water sensor circuit using 555 timer
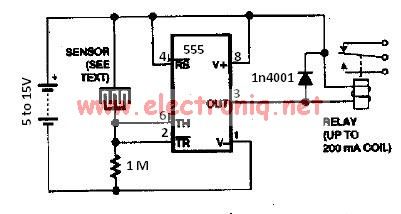
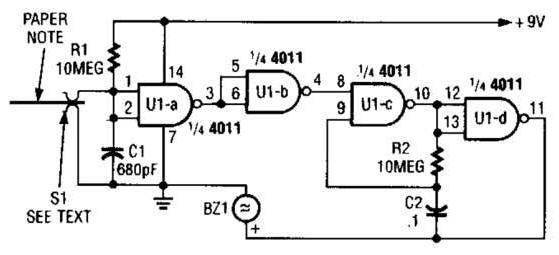
The water sensor circuit utilizes a 555 timer configuration along with standard electronic components. It consists of two metal electrodes positioned closely enough that a drop of water can create a conductive bridge between them. In cases where the water is highly pure, it may be necessary to adjust the resistor value to 2.2 MΩ. If the circuit generates false alarms during sensing, changing the resistor value to 220 kΩ may help resolve the issue.
The water sensor circuit operates by detecting the presence of water through conductivity. The two electrodes serve as a sensing element; when water bridges the gap between them, it completes the circuit, allowing current to flow. The 555 timer is used in a monostable mode, which means that it produces a single output pulse when triggered. In this application, the output pulse indicates the presence of water.
The circuit can be designed with a few key components: the 555 timer IC, two metal electrodes, a resistor, and a power supply. The configuration of the 555 timer is crucial, as it determines the timing characteristics of the output pulse. The resistor value directly influences the sensitivity of the circuit. A higher resistance value, such as 2.2 MΩ, increases the sensitivity, allowing the circuit to detect even minimal amounts of water. Conversely, if the circuit is overly sensitive and generates false alarms, reducing the resistor to 220 kΩ can help mitigate this issue.
In terms of layout, the electrodes should be placed in a location where water accumulation is expected. The circuit board should be designed to prevent corrosion of the electrodes, which can affect long-term reliability. Additionally, proper filtering capacitors may be added to the power supply lines to reduce noise that could interfere with the sensor's operation.
Overall, the water sensor circuit based on a 555 timer is a straightforward yet effective solution for water detection applications, providing a reliable means to monitor moisture levels in various environments.The water sensor circuit is based on a 555 timer circuit and come common electronic components. The water sensor is made by two metal electrodes arranged very close that a drop of water (liquid) will bridge them. If the liquid ( water ) is very pure you may change the resistor value to 2. 2m ohms and if the circuit is give false alarm sensing you may change the value of resistor to 220k. 🔗 External reference
The water sensor circuit operates by detecting the presence of water through conductivity. The two electrodes serve as a sensing element; when water bridges the gap between them, it completes the circuit, allowing current to flow. The 555 timer is used in a monostable mode, which means that it produces a single output pulse when triggered. In this application, the output pulse indicates the presence of water.
The circuit can be designed with a few key components: the 555 timer IC, two metal electrodes, a resistor, and a power supply. The configuration of the 555 timer is crucial, as it determines the timing characteristics of the output pulse. The resistor value directly influences the sensitivity of the circuit. A higher resistance value, such as 2.2 MΩ, increases the sensitivity, allowing the circuit to detect even minimal amounts of water. Conversely, if the circuit is overly sensitive and generates false alarms, reducing the resistor to 220 kΩ can help mitigate this issue.
In terms of layout, the electrodes should be placed in a location where water accumulation is expected. The circuit board should be designed to prevent corrosion of the electrodes, which can affect long-term reliability. Additionally, proper filtering capacitors may be added to the power supply lines to reduce noise that could interfere with the sensor's operation.
Overall, the water sensor circuit based on a 555 timer is a straightforward yet effective solution for water detection applications, providing a reliable means to monitor moisture levels in various environments.The water sensor circuit is based on a 555 timer circuit and come common electronic components. The water sensor is made by two metal electrodes arranged very close that a drop of water (liquid) will bridge them. If the liquid ( water ) is very pure you may change the resistor value to 2. 2m ohms and if the circuit is give false alarm sensing you may change the value of resistor to 220k. 🔗 External reference