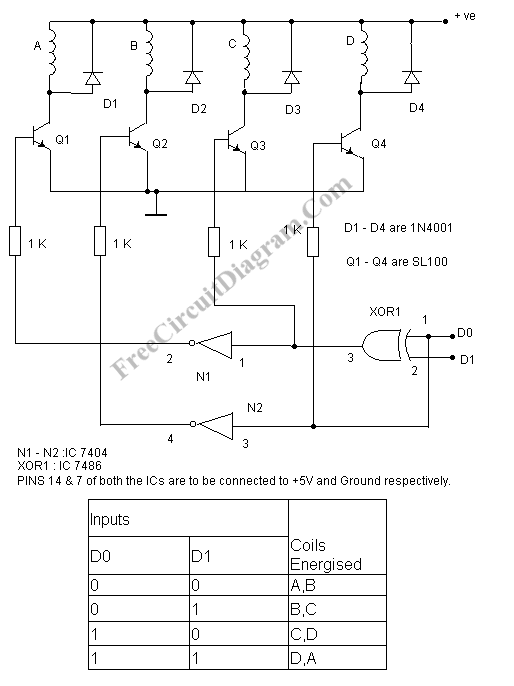
Simple Ripple Suppressor
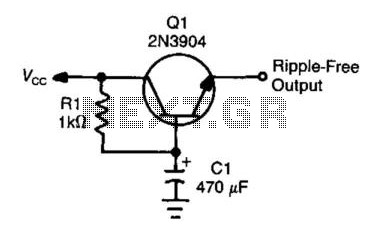
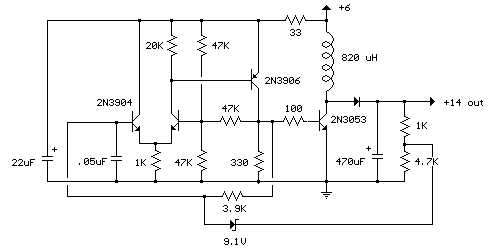
This circuit, often referred to as a capacitance multiplier, is effective for reducing power supply ripple. The capacitance provided by the circuit is equivalent to a capacitor of ( +1) Ci, where Ci represents the capacitance and the gain of transistor Q1 (typically greater than 50).
The capacitance multiplier circuit utilizes a transistor to enhance the effective capacitance of a capacitor connected at its input. The primary function of this circuit is to filter out voltage fluctuations and noise in the power supply, thereby providing a smoother DC output.
In this configuration, the input capacitor (Ci) is connected to the base of the transistor (Q1), which is typically a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The collector of Q1 is connected to the output, while the emitter is linked to ground through a load resistor. The gain of the transistor amplifies the capacitance effect of Ci, resulting in an effective capacitance that can be much larger than the physical capacitor used.
The output voltage is taken from the collector of the transistor, and the ripple voltage at this point is significantly reduced due to the increased effective capacitance. This characteristic makes the capacitance multiplier an ideal choice for power supply circuits where space is limited and additional bulk capacitance cannot be used.
In practical applications, the design parameters such as the choice of transistor, the value of Ci, and load conditions must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance. The circuit can be used in various electronic devices where stable voltage is critical, including audio amplifiers, digital circuits, and other sensitive electronic equipment.
Overall, this circuit provides a compact and efficient solution for improving power supply stability and reducing ripple, leveraging the properties of transistors to achieve enhanced filtering capabilities. This circuit, at times called a capacitance multiplier, is useful for suppression of power-supply ripple. CI provi des filtering that is equal to a capacitor of ( +1) Ci, where = dc current gain of Ql (typically > 50).
The capacitance multiplier circuit utilizes a transistor to enhance the effective capacitance of a capacitor connected at its input. The primary function of this circuit is to filter out voltage fluctuations and noise in the power supply, thereby providing a smoother DC output.
In this configuration, the input capacitor (Ci) is connected to the base of the transistor (Q1), which is typically a bipolar junction transistor (BJT). The collector of Q1 is connected to the output, while the emitter is linked to ground through a load resistor. The gain of the transistor amplifies the capacitance effect of Ci, resulting in an effective capacitance that can be much larger than the physical capacitor used.
The output voltage is taken from the collector of the transistor, and the ripple voltage at this point is significantly reduced due to the increased effective capacitance. This characteristic makes the capacitance multiplier an ideal choice for power supply circuits where space is limited and additional bulk capacitance cannot be used.
In practical applications, the design parameters such as the choice of transistor, the value of Ci, and load conditions must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance. The circuit can be used in various electronic devices where stable voltage is critical, including audio amplifiers, digital circuits, and other sensitive electronic equipment.
Overall, this circuit provides a compact and efficient solution for improving power supply stability and reducing ripple, leveraging the properties of transistors to achieve enhanced filtering capabilities. This circuit, at times called a capacitance multiplier, is useful for suppression of power-supply ripple. CI provi des filtering that is equal to a capacitor of ( +1) Ci, where = dc current gain of Ql (typically > 50).